Moitrayee Chatterjee
Fast Fourier Transformation for Optimizing Convolutional Neural Networks in Object Recognition
Oct 08, 2020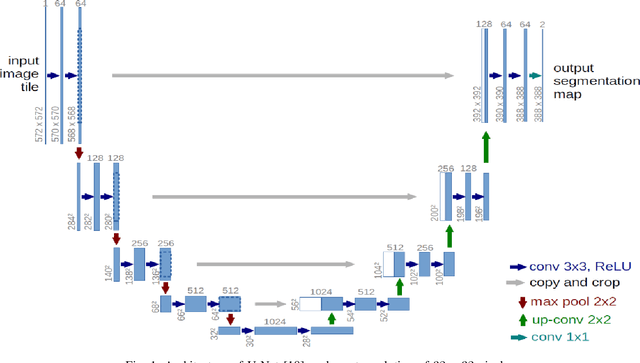
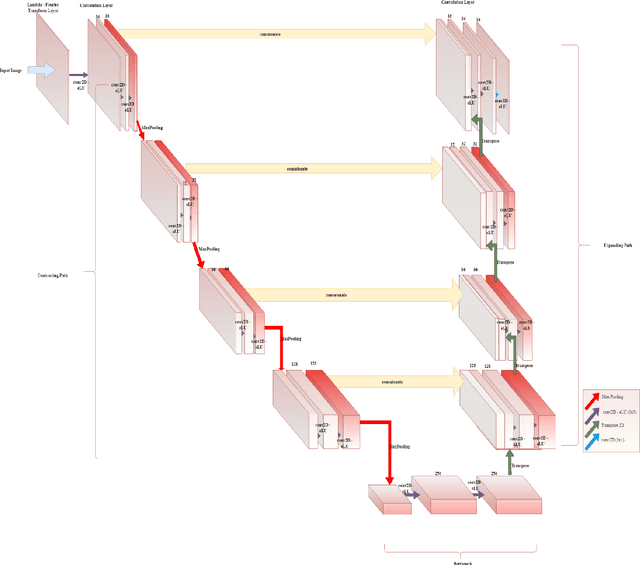
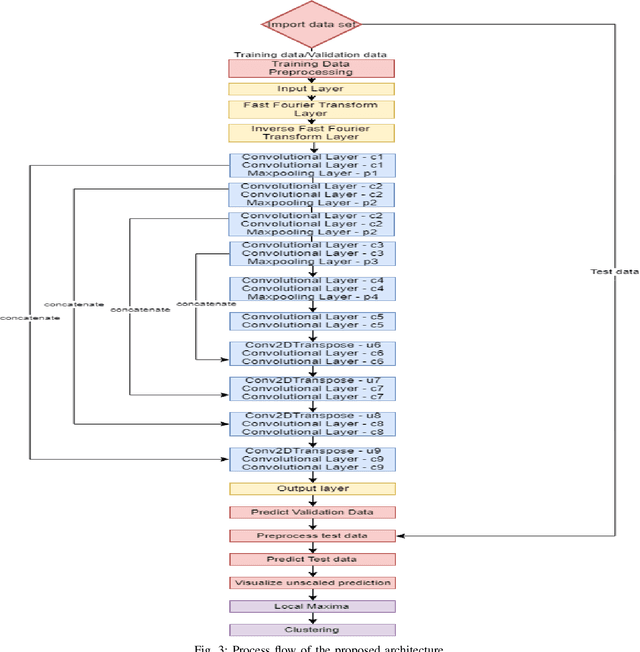
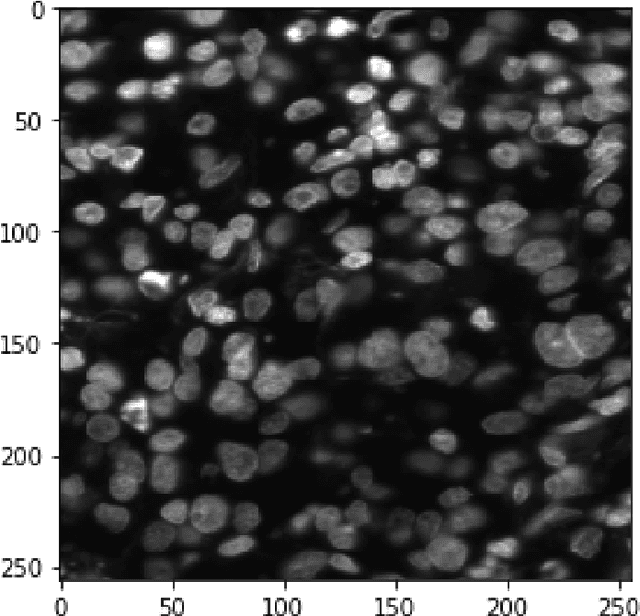
Abstract:This paper proposes to use Fast Fourier Transformation-based U-Net (a refined fully convolutional networks) and perform image convolution in neural networks. Leveraging the Fast Fourier Transformation, it reduces the image convolution costs involved in the Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and thus reduces the overall computational costs. The proposed model identifies the object information from the images. We apply the Fast Fourier transform algorithm on an image data set to obtain more accessible information about the image data, before segmenting them through the U-Net architecture. More specifically, we implement the FFT-based convolutional neural network to improve the training time of the network. The proposed approach was applied to publicly available Broad Bioimage Benchmark Collection (BBBC) dataset. Our model demonstrated improvement in training time during convolution from $600-700$ ms/step to $400-500$ ms/step. We evaluated the accuracy of our model using Intersection over Union (IoU) metric showing significant improvements.
Deep Reinforcement Learning for Detecting Malicious Websites
May 22, 2019
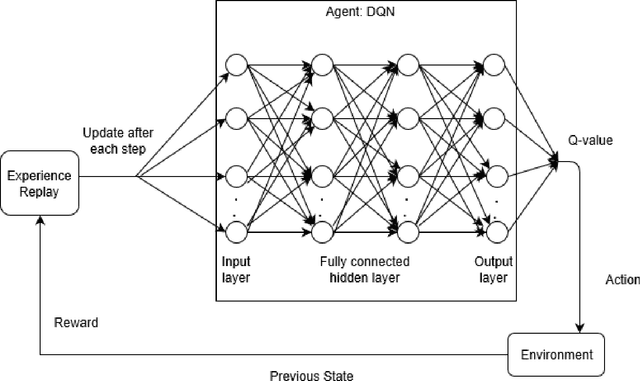
Abstract:Phishing is the simplest form of cybercrime with the objective of baiting people into giving away delicate information such as individually recognizable data, banking and credit card details, or even credentials and passwords. This type of simple yet most effective cyber-attack is usually launched through emails, phone calls, or instant messages. The credential or private data stolen are then used to get access to critical records of the victims and can result in extensive fraud and monetary loss. Hence, sending malicious messages to victims is a stepping stone of the phishing procedure. A \textit{phisher} usually setups a deceptive website, where the victims are conned into entering credentials and sensitive information. It is therefore important to detect these types of malicious websites before causing any harmful damages to victims. Inspired by the evolving nature of the phishing websites, this paper introduces a novel approach based on deep reinforcement learning to model and detect malicious URLs. The proposed model is capable of adapting to the dynamic behavior of the phishing websites and thus learn the features associated with phishing website detection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge