Naghmeh Farzi
Supporting Humans in Evaluating AI Summaries of Legal Depositions
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:While large language models (LLMs) are increasingly used to summarize long documents, this trend poses significant challenges in the legal domain, where the factual accuracy of deposition summaries is crucial. Nugget-based methods have been shown to be extremely helpful for the automated evaluation of summarization approaches. In this work, we translate these methods to the user side and explore how nuggets could directly assist end users. Although prior systems have demonstrated the promise of nugget-based evaluation, its potential to support end users remains underexplored. Focusing on the legal domain, we present a prototype that leverages a factual nugget-based approach to support legal professionals in two concrete scenarios: (1) determining which of two summaries is better, and (2) manually improving an automatically generated summary.
Best in Tau@LLMJudge: Criteria-Based Relevance Evaluation with Llama3
Oct 17, 2024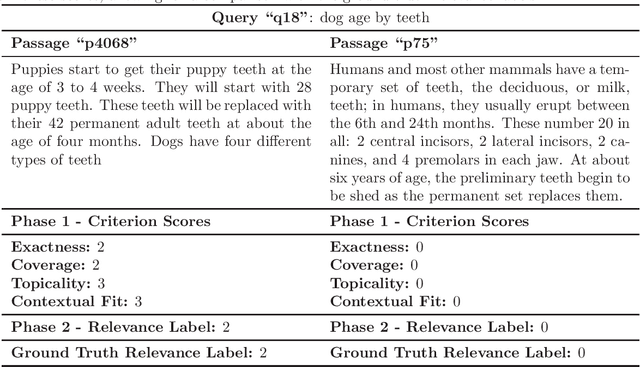



Abstract:Traditional evaluation of information retrieval (IR) systems relies on human-annotated relevance labels, which can be both biased and costly at scale. In this context, large language models (LLMs) offer an alternative by allowing us to directly prompt them to assign relevance labels for passages associated with each query. In this study, we explore alternative methods to directly prompt LLMs for assigned relevance labels, by exploring two hypotheses: Hypothesis 1 assumes that it is helpful to break down "relevance" into specific criteria - exactness, coverage, topicality, and contextual fit. We explore different approaches that prompt large language models (LLMs) to obtain criteria-level grades for all passages, and we consider various ways to aggregate criteria-level grades into a relevance label. Hypothesis 2 assumes that differences in linguistic style between queries and passages may negatively impact the automatic relevance label prediction. We explore whether improvements can be achieved by first synthesizing a summary of the passage in the linguistic style of a query, and then using this summary in place of the passage to assess its relevance. We include an empirical evaluation of our approaches based on data from the LLMJudge challenge run in Summer 2024, where our "Four Prompts" approach obtained the highest scores in Kendall's tau.
An Exam-based Evaluation Approach Beyond Traditional Relevance Judgments
Feb 01, 2024Abstract:Current IR evaluation is based on relevance judgments, created either manually or automatically, with decisions outsourced to Large Language Models (LLMs). We offer an alternative paradigm, that never relies on relevance judgments in any form. Instead, a text is defined as relevant if it contains information that enables the answering of key questions. We use this idea to design the EXAM Answerability Metric to evaluate information retrieval/generation systems for their ability to provide topically relevant information. We envision the role of a human judge to edit and define an exam question bank that will test for the presence of relevant information in text. We support this step by generating an initial set of exam questions. In the next phase, an LLM-based question answering system will automatically grade system responses by tracking which exam questions are answerable with which system responses. We propose two evaluation measures, the recall-oriented EXAM Cover metric, and the precision-oriented EXAM Qrels metric, the latter which can be implemented with trec_eval. This paradigm not only allows for the expansion of the exam question set post-hoc but also facilitates the ongoing evaluation of future information systems, whether they focus on retrieval, generation, or both.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge