Naoya Fushishita
Efficient training for future video generation based on hierarchical disentangled representation of latent variables
Jun 08, 2021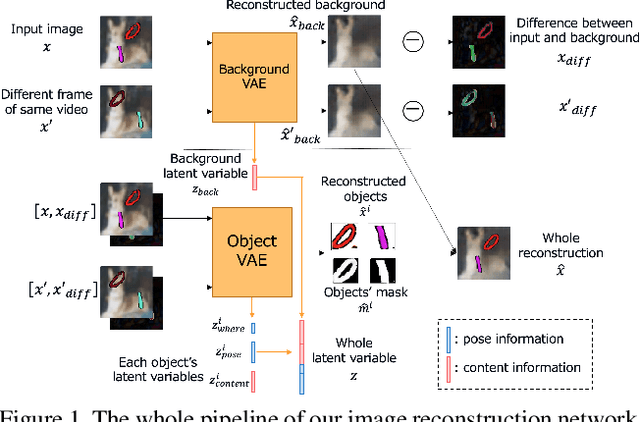
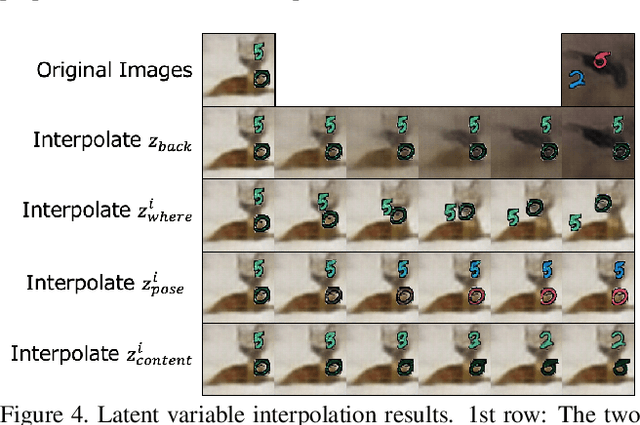
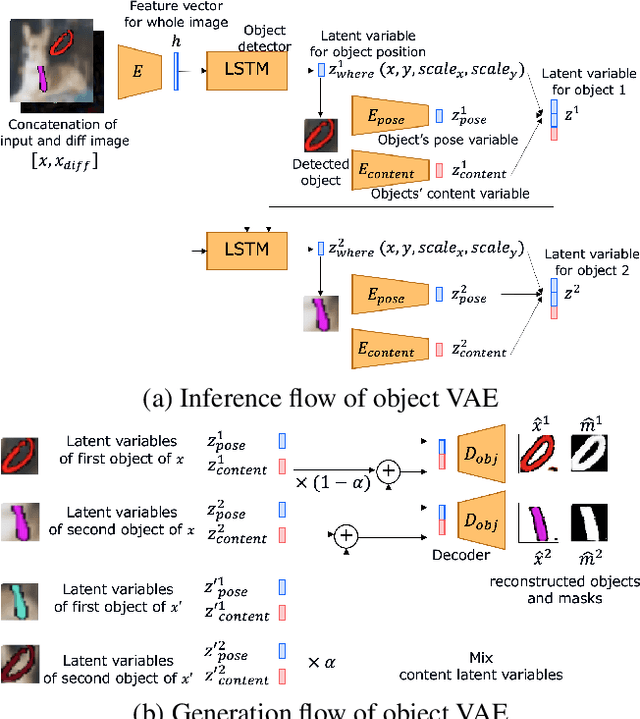


Abstract:Generating videos predicting the future of a given sequence has been an area of active research in recent years. However, an essential problem remains unsolved: most of the methods require large computational cost and memory usage for training. In this paper, we propose a novel method for generating future prediction videos with less memory usage than the conventional methods. This is a critical stepping stone in the path towards generating videos with high image quality, similar to that of generated images in the latest works in the field of image generation. We achieve high-efficiency by training our method in two stages: (1) image reconstruction to encode video frames into latent variables, and (2) latent variable prediction to generate the future sequence. Our method achieves an efficient compression of video into low-dimensional latent variables by decomposing each frame according to its hierarchical structure. That is, we consider that video can be separated into background and foreground objects, and that each object holds time-varying and time-independent information independently. Our experiments show that the proposed method can efficiently generate future prediction videos, even for complex datasets that cannot be handled by previous methods.
Long-Term Video Generation of Multiple Futures Using Human Poses
Apr 17, 2019


Abstract:Predicting the near-future from an input video is a useful task for applications such as autonomous driving and robotics. While most previous works predict a single future, multiple futures with different behaviors can possibly occur. Moreover, if the predicted future is too short, it may not be fully usable by a human or other system. In this paper, we propose a novel method for future video prediction capable of generating multiple long-term futures. This makes the predictions more suitable for real applications. First, from an input human video, we generate sequences of future human poses as the image coordinates of their body-joints by adversarial learning. We generate multiple futures by inputting to the generator combinations of a latent code (to reflect various behaviors) and an attraction point (to reflect various trajectories). In addition, we generate long-term future human poses using a novel approach based on unidimensional convolutional neural networks. Last, we generate an output video based on the generated poses for visualization. We evaluate the generated future poses and videos using three criteria (i.e., realism, diversity and accuracy), and show that our proposed method outperforms other state-of-the-art works.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge