Mozhgan Navardi
MedMambaLite: Hardware-Aware Mamba for Medical Image Classification
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:AI-powered medical devices have driven the need for real-time, on-device inference such as biomedical image classification. Deployment of deep learning models at the edge is now used for applications such as anomaly detection and classification in medical images. However, achieving this level of performance on edge devices remains challenging due to limitations in model size and computational capacity. To address this, we present MedMambaLite, a hardware-aware Mamba-based model optimized through knowledge distillation for medical image classification. We start with a powerful MedMamba model, integrating a Mamba structure for efficient feature extraction in medical imaging. We make the model lighter and faster in training and inference by modifying and reducing the redundancies in the architecture. We then distill its knowledge into a smaller student model by reducing the embedding dimensions. The optimized model achieves 94.5% overall accuracy on 10 MedMNIST datasets. It also reduces parameters 22.8x compared to MedMamba. Deployment on an NVIDIA Jetson Orin Nano achieves 35.6 GOPS/J energy per inference. This outperforms MedMamba by 63% improvement in energy per inference.
MambaLiteSR: Image Super-Resolution with Low-Rank Mamba using Knowledge Distillation
Feb 19, 2025



Abstract:Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) has gained significant attention in recent years, revolutionizing various applications across industries. Among these, advanced vision models for image super-resolution are in high demand, particularly for deployment on edge devices where real-time processing is crucial. However, deploying such models on edge devices is challenging due to limited computing power and memory. In this paper, we present MambaLiteSR, a novel lightweight image Super-Resolution (SR) model that utilizes the architecture of Vision Mamba. It integrates State Space Blocks and a reconstruction module for efficient feature extraction. To optimize efficiency without affecting performance, MambaLiteSR employs knowledge distillation to transfer key insights from a larger Mamba-based teacher model to a smaller student model via hyperparameter tuning. Through mathematical analysis of model parameters and their impact on PSNR, we identify key factors and adjust them accordingly. Our comprehensive evaluation shows that MambaLiteSR outperforms state-of-the-art edge SR methods by reducing power consumption while maintaining competitive PSNR and SSIM scores across benchmark datasets. It also reduces power usage during training via low-rank approximation. Moreover, MambaLiteSR reduces parameters with minimal performance loss, enabling efficient deployment of generative AI models on resource-constrained devices. Deployment on the embedded NVIDIA Jetson Orin Nano confirms the superior balance of MambaLiteSR size, latency, and efficiency. Experiments show that MambaLiteSR achieves performance comparable to both the baseline and other edge models while using 15% fewer parameters. It also improves power consumption by up to 58% compared to state-of-the-art SR edge models, all while maintaining low energy use during training.
Energy-Aware FPGA Implementation of Spiking Neural Network with LIF Neurons
Nov 03, 2024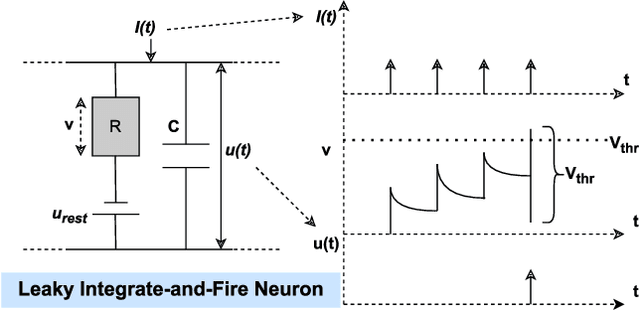
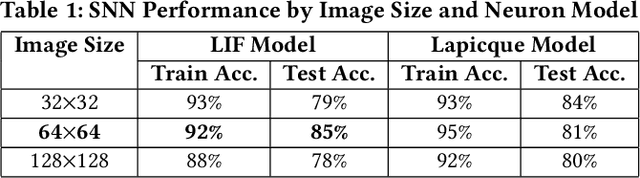
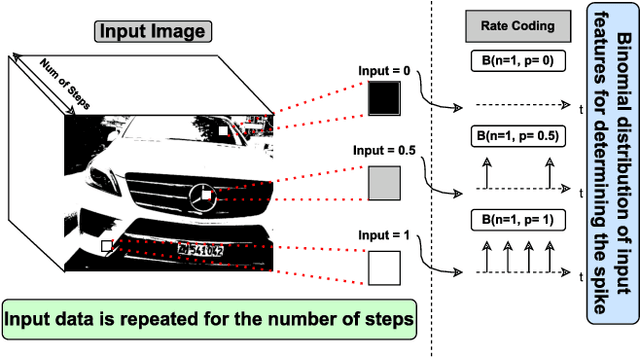
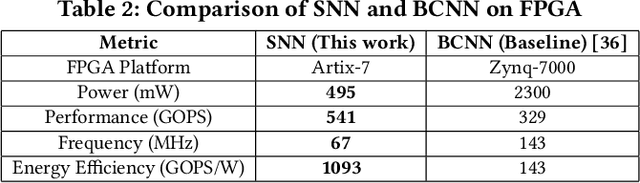
Abstract:Tiny Machine Learning (TinyML) has become a growing field in on-device processing for Internet of Things (IoT) applications, capitalizing on AI algorithms that are optimized for their low complexity and energy efficiency. These algorithms are designed to minimize power and memory footprints, making them ideal for the constraints of IoT devices. Within this domain, Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) stand out as a cutting-edge solution for TinyML, owning to their event-driven processing paradigm which offers an efficient method of handling dataflow. This paper presents a novel SNN architecture based on the 1st Order Leaky Integrate-and-Fire (LIF) neuron model to efficiently deploy vision-based ML algorithms on TinyML systems. A hardware-friendly LIF design is also proposed, and implemented on a Xilinx Artix-7 FPGA. To evaluate the proposed model, a collision avoidance dataset is considered as a case study. The proposed SNN model is compared to the state-of-the-art works and Binarized Convolutional Neural Network (BCNN) as a baseline. The results show the proposed approach is 86% more energy efficient than the baseline.
Squeezed Edge YOLO: Onboard Object Detection on Edge Devices
Dec 18, 2023



Abstract:Demand for efficient onboard object detection is increasing due to its key role in autonomous navigation. However, deploying object detection models such as YOLO on resource constrained edge devices is challenging due to the high computational requirements of such models. In this paper, an compressed object detection model named Squeezed Edge YOLO is examined. This model is compressed and optimized to kilobytes of parameters in order to fit onboard such edge devices. To evaluate Squeezed Edge YOLO, two use cases - human and shape detection - are used to show the model accuracy and performance. Moreover, the model is deployed onboard a GAP8 processor with 8 RISC-V cores and an NVIDIA Jetson Nano with 4GB of memory. Experimental results show Squeezed Edge YOLO model size is optimized by a factor of 8x which leads to 76% improvements in energy efficiency and 3.3x faster throughout.
ReProHRL: Towards Multi-Goal Navigation in the Real World using Hierarchical Agents
Aug 17, 2023Abstract:Robots have been successfully used to perform tasks with high precision. In real-world environments with sparse rewards and multiple goals, learning is still a major challenge and Reinforcement Learning (RL) algorithms fail to learn good policies. Training in simulation environments and then fine-tuning in the real world is a common approach. However, adapting to the real-world setting is a challenge. In this paper, we present a method named Ready for Production Hierarchical RL (ReProHRL) that divides tasks with hierarchical multi-goal navigation guided by reinforcement learning. We also use object detectors as a pre-processing step to learn multi-goal navigation and transfer it to the real world. Empirical results show that the proposed ReProHRL method outperforms the state-of-the-art baseline in simulation and real-world environments in terms of both training time and performance. Although both methods achieve a 100% success rate in a simple environment for single goal-based navigation, in a more complex environment and multi-goal setting, the proposed method outperforms the baseline by 18% and 5%, respectively. For the real-world implementation and proof of concept demonstration, we deploy the proposed method on a nano-drone named Crazyflie with a front camera to perform multi-goal navigation experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge