N'Mah Fodiatu Yilla
Improving Fairness in Large-Scale Object Recognition by CrowdSourced Demographic Information
Jun 02, 2022

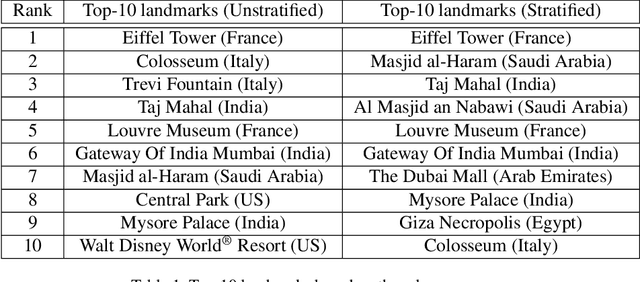
Abstract:There has been increasing awareness of ethical issues in machine learning, and fairness has become an important research topic. Most fairness efforts in computer vision have been focused on human sensing applications and preventing discrimination by people's physical attributes such as race, skin color or age by increasing visual representation for particular demographic groups. We argue that ML fairness efforts should extend to object recognition as well. Buildings, artwork, food and clothing are examples of the objects that define human culture. Representing these objects fairly in machine learning datasets will lead to models that are less biased towards a particular culture and more inclusive of different traditions and values. There exist many research datasets for object recognition, but they have not carefully considered which classes should be included, or how much training data should be collected per class. To address this, we propose a simple and general approach, based on crowdsourcing the demographic composition of the contributors: we define fair relevance scores, estimate them, and assign them to each class. We showcase its application to the landmark recognition domain, presenting a detailed analysis and the final fairer landmark rankings. We present analysis which leads to a much fairer coverage of the world compared to existing datasets. The evaluation dataset was used for the 2021 Google Landmark Challenges, which was the first of a kind with an emphasis on fairness in generic object recognition.
Towards A Fairer Landmark Recognition Dataset
Aug 19, 2021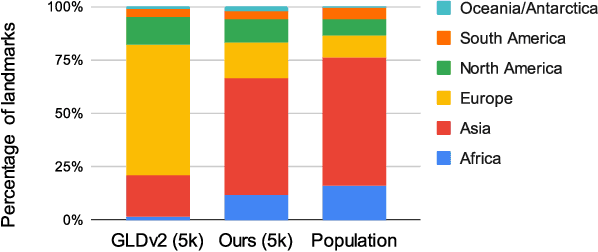
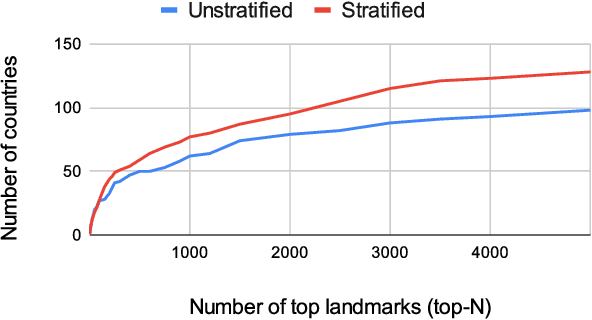

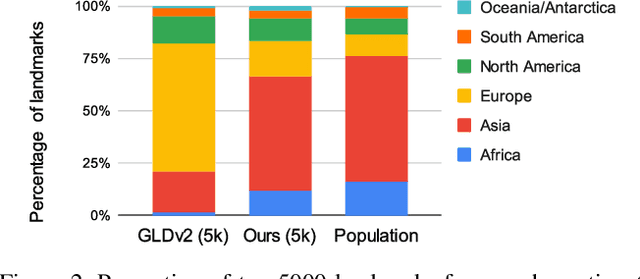
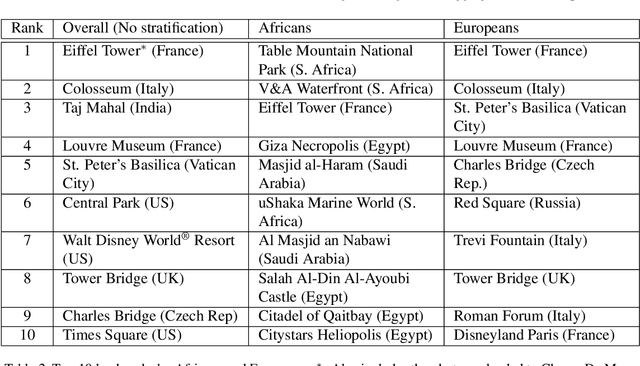
Abstract:We introduce a new landmark recognition dataset, which is created with a focus on fair worldwide representation. While previous work proposes to collect as many images as possible from web repositories, we instead argue that such approaches can lead to biased data. To create a more comprehensive and equitable dataset, we start by defining the fair relevance of a landmark to the world population. These relevances are estimated by combining anonymized Google Maps user contribution statistics with the contributors' demographic information. We present a stratification approach and analysis which leads to a much fairer coverage of the world, compared to existing datasets. The resulting datasets are used to evaluate computer vision models as part of the the Google Landmark Recognition and RetrievalChallenges 2021.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge