Nima TaheriNejad
IMPLY-based Approximate Full Adders for Efficient Arithmetic Operations in Image Processing and Machine Learning
Dec 20, 2024



Abstract:To overcome the performance limitations in modern computing, such as the power wall, emerging computing paradigms are gaining increasing importance. Approximate computing offers a promising solution by substantially enhancing energy efficiency and reducing latency, albeit with a trade-off in accuracy. Another emerging method is memristor-based In-Memory Computing (IMC) which has the potential to overcome the Von Neumann bottleneck. In this work, we combine these two approaches and propose two Serial APProximate IMPLY-based full adders (SAPPI). When embedded in a Ripple Carry Adder (RCA), our designs reduce the number of steps by 39%-41% and the energy consumption by 39%-42% compared to the exact algorithm. We evaluated our approach at the circuit level and compared it with State-of-the-Art (SoA) approximations where our adders improved the speed by up to 10% and the energy efficiency by up to 13%. We applied our designs in three common image processing applications where we achieved acceptable image quality with up to half of the RCA approximated. We performed a case study to demonstrate the applicability of our approximations in Machine Learning (ML) underscoring the potential gains in more complex scenarios. The proposed approach demonstrates energy savings of up to 296 mJ (21%) and a reduction of 1.3 billion (20%) computational steps when applied to Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) trained on the MNIST dataset while maintaining accuracy.
Learning on Hardware: A Tutorial on Neural Network Accelerators and Co-Processors
Apr 19, 2021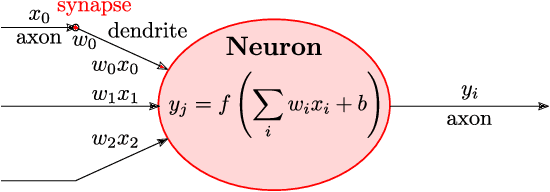
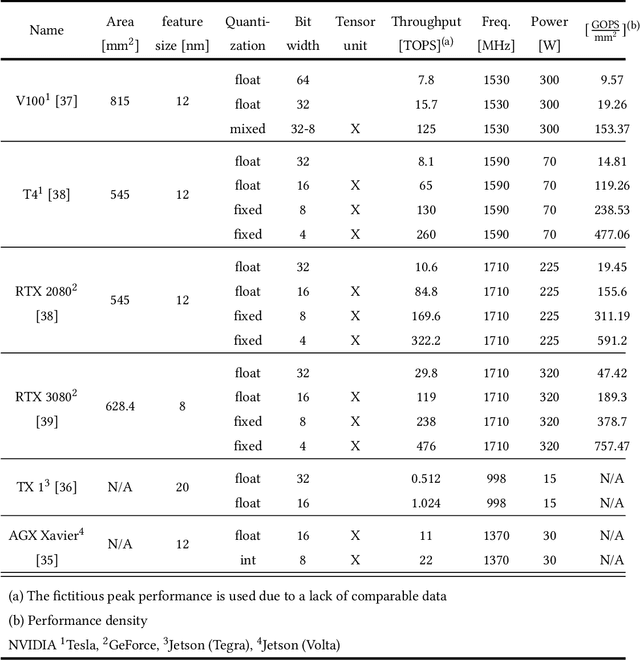
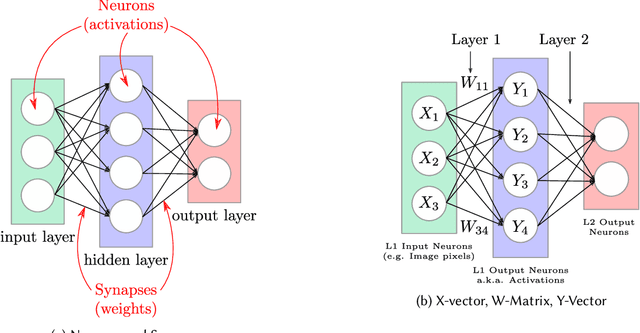
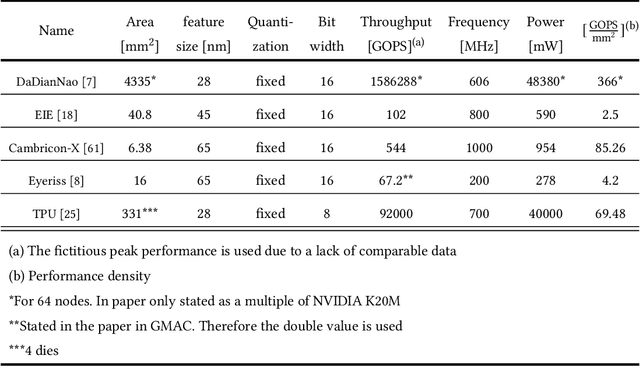
Abstract:Deep neural networks (DNNs) have the advantage that they can take into account a large number of parameters, which enables them to solve complex tasks. In computer vision and speech recognition, they have a better accuracy than common algorithms, and in some tasks, they boast an even higher accuracy than human experts. With the progress of DNNs in recent years, many other fields of application such as diagnosis of diseases and autonomous driving are taking advantage of them. The trend at DNNs is clear: The network size is growing exponentially, which leads to an exponential increase in computational effort and required memory size. For this reason, optimized hardware accelerators are used to increase the performance of the inference of neuronal networks. However, there are various neural network hardware accelerator platforms, such as graphics processing units (GPUs), application specific integrated circuits (ASICs) and field programmable gate arrays (FPGAs). Each of these platforms offer certain advantages and disadvantages. Also, there are various methods for reducing the computational effort of DNNs, which are differently suitable for each hardware accelerator. In this article an overview of existing neural network hardware accelerators and acceleration methods is given. Their strengths and weaknesses are shown and a recommendation of suitable applications is given. In particular, we focus on acceleration of the inference of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) used for image recognition tasks. Given that there exist many different hardware architectures. FPGA-based implementations are well-suited to show the effect of DNN optimization methods on accuracy and throughput. For this reason, the focus of this work is more on FPGA-based implementations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge