Ng Bee Chin
Written and spoken corpus of real and fake social media postings about COVID-19
Oct 06, 2023Abstract:This study investigates the linguistic traits of fake news and real news. There are two parts to this study: text data and speech data. The text data for this study consisted of 6420 COVID-19 related tweets re-filtered from Patwa et al. (2021). After cleaning, the dataset contained 3049 tweets, with 2161 labeled as 'real' and 888 as 'fake'. The speech data for this study was collected from TikTok, focusing on COVID-19 related videos. Research assistants fact-checked each video's content using credible sources and labeled them as 'Real', 'Fake', or 'Questionable', resulting in a dataset of 91 real entries and 109 fake entries from 200 TikTok videos with a total word count of 53,710 words. The data was analysed using the Linguistic Inquiry and Word Count (LIWC) software to detect patterns in linguistic data. The results indicate a set of linguistic features that distinguish fake news from real news in both written and speech data. This offers valuable insights into the role of language in shaping trust, social media interactions, and the propagation of fake news.
MICE: A Crosslinguistic Emotion Corpus in Malay, Indonesian, Chinese and English
Jun 09, 2021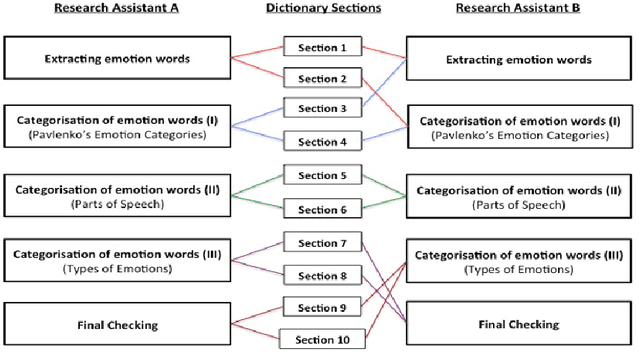

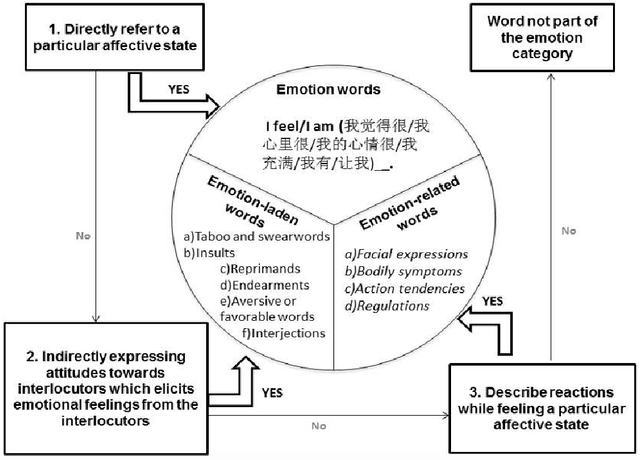
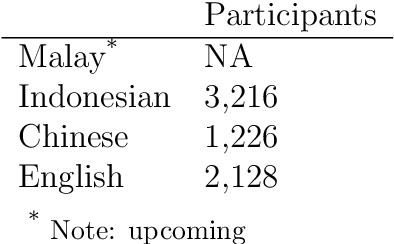
Abstract:MICE is a corpus of emotion words in four languages which is currently working progress. There are two sections to this study, Part I: Emotion word corpus and Part II: Emotion word survey. In Part 1, the method of how the emotion data is culled for each of the four languages will be described and very preliminary data will be presented. In total, we identified 3,750 emotion expressions in Malay, 6,657 in Indonesian, 3,347 in Mandarin Chinese and 8,683 in English. We are currently evaluating and double checking the corpus and doing further analysis on the distribution of these emotion expressions. Part II Emotion word survey involved an online language survey which collected information on how speakers assigned the emotion words into basic emotion categories, the rating for valence and intensity as well as biographical information of all the respondents.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge