Olympio Hacquard
LMO, DATASHAPE
Hypergraph clustering using Ricci curvature: an edge transport perspective
Dec 20, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we introduce a novel method for extending Ricci flow to hypergraphs by defining probability measures on the edges and transporting them on the line expansion. This approach yields a new weighting on the edges, which proves particularly effective for community detection. We extensively compare this method with a similar notion of Ricci flow defined on the clique expansion, demonstrating its enhanced sensitivity to the hypergraph structure, especially in the presence of large hyperedges. The two methods are complementary and together form a powerful and highly interpretable framework for community detection in hypergraphs.
Euler Characteristic Tools For Topological Data Analysis
Mar 24, 2023Abstract:In this article, we study Euler characteristic techniques in topological data analysis. Pointwise computing the Euler characteristic of a family of simplicial complexes built from data gives rise to the so-called Euler characteristic profile. We show that this simple descriptor achieve state-of-the-art performance in supervised tasks at a very low computational cost. Inspired by signal analysis, we compute hybrid transforms of Euler characteristic profiles. These integral transforms mix Euler characteristic techniques with Lebesgue integration to provide highly efficient compressors of topological signals. As a consequence, they show remarkable performances in unsupervised settings. On the qualitative side, we provide numerous heuristics on the topological and geometric information captured by Euler profiles and their hybrid transforms. Finally, we prove stability results for these descriptors as well as asymptotic guarantees in random settings.
Statistical learning on measures: an application to persistence diagrams
Mar 15, 2023Abstract:We consider a binary supervised learning classification problem where instead of having data in a finite-dimensional Euclidean space, we observe measures on a compact space $\mathcal{X}$. Formally, we observe data $D_N = (\mu_1, Y_1), \ldots, (\mu_N, Y_N)$ where $\mu_i$ is a measure on $\mathcal{X}$ and $Y_i$ is a label in $\{0, 1\}$. Given a set $\mathcal{F}$ of base-classifiers on $\mathcal{X}$, we build corresponding classifiers in the space of measures. We provide upper and lower bounds on the Rademacher complexity of this new class of classifiers that can be expressed simply in terms of corresponding quantities for the class $\mathcal{F}$. If the measures $\mu_i$ are uniform over a finite set, this classification task boils down to a multi-instance learning problem. However, our approach allows more flexibility and diversity in the input data we can deal with. While such a framework has many possible applications, this work strongly emphasizes on classifying data via topological descriptors called persistence diagrams. These objects are discrete measures on $\mathbb{R}^2$, where the coordinates of each point correspond to the range of scales at which a topological feature exists. We will present several classifiers on measures and show how they can heuristically and theoretically enable a good classification performance in various settings in the case of persistence diagrams.
Topologically penalized regression on manifolds
Oct 26, 2021


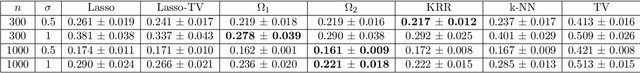
Abstract:We study a regression problem on a compact manifold M. In order to take advantage of the underlying geometry and topology of the data, the regression task is performed on the basis of the first several eigenfunctions of the Laplace-Beltrami operator of the manifold, that are regularized with topological penalties. The proposed penalties are based on the topology of the sub-level sets of either the eigenfunctions or the estimated function. The overall approach is shown to yield promising and competitive performance on various applications to both synthetic and real data sets. We also provide theoretical guarantees on the regression function estimates, on both its prediction error and its smoothness (in a topological sense). Taken together, these results support the relevance of our approach in the case where the targeted function is "topologically smooth".
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge