Oliver Roesler
Investigating the Utility of Multimodal Conversational Technology and Audiovisual Analytic Measures for the Assessment and Monitoring of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis at Scale
Apr 15, 2021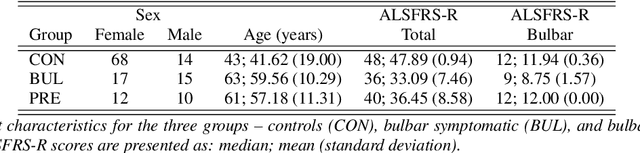
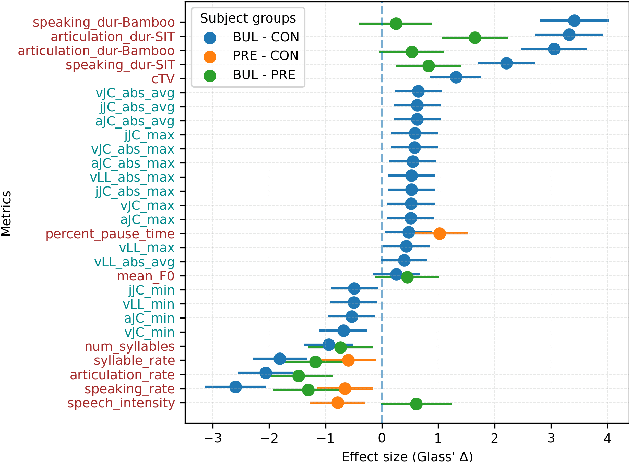
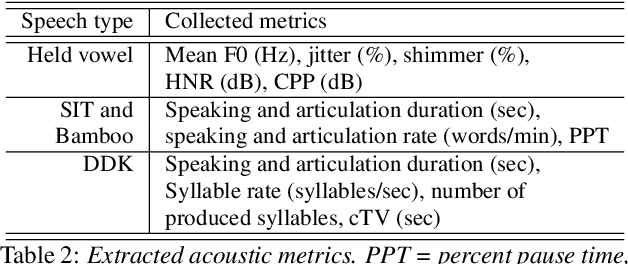
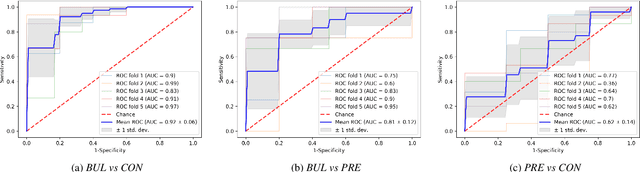
Abstract:We propose a cloud-based multimodal dialog platform for the remote assessment and monitoring of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) at scale. This paper presents our vision, technology setup, and an initial investigation of the efficacy of the various acoustic and visual speech metrics automatically extracted by the platform. 82 healthy controls and 54 people with ALS (pALS) were instructed to interact with the platform and completed a battery of speaking tasks designed to probe the acoustic, articulatory, phonatory, and respiratory aspects of their speech. We find that multiple acoustic (rate, duration, voicing) and visual (higher order statistics of the jaw and lip) speech metrics show statistically significant differences between controls, bulbar symptomatic and bulbar pre-symptomatic patients. We report on the sensitivity and specificity of these metrics using five-fold cross-validation. We further conducted a LASSO-LARS regression analysis to uncover the relative contributions of various acoustic and visual features in predicting the severity of patients' ALS (as measured by their self-reported ALSFRS-R scores). Our results provide encouraging evidence of the utility of automatically extracted audiovisual analytics for scalable remote patient assessment and monitoring in ALS.
Unsupervised Online Grounding of Natural Language during Human-Robot Interactions
Jul 05, 2020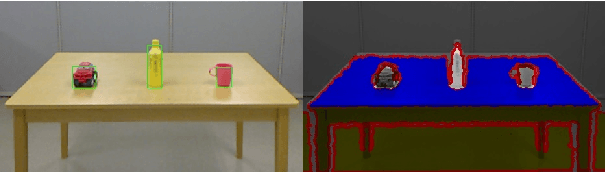
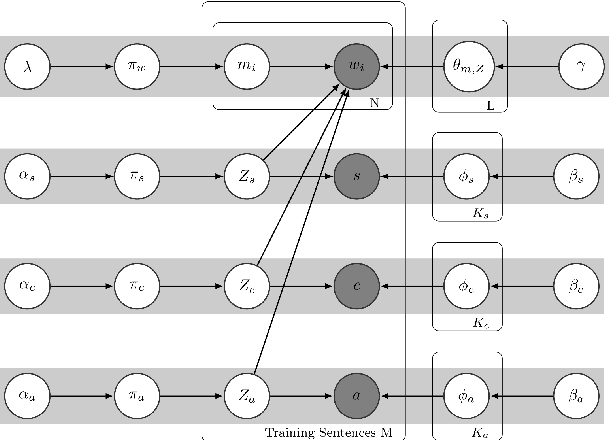
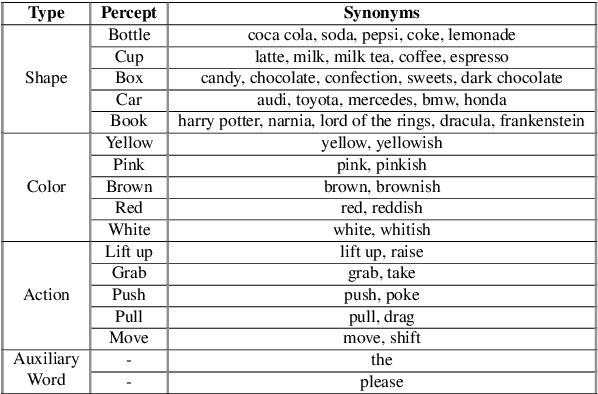
Abstract:Allowing humans to communicate through natural language with robots requires connections between words and percepts. The process of creating these connections is called symbol grounding and has been studied for nearly three decades. Although many studies have been conducted, not many considered grounding of synonyms and the employed algorithms either work only offline or in a supervised manner. In this paper, a cross-situational learning based grounding framework is proposed that allows grounding of words and phrases through corresponding percepts without human supervision and online, i.e. it does not require any explicit training phase, but instead updates the obtained mappings for every new encountered situation. The proposed framework is evaluated through an interaction experiment between a human tutor and a robot, and compared to an existing unsupervised grounding framework. The results show that the proposed framework is able to ground words through their corresponding percepts online and in an unsupervised manner, while outperforming the baseline framework.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge