Nicola Fioraio
NVS-HO: A Benchmark for Novel View Synthesis of Handheld Objects
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:We propose NVS-HO, the first benchmark designed for novel view synthesis of handheld objects in real-world environments using only RGB inputs. Each object is recorded in two complementary RGB sequences: (1) a handheld sequence, where the object is manipulated in front of a static camera, and (2) a board sequence, where the object is fixed on a ChArUco board to provide accurate camera poses via marker detection. The goal of NVS-HO is to learn a NVS model that captures the full appearance of an object from (1), whereas (2) provides the ground-truth images used for evaluation. To establish baselines, we consider both a classical SfM pipeline and a state-of-the-art pre-trained feed-forward neural network (VGGT) as pose estimators, and train NVS models based on NeRF and Gaussian Splatting. Our experiments reveal significant performance gaps in current methods under unconstrained handheld conditions, highlighting the need for more robust approaches. NVS-HO thus offers a challenging real-world benchmark to drive progress in RGB-based novel view synthesis of handheld objects.
The Eyecandies Dataset for Unsupervised Multimodal Anomaly Detection and Localization
Oct 10, 2022
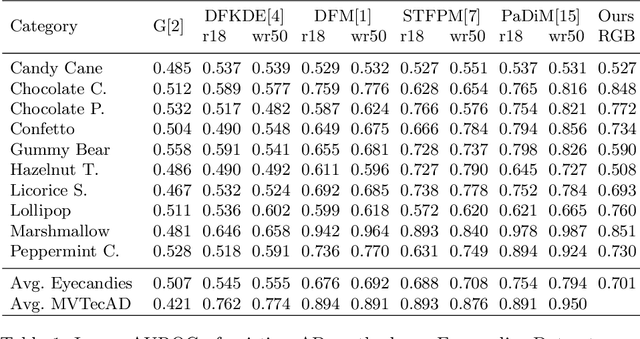
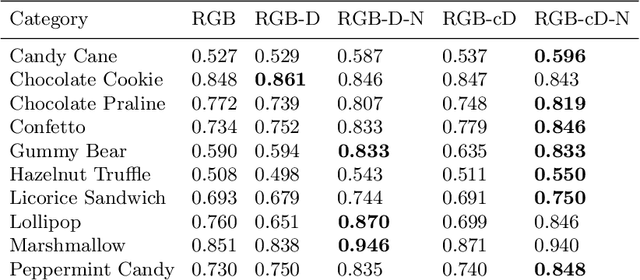
Abstract:We present Eyecandies, a novel synthetic dataset for unsupervised anomaly detection and localization. Photo-realistic images of procedurally generated candies are rendered in a controlled environment under multiple lightning conditions, also providing depth and normal maps in an industrial conveyor scenario. We make available anomaly-free samples for model training and validation, while anomalous instances with precise ground-truth annotations are provided only in the test set. The dataset comprises ten classes of candies, each showing different challenges, such as complex textures, self-occlusions and specularities. Furthermore, we achieve large intra-class variation by randomly drawing key parameters of a procedural rendering pipeline, which enables the creation of an arbitrary number of instances with photo-realistic appearance. Likewise, anomalies are injected into the rendering graph and pixel-wise annotations are automatically generated, overcoming human-biases and possible inconsistencies. We believe this dataset may encourage the exploration of original approaches to solve the anomaly detection task, e.g. by combining color, depth and normal maps, as they are not provided by most of the existing datasets. Indeed, in order to demonstrate how exploiting additional information may actually lead to higher detection performance, we show the results obtained by training a deep convolutional autoencoder to reconstruct different combinations of inputs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge