Muhammad Shoaib Farooq
A Deep Learning Architectures for Kidney Disease Classification
Mar 23, 2024Abstract:Deep learning has become an extremely powerful tool for complex tasks such as image classification and segmentation. The medical industry often lacks high-quality, balanced datasets, which can be a challenge for deep learning algorithms that need sufficiently large amounts of data to train and increase their performance. This is especially important in the context of kidney issues such as for stones, cysts and tumors. We used deep learning models for this study to classify or detect several types of kidney diseases. We use different classification models, such as VGG-19, (CNNs) Convolutional Neural Networks, ResNet-101, VGG-16, ResNet-50, and DenseNet-169, which can be enhanced through techniques such as classification, segmentation, and transfer learning. These algorithms can help improve model accuracy by allowing them to learn from multiple datasets. This technique has the potential to revolutionize the diagnosis and treatment of kidney problems as it enables more accurate and effective classification of CT-scan images. This may ultimately lead to better patient outcomes and improved overall health outcomes.
Predicting environment effects on breast cancer by implementing machine learning
Sep 25, 2023



Abstract:The biggest Breast cancer is increasingly a major factor in female fatalities, overtaking heart disease. While genetic factors are important in the growth of breast cancer, new research indicates that environmental factors also play a substantial role in its occurrence and progression. The literature on the various environmental factors that may affect breast cancer risk, incidence, and outcomes is thoroughly reviewed in this study report. The study starts by looking at how lifestyle decisions, such as eating habits, exercise routines, and alcohol consumption, may affect hormonal imbalances and inflammation, two important factors driving the development of breast cancer. Additionally, it explores the part played by environmental contaminants such pesticides, endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs), and industrial emissions, all of which have been linked to a higher risk of developing breast cancer due to their interference with hormone signaling and DNA damage. Algorithms for machine learning are used to express predictions. Logistic Regression, Random Forest, KNN Algorithm, SVC and extra tree classifier. Metrics including the confusion matrix correlation coefficient, F1-score, Precision, Recall, and ROC curve were used to evaluate the models. The best accuracy among all the classifiers is Random Forest with 0.91% accuracy and ROC curve 0.901% of Logistic Regression. The accuracy of the multiple algorithms for machine learning utilized in this research was good, which is important and indicates that these techniques could serve as replacement forecasting techniques in breast cancer survival analysis, notably in the Asia region.
Urdu Poetry Generated by Using Deep Learning Techniques
Sep 25, 2023Abstract:This study provides Urdu poetry generated using different deep-learning techniques and algorithms. The data was collected through the Rekhta website, containing 1341 text files with several couplets. The data on poetry was not from any specific genre or poet. Instead, it was a collection of mixed Urdu poems and Ghazals. Different deep learning techniques, such as the model applied Long Short-term Memory Networks (LSTM) and Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU), have been used. Natural Language Processing (NLP) may be used in machine learning to understand, analyze, and generate a language humans may use and understand. Much work has been done on generating poetry for different languages using different techniques. The collection and use of data were also different for different researchers. The primary purpose of this project is to provide a model that generates Urdu poems by using data completely, not by sampling data. Also, this may generate poems in pure Urdu, not Roman Urdu, as in the base paper. The results have shown good accuracy in the poems generated by the model.
A Federated learning model for Electric Energy management using Blockchain Technology
Jul 18, 2023Abstract:Energy shortfall and electricity load shedding are the main problems for developing countries. The main causes are lack of management in the energy sector and the use of non-renewable energy sources. The improved energy management and use of renewable sources can be significant to resolve energy crisis. It is necessary to increase the use of renewable energy sources (RESs) to meet the increasing energy demand due to high prices of fossil-fuel based energy. Federated learning (FL) is the most emerging technique in the field of artificial intelligence. Federated learning helps to generate global model at server side by ensemble locally trained models at remote edges sites while preserving data privacy. The global model used to predict energy demand to satisfy the needs of consumers. In this article, we have proposed Blockchain based safe distributed ledger technology for transaction of data between prosumer and consumer to ensure their transparency, traceability and security. Furthermore, we have also proposed a Federated learning model to forecast the energy requirements of consumer and prosumer. Moreover, Blockchain has been used to store excess energy data from prosumer for better management of energy between prosumer and grid. Lastly, the experiment results revealed that renewable energy sources have produced better and comparable results to other non-renewable energy resources.
Web of Things and Trends in Agriculture: A Systematic Literature Review
Jun 15, 2023Abstract:In the past few years, the Web of Things (WOT) became a beneficial game-changing technology within the Agriculture domain as it introduces innovative and promising solutions to the Internet of Things (IoT) agricultural applications problems by providing its services. WOT provides the support for integration, interoperability for heterogeneous devices, infrastructures, platforms, and the emergence of various other technologies. The main aim of this study is about understanding and providing a growing and existing research content, issues, and directions for the future regarding WOT-based agriculture. Therefore, a systematic literature review (SLR) of research articles is presented by categorizing the selected studies published between 2010 and 2020 into the following categories: research type, approaches, and their application domains. Apart from reviewing the state-of-the-art articles on WOT solutions for the agriculture field, a taxonomy of WOT-base agriculture application domains has also been presented in this study. A model has also presented to show the picture of WOT based Smart Agriculture. Lastly, the findings of this SLR and the research gaps in terms of open issues have been presented to provide suggestions on possible future directions for the researchers for future research.
Prediction of Citrus Diseases Using Machine Learning And Deep Learning: Classifier, Models SLR
Jun 02, 2023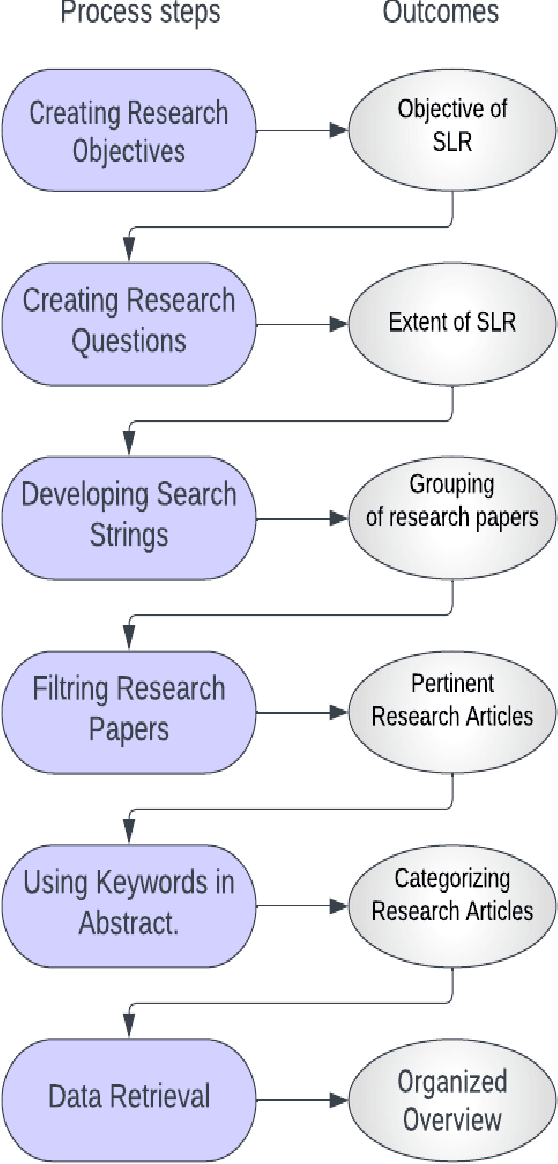
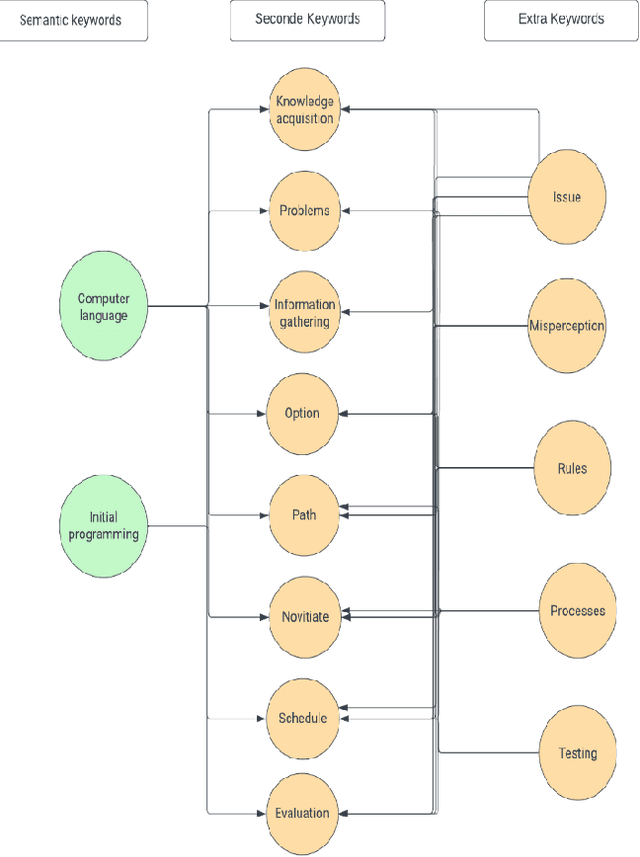
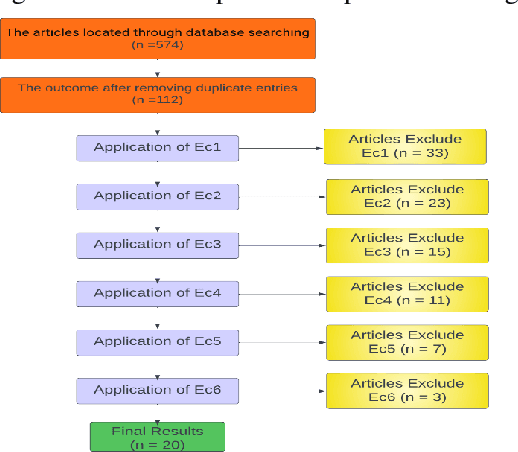
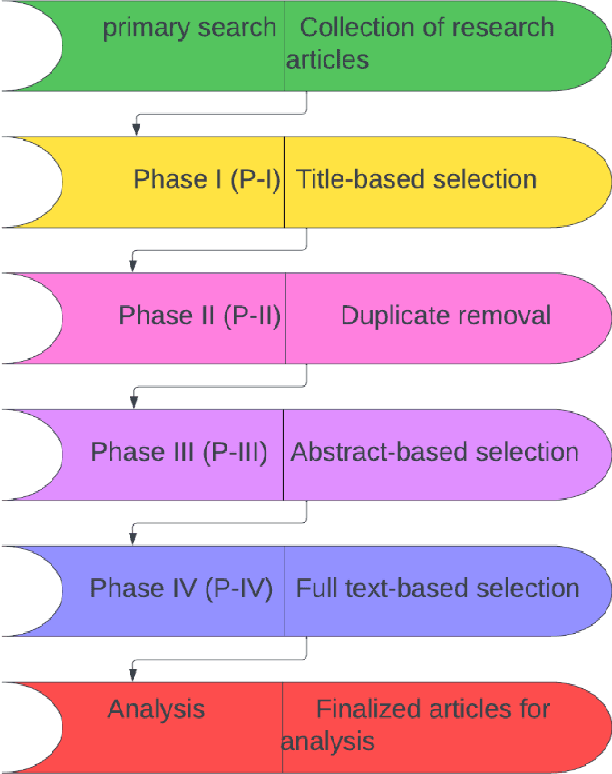
Abstract:Citrus diseases have been major issues for citrus growing worldwide for many years they can lead significantly reduce fruit quality. the most harmful citrus diseases are citrus canker, citrus greening, citrus black spot, citrus leaf miner which can have significant economic losses of citrus industry in worldwide prevention and management strategies like chemical treatments. Citrus diseases existing in all over the world where citrus is growing its effects the citrus tree root, citrus tree leaf, citrus tree orange etc. Existing of citrus diseases is highly impact on economic factor that can also produce low quality fruits and increased the rate for diseases management. Sanitation and routine monitoring can be effective in managing certain citrus diseases, but others may require more intensive treatments like chemical or biological control methods.
Comparative Analysis of Widely use Object-Oriented Languages
Jun 02, 2023



Abstract:Programming is an integral part of computer science discipline. Every day the programming environment is not only rapidly growing but also changing and languages are constantly evolving. Learning of object-oriented paradigm is compulsory in every computer science major so the choice of language to teach object-oriented principles is very important. Due to large pool of object-oriented languages, it is difficult to choose which should be the first programming language in order to teach object-oriented principles. Many studies shown which should be the first language to tech object-oriented concepts but there is no method to compare and evaluate these languages. In this article we proposed a comprehensive framework to evaluate the widely used object-oriented languages. The languages are evaluated basis of their technical and environmental features.
Beta Thalassemia Carriers detection empowered federated Learning
Jun 02, 2023Abstract:Thalassemia is a group of inherited blood disorders that happen when hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen, is not made enough. It is found all over the body and is needed for survival. If both parents have thalassemia, a child's chance of getting it increases. Genetic counselling and early diagnosis are essential for treating thalassemia and stopping it from being passed on to future generations. It may be hard for healthcare professionals to differentiate between people with thalassemia carriers and those without. The current blood tests for beta thalassemia carriers are too expensive, take too long, and require too much screening equipment. The World Health Organization says there is a high death rate for people with thalassemia. Therefore, it is essential to find thalassemia carriers to act quickly. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), the standard test method, has problems such as cost, time, and equipment needs. So, there must be a quick and cheap way to find people carrying the thalassemia gene. Using federated learning (FL) techniques, this study shows a new way to find people with the beta-thalassemia gene. FL allows data to be collected and processed on-site while following privacy rules, making it an excellent choice for sensitive health data. Researchers used FL to train a model for beta-thalassemia carriers by looking at the complete blood count results and red blood cell indices. The model was 92.38 % accurate at telling the difference between beta-thalassemia carriers and people who did not have the disease. The proposed FL model is better than other published methods in terms of how well it works, how reliable it is, and how private it is. This research shows a promising, quick, accurate, and low-cost way to find thalassemia carriers and opens the door for screening them on a large scale.
Heart Diseases Prediction Using Block-chain and Machine Learning
Jun 02, 2023Abstract:Most people around the globe are dying due to heart disease. The main reason behind the rapid increase in the death rate due to heart disease is that there is no infrastructure developed for the healthcare department that can provide a secure way of data storage and transmission. Due to redundancy in the patient data, it is difficult for cardiac Professionals to predict the disease early on. This rapid increase in the death rate due to heart disease can be controlled by monitoring and eliminating some of the key attributes in the early stages such as blood pressure, cholesterol level, body weight, and addiction to smoking. Patient data can be monitored by cardiac Professionals (Cp) by using the advanced framework in the healthcare departments. Blockchain is the world's most reliable provider. The use of advanced systems in the healthcare departments providing new ways of dealing with diseases has been developed as well. In this article Machine Learning (ML) algorithm known as a sine-cosine weighted k-nearest neighbor (SCA-WKNN) is used for predicting the Hearth disease with the maximum accuracy among the existing approaches. Blockchain technology has been used in the research to secure the data throughout the session and can give more accurate results using this technology. The performance of the system can be improved by using this algorithm and the dataset proposed has been improved by using different resources as well.
Developing and Building Ontologies in Cyber Security
Jun 01, 2023Abstract:Cyber Security is one of the most arising disciplines in our modern society. We work on Cybersecurity domain and in this the topic we chose is Cyber Security Ontologies. In this we gather all latest and previous ontologies and compare them on the basis of different analyzing factors to get best of them. Reason to select this topic is to assemble different ontologies from different era of time. Because, researches that included in this SLR is mostly studied single ontology. If any researcher wants to study ontologies, he has to study every single ontology and select which one is best for his research. So, we assemble different types of ontology and compare them against each other to get best of them. A total 24 papers between years 2010-2020 are carefully selected through systematic process and classified accordingly. Lastly, this SLR have been presented to provide the researchers promising future directions in the domain of cybersecurity ontologies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge