Olga Solovyova
Compressor-Based Classification for Atrial Fibrillation Detection
Aug 25, 2023Abstract:Atrial fibrillation (AF) is one of the most common arrhythmias with challenging public health implications. Automatic detection of AF episodes is therefore one of the most important tasks in biomedical engineering. In this paper, we apply the recently introduced method of compressor-based text classification to the task of AF detection (binary classification between heart rhythms). We investigate the normalised compression distance applied to $\Delta$RR and RR-interval sequences, the configuration of the k-Nearest Neighbour classifier, and an optimal window length. We achieve good classification results (avg. sensitivity = 97.1%, avg. specificity = 91.7%, best sensitivity of 99.8%, best specificity of 97.6% with 5-fold cross-validation). Obtained performance is close to the best specialised AF detection algorithms. Our results suggest that gzip classification, originally proposed for texts, is suitable for biomedical data and continuous stochastic sequences in general.
Effects of lead position, cardiac rhythm variation and drug-induced QT prolongation on performance of machine learning methods for ECG processing
Dec 10, 2019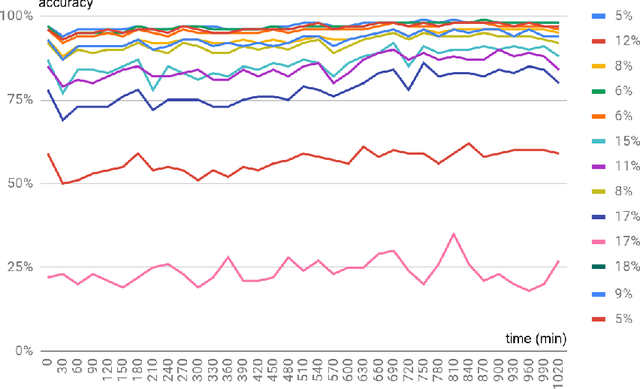
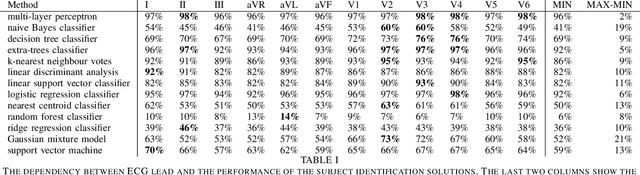
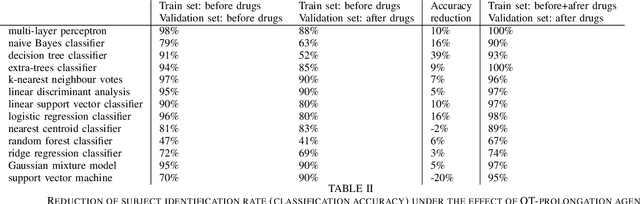
Abstract:Machine learning shows great performance in various problems of electrocardiography (ECG) signal analysis. However, collecting of any dataset for biomedical engineering is a very difficult task. Any datasets for ECG processing contains from 100 to 10,000 times fewer cases than datasets for image or text analysis. This issue is especially important because of physiological phenomena that can significantly change the morphology of heartbeats in ECG signals. In this preliminary study, we analyze the effects of lead choice from the standard ECG recordings, a variation of ECG during 24-hours, and the effects of QT-prolongation agents on the performance of machine learning methods for ECG processing. We choose the problem of subject identification for analysis, because this problem may be solved for almost any available dataset of ECG data. In a discussion, we compare our findings with observations from other works that use machine learning for ECG processing with different problem statements. Our results show the importance of training dataset enrichment with ECG signals that acquired in specific physiological conditions for obtaining good performance of ECG processing for real applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge