Ofir Abu
Promoting Resilience in Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning via Confusion-Based Communication
Nov 12, 2021
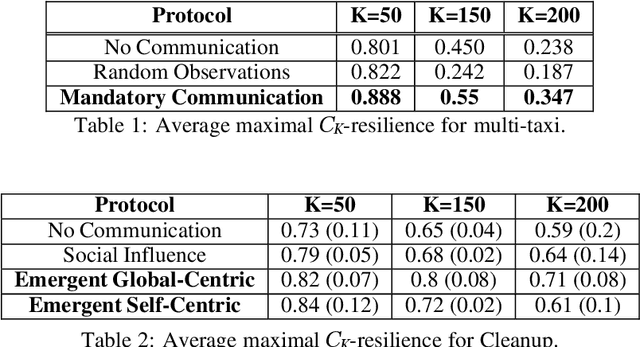
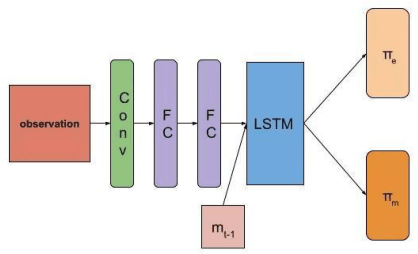
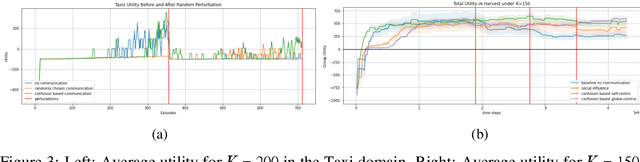
Abstract:Recent advances in multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) provide a variety of tools that support the ability of agents to adapt to unexpected changes in their environment, and to operate successfully given their environment's dynamic nature (which may be intensified by the presence of other agents). In this work, we highlight the relationship between a group's ability to collaborate effectively and the group's resilience, which we measure as the group's ability to adapt to perturbations in the environment. To promote resilience, we suggest facilitating collaboration via a novel confusion-based communication protocol according to which agents broadcast observations that are misaligned with their previous experiences. We allow decisions regarding the width and frequency of messages to be learned autonomously by agents, which are incentivized to reduce confusion. We present empirical evaluation of our approach in a variety of MARL settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge