Muhammad Hamza
Computer Science and Technology, University of Science and Technology of China
Feature Attention Network (FA-Net): A Deep-Learning Based Approach for Underwater Single Image Enhancement
Aug 30, 2023Abstract:Underwater image processing and analysis have been a hotspot of study in recent years, as more emphasis has been focused to underwater monitoring and usage of marine resources. Compared with the open environment, underwater image encountered with more complicated conditions such as light abortion, scattering, turbulence, nonuniform illumination and color diffusion. Although considerable advances and enhancement techniques achieved in resolving these issues, they treat low-frequency information equally across the entire channel, which results in limiting the network's representativeness. We propose a deep learning and feature-attention-based end-to-end network (FA-Net) to solve this problem. In particular, we propose a Residual Feature Attention Block (RFAB), containing the channel attention, pixel attention, and residual learning mechanism with long and short skip connections. RFAB allows the network to focus on learning high-frequency information while skipping low-frequency information on multi-hop connections. The channel and pixel attention mechanism considers each channel's different features and the uneven distribution of haze over different pixels in the image. The experimental results shows that the FA-Net propose by us provides higher accuracy, quantitatively and qualitatively and superiority to previous state-of-the-art methods.
* Fourteenth International Conference on Digital Image Processing (ICDIP 2022), 2022, Wuhan, China, May 20-23, 2022.8 pages.5 Figures.doi: 10.1117/12.2644516
Forecasting sales with Bayesian networks: a case study of a supermarket product in the presence of promotions
Dec 16, 2021
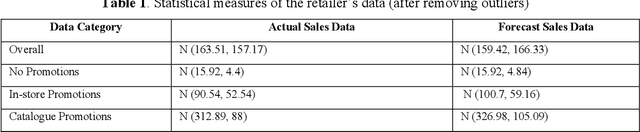
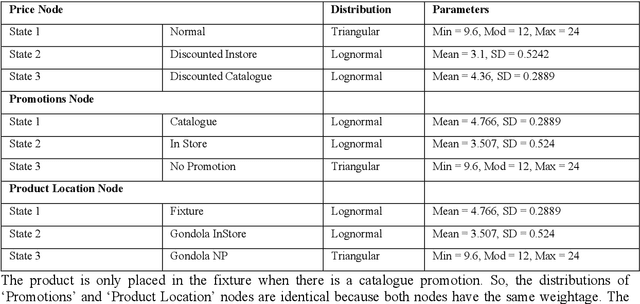
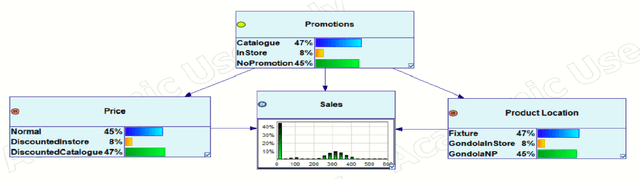
Abstract:Sales forecasting is the prerequisite for a lot of managerial decisions such as production planning, material resource planning and budgeting in the supply chain. Promotions are one of the most important business strategies that are often used to boost sales. While promotions are attractive for generating demand, it is often difficult to forecast demand in their presence. In the past few decades, several quantitative models have been developed to forecast sales including statistical and machine learning models. However, these methods may not be adequate to account for all the internal and external factors that may impact sales. As a result, qualitative models have been adopted along with quantitative methods as consulting experts has been proven to improve forecast accuracy by providing contextual information. Such models are being used extensively to account for factors that can lead to a rapid change in sales, such as during promotions. In this paper, we aim to use Bayesian Networks to forecast promotional sales where a combination of factors such as price, type of promotions, and product location impacts sales. We choose to develop a BN model because BN models essentially have the capability to combine various qualitative and quantitative factors with causal forms, making it an attractive tool for sales forecasting during promotions. This can be used to adjust a company's promotional strategy in the context of this case study. We gather sales data for a particular product from a retailer that sells products in Australia. We develop a Bayesian Network for this product and validate our results by empirical analysis. This paper confirms that BNs can be effectively used to forecast sales, especially during promotions. In the end, we provide some research avenues for using BNs in forecasting sales.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge