Nikolaos Kondylidis
Establishing Shared Query Understanding in an Open Multi-Agent System
May 16, 2023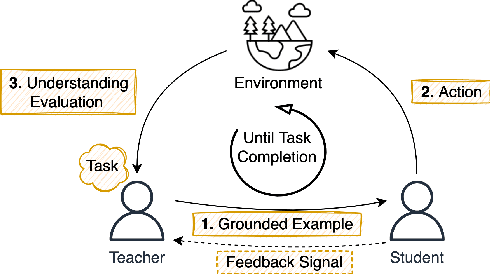
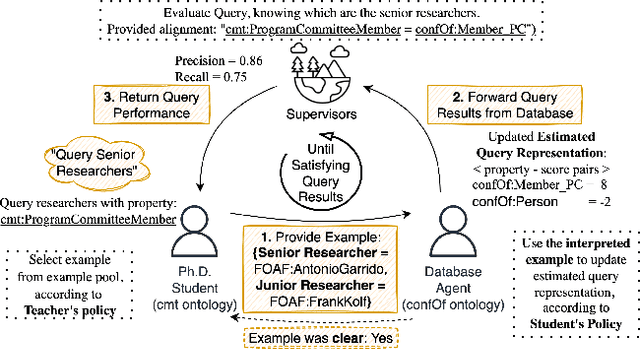
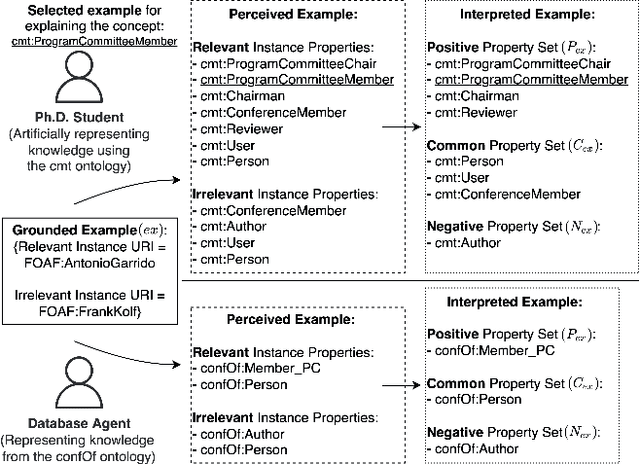
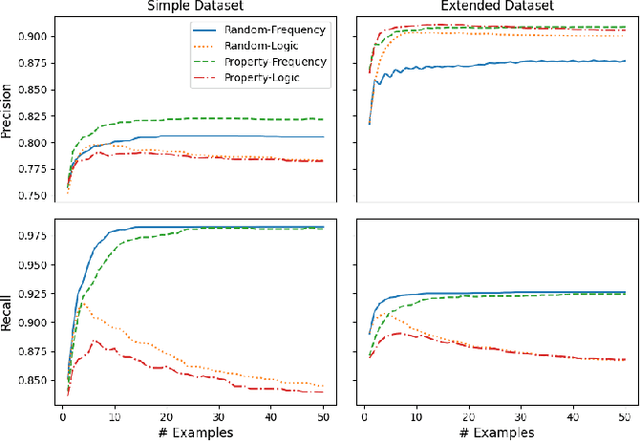
Abstract:We propose a method that allows to develop shared understanding between two agents for the purpose of performing a task that requires cooperation. Our method focuses on efficiently establishing successful task-oriented communication in an open multi-agent system, where the agents do not know anything about each other and can only communicate via grounded interaction. The method aims to assist researchers that work on human-machine interaction or scenarios that require a human-in-the-loop, by defining interaction restrictions and efficiency metrics. To that end, we point out the challenges and limitations of such a (diverse) setup, while also restrictions and requirements which aim to ensure that high task performance truthfully reflects the extent to which the agents correctly understand each other. Furthermore, we demonstrate a use-case where our method can be applied for the task of cooperative query answering. We design the experiments by modifying an established ontology alignment benchmark. In this example, the agents want to query each other, while representing different databases, defined in their own ontologies that contain different and incomplete knowledge. Grounded interaction here has the form of examples that consists of common instances, for which the agents are expected to have similar knowledge. Our experiments demonstrate successful communication establishment under the required restrictions, and compare different agent policies that aim to solve the task in an efficient manner.
Category Aware Explainable Conversational Recommendation
Mar 15, 2021



Abstract:Most conversational recommendation approaches are either not explainable, or they require external user's knowledge for explaining or their explanations cannot be applied in real time due to computational limitations. In this work, we present a real time category based conversational recommendation approach, which can provide concise explanations without prior user knowledge being required. We first perform an explainable user model in the form of preferences over the items' categories, and then use the category preferences to recommend items. The user model is performed by applying a BERT-based neural architecture on the conversation. Then, we translate the user model into item recommendation scores using a Feed Forward Network. User preferences during the conversation in our approach are represented by category vectors which are directly interpretable. The experimental results on the real conversational recommendation dataset ReDial demonstrate comparable performance to the state-of-the-art, while our approach is explainable. We also show the potential power of our framework by involving an oracle setting of category preference prediction.
* Workshop on Mixed-Initiative ConveRsatiOnal Systems (MICROS) @ECIR, 2021
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge