Nelson H. C. Yung
Consistency Analysis for the Doubly Stochastic Dirichlet Process
May 24, 2016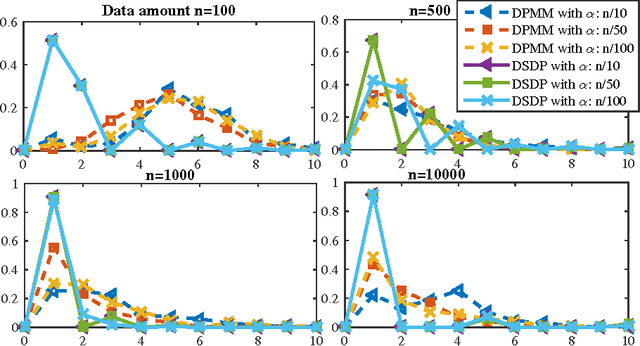
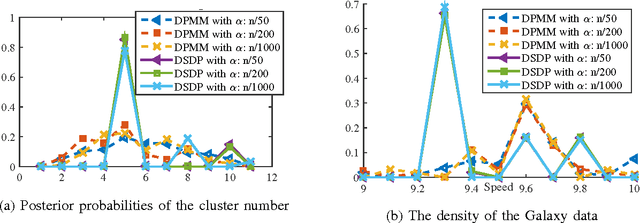
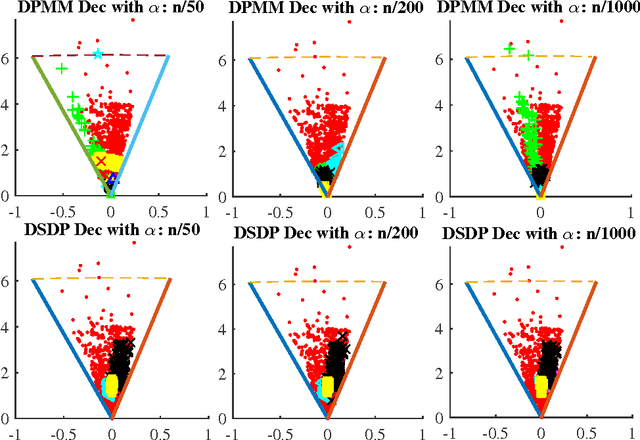
Abstract:This technical report proves components consistency for the Doubly Stochastic Dirichlet Process with exponential convergence of posterior probability. We also present the fundamental properties for DSDP as well as inference algorithms. Simulation toy experiment and real-world experiment results for single and multi-cluster also support the consistency proof. This report is also a support document for the paper "Computationally Efficient Hyperspectral Data Learning Based on the Doubly Stochastic Dirichlet Process".
Outlier Detection In Large-scale Traffic Data By Naïve Bayes Method and Gaussian Mixture Model Method
Dec 28, 2015



Abstract:It is meaningful to detect outliers in traffic data for traffic management. However, this is a massive task for people from large-scale database to distinguish outliers. In this paper, we present two methods: Kernel Smoothing Na\"ive Bayes (NB) method and Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM) method to automatically detect any hardware errors as well as abnormal traffic events in traffic data collected at a four-arm junction in Hong Kong. Traffic data was recorded in a video format, and converted to spatial-temporal (ST) traffic signals by statistics. The ST signals are then projected to a two-dimensional (2D) (x,y)-coordinate plane by Principal Component Analysis (PCA) for dimension reduction. We assume that inlier data are normal distributed. As such, the NB and GMM methods are successfully applied in outlier detection (OD) for traffic data. The kernel smooth NB method assumes the existence of kernel distributions in traffic data and uses Bayes' Theorem to perform OD. In contrast, the GMM method believes the traffic data is formed by the mixture of Gaussian distributions and exploits confidence region for OD. This paper would address the modeling of each method and evaluate their respective performances. Experimental results show that the NB algorithm with Triangle kernel and GMM method achieve up to 93.78% and 94.50% accuracies, respectively.
Automatic Incident Classification for Big Traffic Data by Adaptive Boosting SVM
Dec 28, 2015



Abstract:Modern cities experience heavy traffic flows and congestions regularly across space and time. Monitoring traffic situations becomes an important challenge for the Traffic Control and Surveillance Systems (TCSS). In advanced TCSS, it is helpful to automatically detect and classify different traffic incidents such as severity of congestion, abnormal driving pattern, abrupt or illegal stop on road, etc. Although most TCSS are equipped with basic incident detection algorithms, they are however crude to be really useful as an automated tool for further classification. In literature, there is a lack of research for Automated Incident Classification (AIC). Therefore, a novel AIC method is proposed in this paper to tackle such challenges. In the proposed method, traffic signals are firstly extracted from captured videos and converted as spatial-temporal (ST) signals. Based on the characteristics of the ST signals, a set of realistic simulation data are generated to construct an extended big traffic database to cover a variety of traffic situations. Next, a Mean-Shift filter is introduced to suppress the effect of noise and extract significant features from the ST signals. The extracted features are then associated with various types of traffic data: one normal type (inliers) and multiple abnormal types (outliers). For the classification, an adaptive boosting classifier is trained to detect outliers in traffic data automatically. Further, a Support Vector Machine (SVM) based method is adopted to train the model for identifying the categories of outliers. In short, this hybrid approach is called an Adaptive Boosting Support Vector Machines (AB-SVM) method. Experimental results show that the proposed AB-SVM method achieves a satisfied result with more than 92% classification accuracy on average.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge