Padmanaba Srinivasan
Behavior Preference Regression for Offline Reinforcement Learning
Mar 02, 2025Abstract:Offline reinforcement learning (RL) methods aim to learn optimal policies with access only to trajectories in a fixed dataset. Policy constraint methods formulate policy learning as an optimization problem that balances maximizing reward with minimizing deviation from the behavior policy. Closed form solutions to this problem can be derived as weighted behavioral cloning objectives that, in theory, must compute an intractable partition function. Reinforcement learning has gained popularity in language modeling to align models with human preferences; some recent works consider paired completions that are ranked by a preference model following which the likelihood of the preferred completion is directly increased. We adapt this approach of paired comparison. By reformulating the paired-sample optimization problem, we fit the maximum-mode of the Q function while maximizing behavioral consistency of policy actions. This yields our algorithm, Behavior Preference Regression for offline RL (BPR). We empirically evaluate BPR on the widely used D4RL Locomotion and Antmaze datasets, as well as the more challenging V-D4RL suite, which operates in image-based state spaces. BPR demonstrates state-of-the-art performance over all domains. Our on-policy experiments suggest that BPR takes advantage of the stability of on-policy value functions with minimal perceptible performance degradation on Locomotion datasets.
Offline Model-Based Reinforcement Learning with Anti-Exploration
Aug 20, 2024Abstract:Model-based reinforcement learning (MBRL) algorithms learn a dynamics model from collected data and apply it to generate synthetic trajectories to enable faster learning. This is an especially promising paradigm in offline reinforcement learning (RL) where data may be limited in quantity, in addition to being deficient in coverage and quality. Practical approaches to offline MBRL usually rely on ensembles of dynamics models to prevent exploitation of any individual model and to extract uncertainty estimates that penalize values in states far from the dataset support. Uncertainty estimates from ensembles can vary greatly in scale, making it challenging to generalize hyperparameters well across even similar tasks. In this paper, we present Morse Model-based offline RL (MoMo), which extends the anti-exploration paradigm found in offline model-free RL to the model-based space. We develop model-free and model-based variants of MoMo and show how the model-free version can be extended to detect and deal with out-of-distribution (OOD) states using explicit uncertainty estimation without the need for large ensembles. MoMo performs offline MBRL using an anti-exploration bonus to counteract value overestimation in combination with a policy constraint, as well as a truncation function to terminate synthetic rollouts that are excessively OOD. Experimentally, we find that both model-free and model-based MoMo perform well, and the latter outperforms prior model-based and model-free baselines on the majority of D4RL datasets tested.
Time-series Transformer Generative Adversarial Networks
May 23, 2022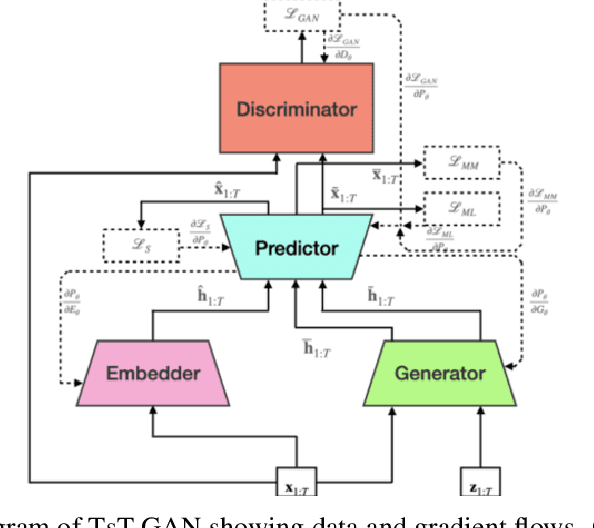
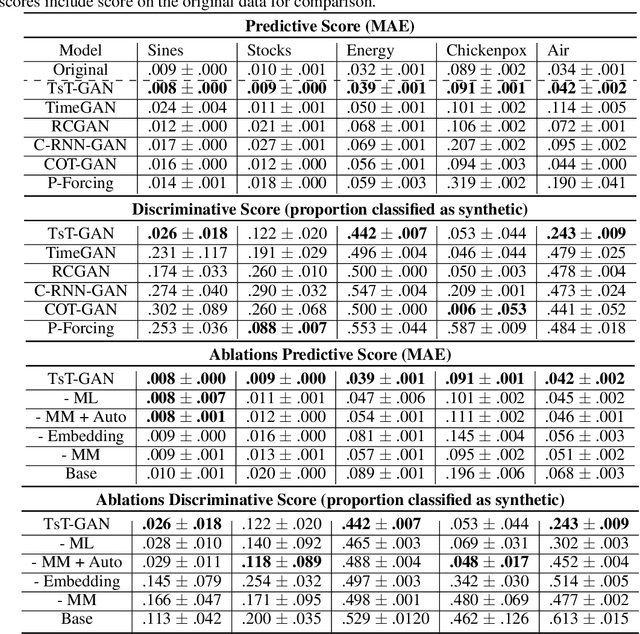
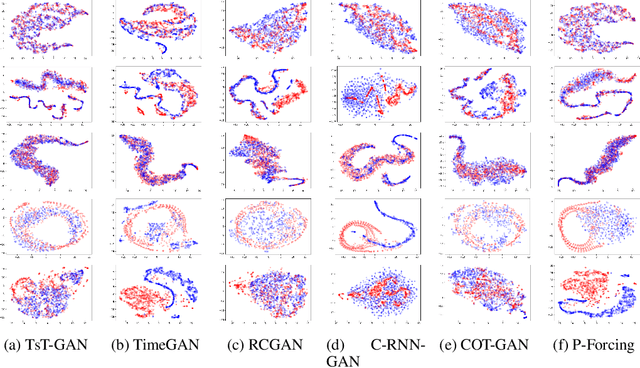
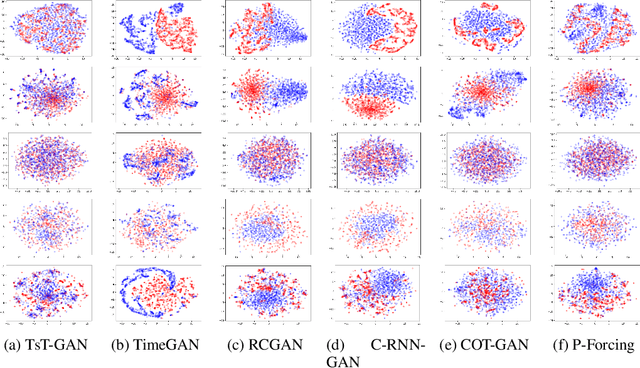
Abstract:Many real-world tasks are plagued by limitations on data: in some instances very little data is available and in others, data is protected by privacy enforcing regulations (e.g. GDPR). We consider limitations posed specifically on time-series data and present a model that can generate synthetic time-series which can be used in place of real data. A model that generates synthetic time-series data has two objectives: 1) to capture the stepwise conditional distribution of real sequences, and 2) to faithfully model the joint distribution of entire real sequences. Autoregressive models trained via maximum likelihood estimation can be used in a system where previous predictions are fed back in and used to predict future ones; in such models, errors can accrue over time. Furthermore, a plausible initial value is required making MLE based models not really generative. Many downstream tasks learn to model conditional distributions of the time-series, hence, synthetic data drawn from a generative model must satisfy 1) in addition to performing 2). We present TsT-GAN, a framework that capitalises on the Transformer architecture to satisfy the desiderata and compare its performance against five state-of-the-art models on five datasets and show that TsT-GAN achieves higher predictive performance on all datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge