Olufunto A Olusanya
Association Between Neighborhood Factors and Adult Obesity in Shelby County, Tennessee: Geospatial Machine Learning Approach
Aug 09, 2022
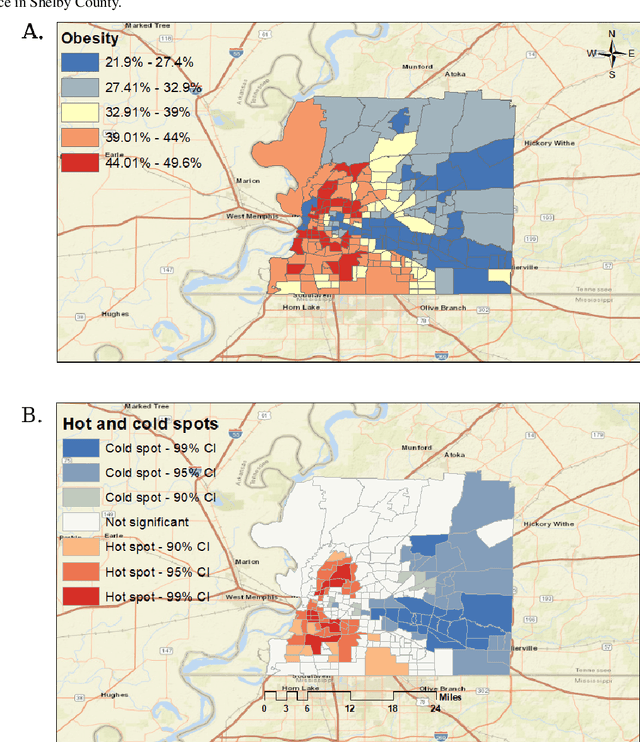
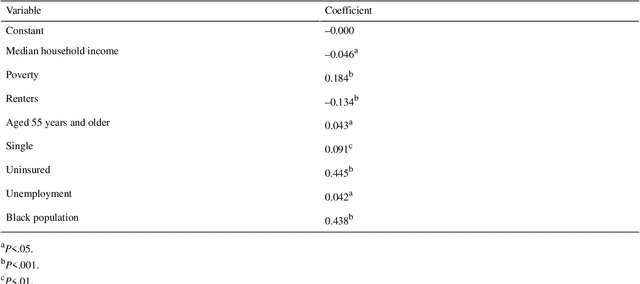
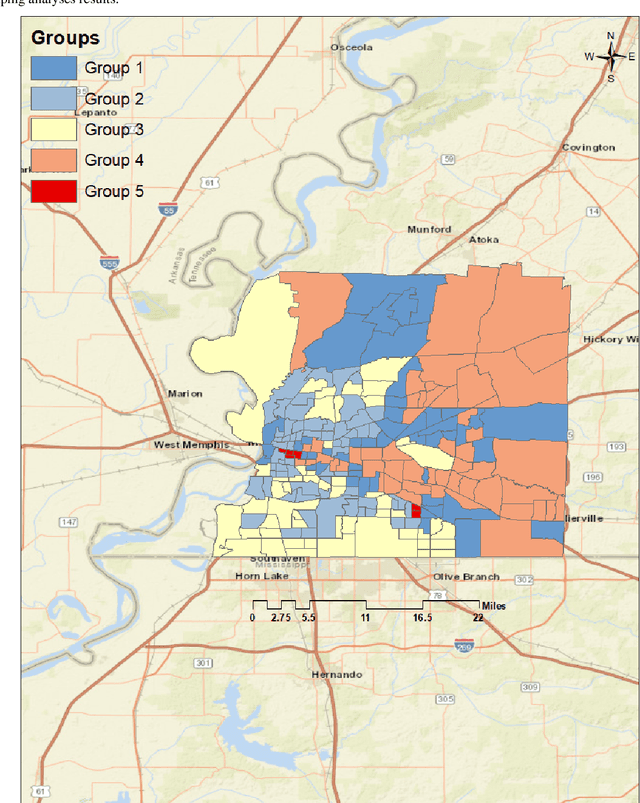
Abstract:Obesity is a global epidemic causing at least 2.8 million deaths per year. This complex disease is associated with significant socioeconomic burden, reduced work productivity, unemployment, and other social determinants of Health (SDoH) disparities. Objective: The objective of this study was to investigate the effects of SDoH on obesity prevalence among adults in Shelby County, Tennessee, USA using a geospatial machine-learning approach. Obesity prevalence was obtained from publicly available CDC 500 cities database while SDoH indicators were extracted from the U.S. Census and USDA. We examined the geographic distributions of obesity prevalence patterns using Getis-Ord Gi* statistics and calibrated multiple models to study the association between SDoH and adult obesity. Also, unsupervised machine learning was used to conduct grouping analysis to investigate the distribution of obesity prevalence and associated SDoH indicators. Results depicted a high percentage of neighborhoods experiencing high adult obesity prevalence within Shelby County. In the census tract, median household income, as well as the percentage of individuals who were black, home renters, living below the poverty level, fifty-five years or older, unmarried, and uninsured, had a significant association with adult obesity prevalence. The grouping analysis revealed disparities in obesity prevalence amongst disadvantaged neighborhoods. More research is needed that examines linkages between geographical location, SDoH, and chronic diseases. These findings, which depict a significantly higher prevalence of obesity within disadvantaged neighborhoods, and other geospatial information can be leveraged to offer valuable insights informing health decision-making and interventions that mitigate risk factors for increasing obesity prevalence.
* 12 Pages, 3 Figures, 5 Tables
Public sentiment analysis and topic modeling regarding COVID-19 vaccines on the Reddit social media platform: A call to action for strengthening vaccine confidence
Aug 22, 2021


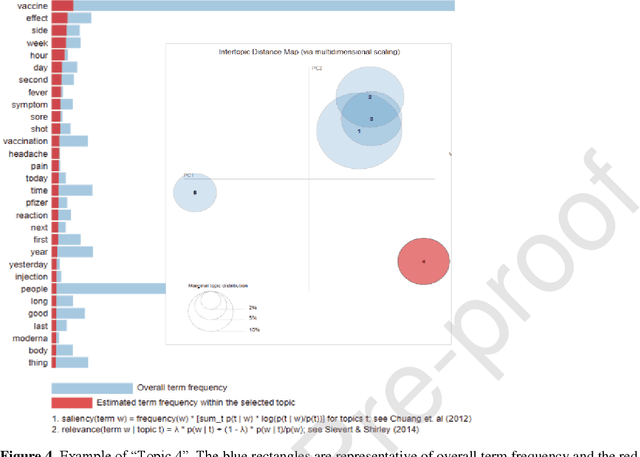
Abstract:The COVID-19 pandemic fueled one of the most rapid vaccine developments in history. However, misinformation spread through online social media often leads to negative vaccine sentiment and hesitancy. To investigate COVID-19 vaccine-related discussion in social media, we conducted a sentiment analysis and Latent Dirichlet Allocation topic modeling on textual data collected from 13 Reddit communities focusing on the COVID-19 vaccine from Dec 1, 2020, to May 15, 2021. Data were aggregated and analyzed by month to detect changes in any sentiment and latent topics. ty analysis suggested these communities expressed more positive sentiment than negative regarding the vaccine-related discussions and has remained static over time. Topic modeling revealed community members mainly focused on side effects rather than outlandish conspiracy theories. Covid-19 vaccine-related content from 13 subreddits show that the sentiments expressed in these communities are overall more positive than negative and have not meaningfully changed since December 2020. Keywords indicating vaccine hesitancy were detected throughout the LDA topic modeling. Public sentiment and topic modeling analysis regarding vaccines could facilitate the implementation of appropriate messaging, digital interventions, and new policies to promote vaccine confidence.
* 8 pages, 4 Figures, 2 Tables
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge