Neha Baranwal
Literature on Hand GESTURE Recognition using Graph based methods
Jul 01, 2022



Abstract:Skeleton based recognition systems are gaining popularity and machine learning models focusing on points or joints in a skeleton have proved to be computationally effective and application in many areas like Robotics. It is easy to track points and thereby preserving spatial and temporal information, which plays an important role in abstracting the required information, classification becomes an easy task. In this paper, we aim to study these points but using a cloud mechanism, where we define a cloud as collection of points. However, when we add temporal information, it may not be possible to retrieve the coordinates of a point in each frame and hence instead of focusing on a single point, we can use k-neighbors to retrieve the state of the point under discussion. Our focus is to gather such information using weight sharing but making sure that when we try to retrieve the information from neighbors, we do not carry noise with it. LSTM which has capability of long-term modelling and can carry both temporal and spatial information. In this article we tried to summarise graph based gesture recognition method.
Improved Mispronunciation detection system using a hybrid CTC-ATT based approach for L2 English speakers
Jan 25, 2022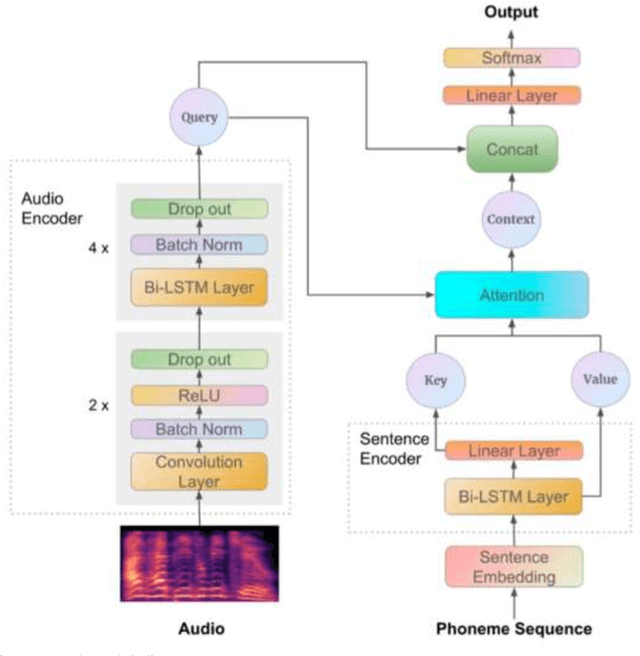
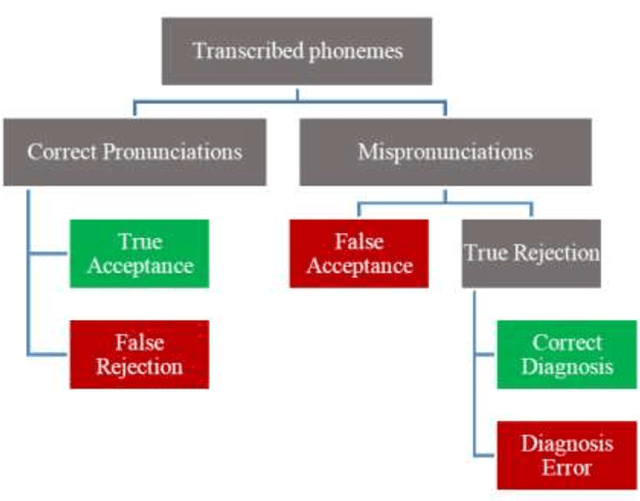
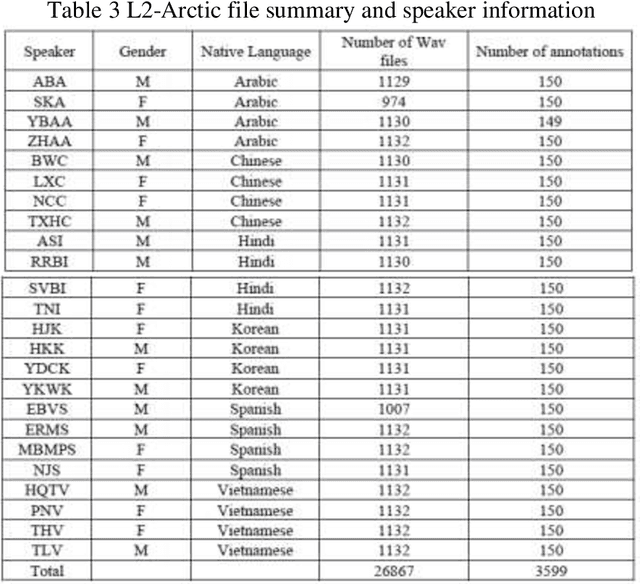
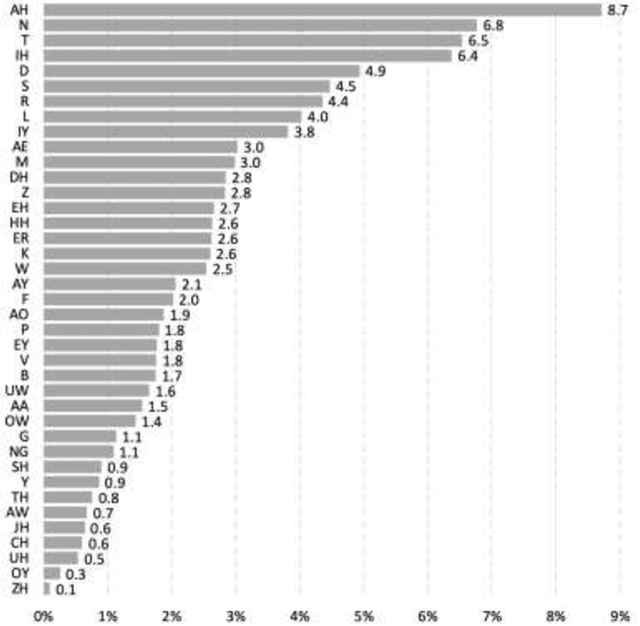
Abstract:This report proposes state-of-the-art research in the field of Computer Assisted Language Learning (CALL). Mispronunciation detection is one of the core components of Computer Assisted Pronunciation Training (CAPT) systems which is a subset of CALL. Studies on automated pronunciation error detection began in the 1990s, but the development of fullfledged CAPTs has only accelerated in the last decade due to an increase in computing power and availability of mobile devices for recording speech required for pronunciation analysis. Detecting Pronunciation errors is a hard problem to solve as there is no formal definition of correct and incorrect pronunciation. As a result, typically prosodic and phoneme errors such as phoneme substitution, insertion, and deletion are detected. Also, it has been agreed upon that learning pronunciation should focus on speaker intelligibility rather than sounding like an L1 English speaker. Initially, methods were developed on posterior likelihood called Good of Pronunciation using Gaussian Mixture Model-Hidden Markov Model and Deep Neural Network-Hidden Markov Model approaches. These are complex systems to implement when compared with the recently proposed ASR based End-to-End mispronunciations detection systems. The purpose of this research is to create End-to-End (E2E) models using Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC) and Attention-based sequence decoder. Recently, E2E models have shown considerable improvement in mispronunciation detection accuracy. This research will draw comparison amongst baseline models CNN-RNN-CTC, CNN-RNN-CTC with character sequence-based attention decoder, and CNN-RNN-CTC with phoneme-based decoder systems. This study will help us in deciding a better approach towards developing an efficient mispronunciation detection system.
Classification of Histopathology Images of Lung Cancer Using Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)
Dec 27, 2021



Abstract:Cancer is the uncontrollable cell division of abnormal cells inside the human body, which can spread to other body organs. It is one of the non-communicable diseases (NCDs) and NCDs accounts for 71% of total deaths worldwide whereas lung cancer is the second most diagnosed cancer after female breast cancer. Cancer survival rate of lung cancer is only 19%. There are various methods for the diagnosis of lung cancer, such as X-ray, CT scan, PET-CT scan, bronchoscopy and biopsy. However, to know the subtype of lung cancer based on the tissue type H and E staining is widely used, where the staining is done on the tissue aspirated from a biopsy. Studies have reported that the type of histology is associated with prognosis and treatment in lung cancer. Therefore, early and accurate detection of lung cancer histology is an urgent need and as its treatment is dependent on the type of histology, molecular profile and stage of the disease, it is most essential to analyse the histopathology images of lung cancer. Hence, to speed up the vital process of diagnosis of lung cancer and reduce the burden on pathologists, Deep learning techniques are used. These techniques have shown improved efficacy in the analysis of histopathology slides of cancer. Several studies reported the importance of convolution neural networks (CNN) in the classification of histopathological pictures of various cancer types such as brain, skin, breast, lung, colorectal cancer. In this study tri-category classification of lung cancer images (normal, adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma) are carried out by using ResNet 50, VGG-19, Inception_ResNet_V2 and DenseNet for the feature extraction and triplet loss to guide the CNN such that it increases inter-cluster distance and reduces intra-cluster distance.
On Human Robot Interaction using Multiple Modes
Nov 17, 2018



Abstract:Humanoid robots have apparently similar body structure like human beings. Due to their technical design, they are sharing the same workspace with humans. They are placed to clean things, to assist old age people, to entertain us and most importantly to serve us. To be acceptable in the household, they must have higher level of intelligence than industrial robots and they must be social and capable of interacting people around it, who are not supposed to be robot specialist. All these come under the field of human robot interaction (HRI). There are various modes like speech, gesture, behavior etc. through which human can interact with robots. To solve all these challenges, a multimodel technique has been introduced where gesture as well as speech is used as a mode of interaction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge