Osama Mawlawi
Posterior-Mean Denoising Diffusion Model for Realistic PET Image Reconstruction
Mar 11, 2025


Abstract:Positron Emission Tomography (PET) is a functional imaging modality that enables the visualization of biochemical and physiological processes across various tissues. Recently, deep learning (DL)-based methods have demonstrated significant progress in directly mapping sinograms to PET images. However, regression-based DL models often yield overly smoothed reconstructions lacking of details (i.e., low distortion, low perceptual quality), whereas GAN-based and likelihood-based posterior sampling models tend to introduce undesirable artifacts in predictions (i.e., high distortion, high perceptual quality), limiting their clinical applicability. To achieve a robust perception-distortion tradeoff, we propose Posterior-Mean Denoising Diffusion Model (PMDM-PET), a novel approach that builds upon a recently established mathematical theory to explore the closed-form expression of perception-distortion function in diffusion model space for PET image reconstruction from sinograms. Specifically, PMDM-PET first obtained posterior-mean PET predictions under minimum mean square error (MSE), then optimally transports the distribution of them to the ground-truth PET images distribution. Experimental results demonstrate that PMDM-PET not only generates realistic PET images with possible minimum distortion and optimal perceptual quality but also outperforms five recent state-of-the-art (SOTA) DL baselines in both qualitative visual inspection and quantitative pixel-wise metrics PSNR (dB)/SSIM/NRMSE.
LegoPET: Hierarchical Feature Guided Conditional Diffusion for PET Image Reconstruction
Nov 25, 2024



Abstract:Positron emission tomography (PET) is widely utilized for cancer detection due to its ability to visualize functional and biological processes in vivo. PET images are usually reconstructed from histogrammed raw data (sinograms) using traditional iterative techniques (e.g., OSEM, MLEM). Recently, deep learning (DL) methods have shown promise by directly mapping raw sinogram data to PET images. However, DL approaches that are regression-based or GAN-based often produce overly smoothed images or introduce various artifacts respectively. Image-conditioned diffusion probabilistic models (cDPMs) are another class of likelihood-based DL techniques capable of generating highly realistic and controllable images. While cDPMs have notable strengths, they still face challenges such as maintain correspondence and consistency between input and output images when they are from different domains (e.g., sinogram vs. image domain) as well as slow convergence rates. To address these limitations, we introduce LegoPET, a hierarchical feature guided conditional diffusion model for high-perceptual quality PET image reconstruction from sinograms. We conducted several experiments demonstrating that LegoPET not only improves the performance of cDPMs but also surpasses recent DL-based PET image reconstruction techniques in terms of visual quality and pixel-level PSNR/SSIM metrics. Our code is available at https://github.com/yransun/LegoPET.
DIFR3CT: Latent Diffusion for Probabilistic 3D CT Reconstruction from Few Planar X-Rays
Aug 27, 2024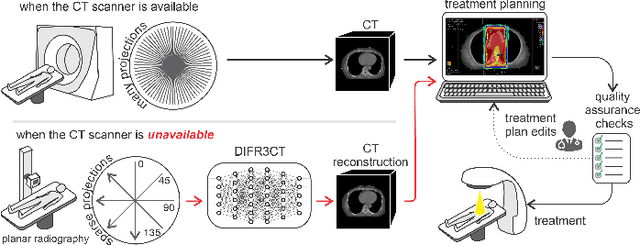
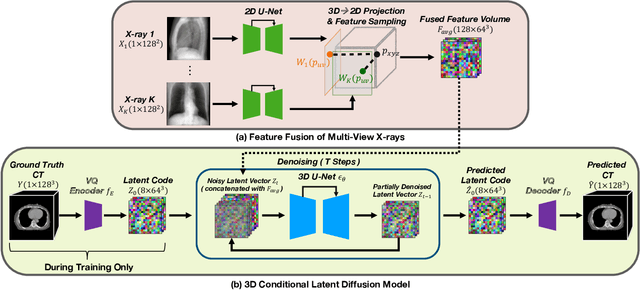
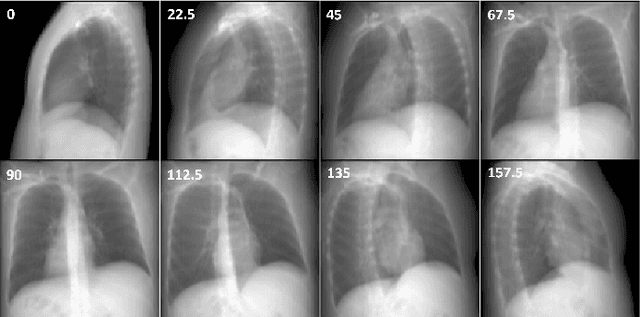
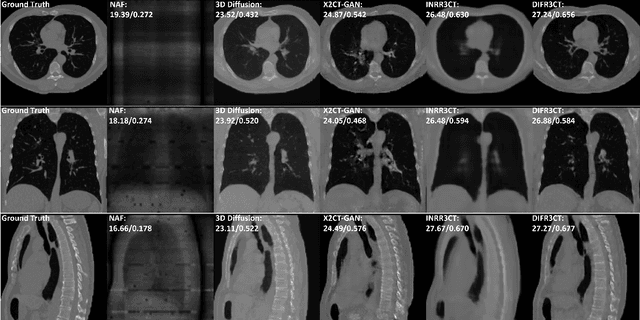
Abstract:Computed Tomography (CT) scans are the standard-of-care for the visualization and diagnosis of many clinical ailments, and are needed for the treatment planning of external beam radiotherapy. Unfortunately, the availability of CT scanners in low- and mid-resource settings is highly variable. Planar x-ray radiography units, in comparison, are far more prevalent, but can only provide limited 2D observations of the 3D anatomy. In this work we propose DIFR3CT, a 3D latent diffusion model, that can generate a distribution of plausible CT volumes from one or few (<10) planar x-ray observations. DIFR3CT works by fusing 2D features from each x-ray into a joint 3D space, and performing diffusion conditioned on these fused features in a low-dimensional latent space. We conduct extensive experiments demonstrating that DIFR3CT is better than recent sparse CT reconstruction baselines in terms of standard pixel-level (PSNR, SSIM) on both the public LIDC and in-house post-mastectomy CT datasets. We also show that DIFR3CT supports uncertainty quantification via Monte Carlo sampling, which provides an opportunity to measure reconstruction reliability. Finally, we perform a preliminary pilot study evaluating DIFR3CT for automated breast radiotherapy contouring and planning -- and demonstrate promising feasibility. Our code is available at https://github.com/yransun/DIFR3CT.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge