Pallavi Asthana
Deep 3D Convolutional Neural Network for Automated Lung Cancer Diagnosis
May 04, 2019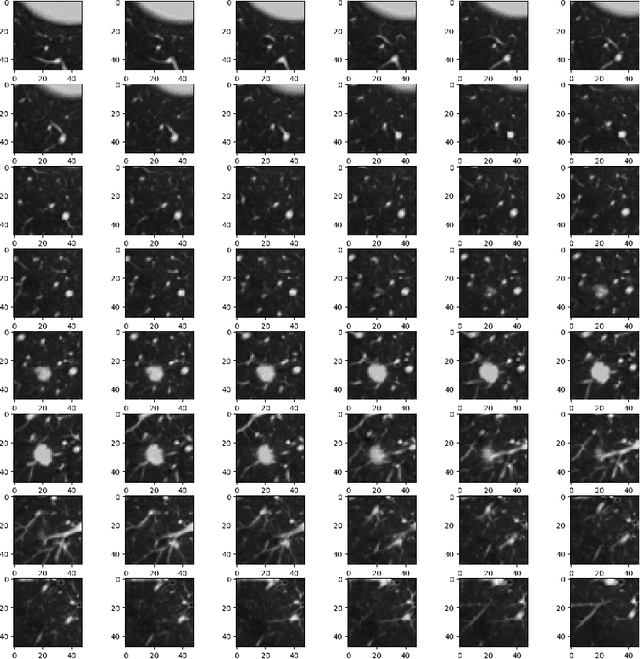
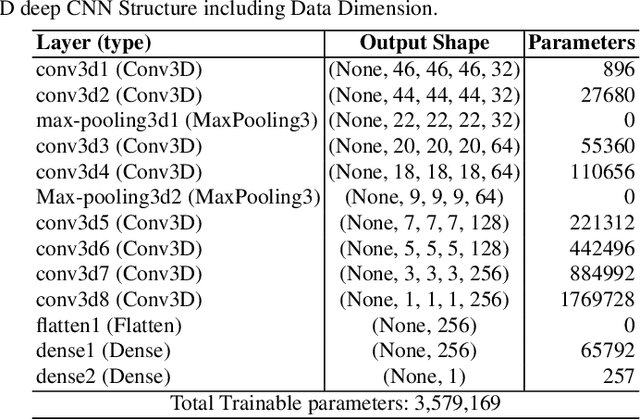
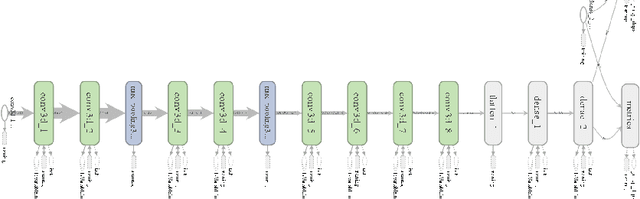
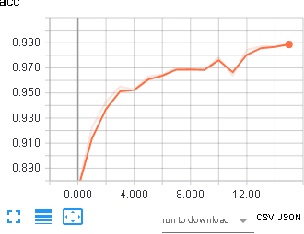
Abstract:Computer Aided Diagnosis has emerged as an indispensible technique for validating the opinion of radiologists in CT interpretation. This paper presents a deep 3D Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) architecture for automated CT scan-based lung cancer detection system. It utilizes three dimensional spatial information to learn highly discriminative 3 dimensional features instead of 2D features like texture or geometric shape whick need to be generated manually. The proposed deep learning method automatically extracts the 3D features on the basis of spatio-temporal statistics.The developed model is end-to-end and is able to predict malignancy of each voxel for given input scan. Simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of proposed 3D CNN network for classification of lung nodule in-spite of limited computational capabilities.
Automated Detection of Acute Leukemia using K-mean Clustering Algorithm
Mar 06, 2018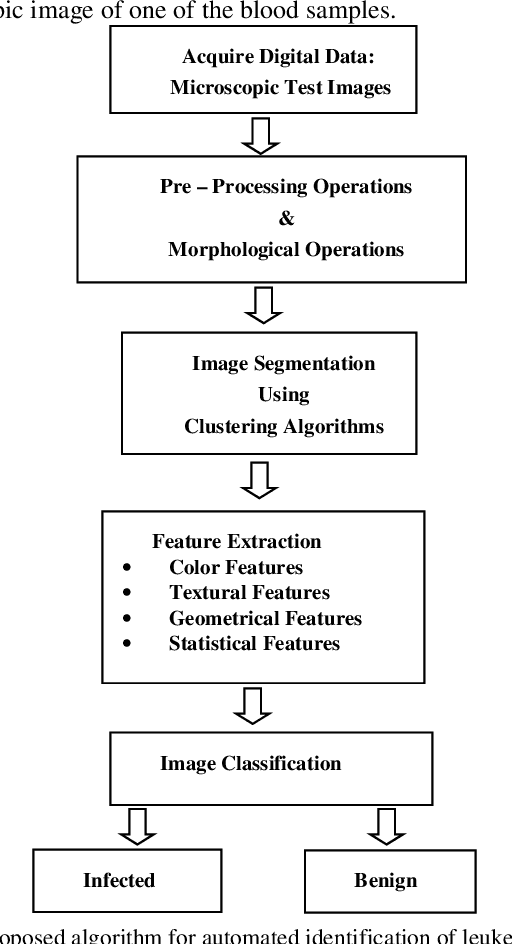
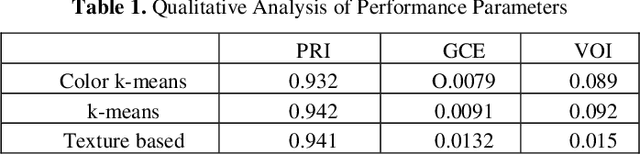
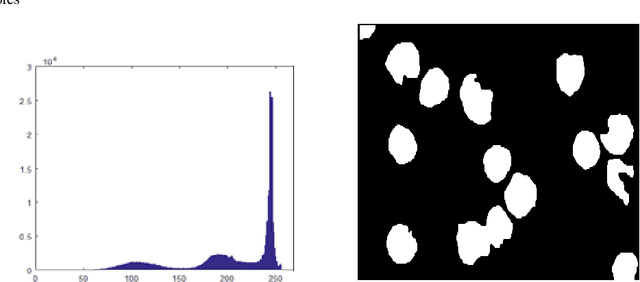
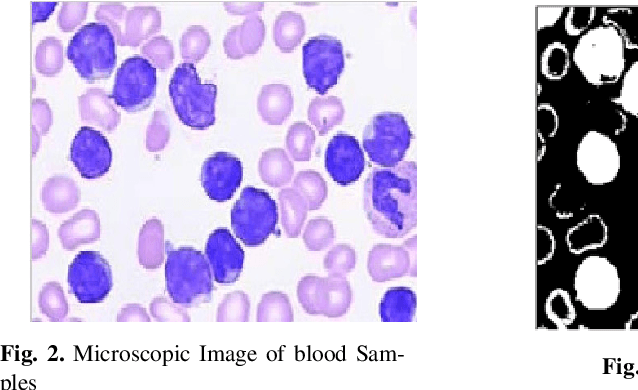
Abstract:Leukemia is a hematologic cancer which develops in blood tissue and triggers rapid production of immature and abnormal shaped white blood cells. Based on statistics it is found that the leukemia is one of the leading causes of death in men and women alike. Microscopic examination of blood sample or bone marrow smear is the most effective technique for diagnosis of leukemia. Pathologists analyze microscopic samples to make diagnostic assessments on the basis of characteristic cell features. Recently, computerized methods for cancer detection have been explored towards minimizing human intervention and providing accurate clinical information. This paper presents an algorithm for automated image based acute leukemia detection systems. The method implemented uses basic enhancement, morphology, filtering and segmenting technique to extract region of interest using k-means clustering algorithm. The proposed algorithm achieved an accuracy of 92.8% and is tested with Nearest Neighbor (KNN) and Naive Bayes Classifier on the data-set of 60 samples.
* Presented in ICCCCS 2016
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge