Mohit Prashant
Improving Reinforcement Learning Sample-Efficiency using Local Approximation
Jul 16, 2025Abstract:In this study, we derive Probably Approximately Correct (PAC) bounds on the asymptotic sample-complexity for RL within the infinite-horizon Markov Decision Process (MDP) setting that are sharper than those in existing literature. The premise of our study is twofold: firstly, the further two states are from each other, transition-wise, the less relevant the value of the first state is when learning the $\epsilon$-optimal value of the second; secondly, the amount of 'effort', sample-complexity-wise, expended in learning the $\epsilon$-optimal value of a state is independent of the number of samples required to learn the $\epsilon$-optimal value of a second state that is a sufficient number of transitions away from the first. Inversely, states within each other's vicinity have values that are dependent on each other and will require a similar number of samples to learn. By approximating the original MDP using smaller MDPs constructed using subsets of the original's state-space, we are able to reduce the sample-complexity by a logarithmic factor to $O(SA \log A)$ timesteps, where $S$ and $A$ are the state and action space sizes. We are able to extend these results to an infinite-horizon, model-free setting by constructing a PAC-MDP algorithm with the aforementioned sample-complexity. We conclude with showing how significant the improvement is by comparing our algorithm against prior work in an experimental setting.
Guaranteeing Out-Of-Distribution Detection in Deep RL via Transition Estimation
Mar 07, 2025Abstract:An issue concerning the use of deep reinforcement learning (RL) agents is whether they can be trusted to perform reliably when deployed, as training environments may not reflect real-life environments. Anticipating instances outside their training scope, learning-enabled systems are often equipped with out-of-distribution (OOD) detectors that alert when a trained system encounters a state it does not recognize or in which it exhibits uncertainty. There exists limited work conducted on the problem of OOD detection within RL, with prior studies being unable to achieve a consensus on the definition of OOD execution within the context of RL. By framing our problem using a Markov Decision Process, we assume there is a transition distribution mapping each state-action pair to another state with some probability. Based on this, we consider the following definition of OOD execution within RL: A transition is OOD if its probability during real-life deployment differs from the transition distribution encountered during training. As such, we utilize conditional variational autoencoders (CVAE) to approximate the transition dynamics of the training environment and implement a conformity-based detector using reconstruction loss that is able to guarantee OOD detection with a pre-determined confidence level. We evaluate our detector by adapting existing benchmarks and compare it with existing OOD detection models for RL.
PAC-Based Formal Verification for Out-of-Distribution Data Detection
Apr 04, 2023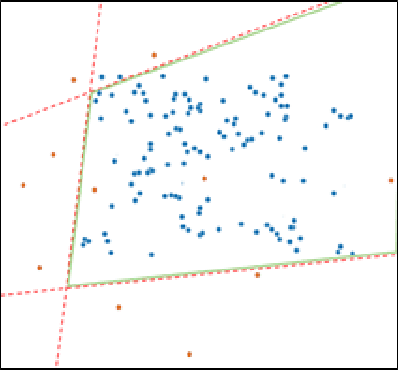
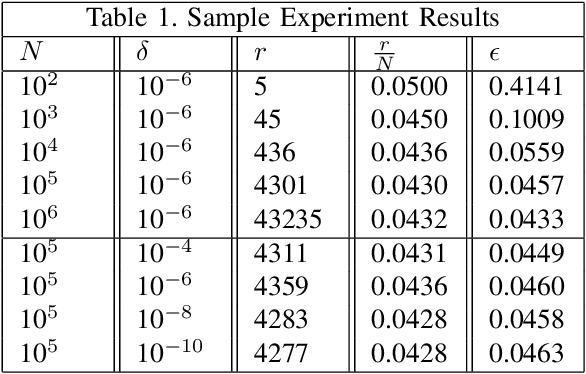
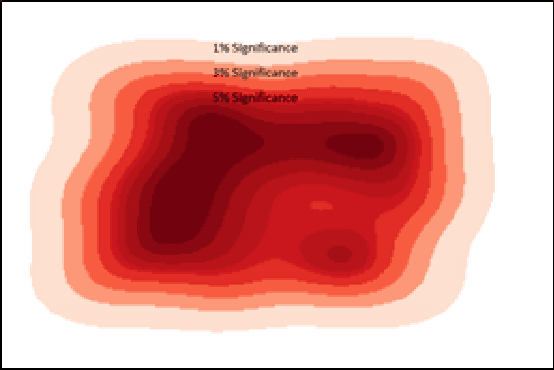
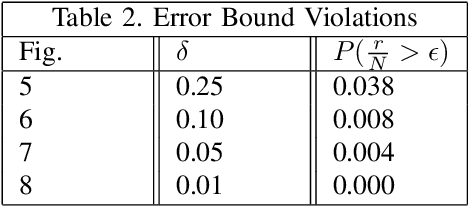
Abstract:Cyber-physical systems (CPS) like autonomous vehicles, that utilize learning components, are often sensitive to noise and out-of-distribution (OOD) instances encountered during runtime. As such, safety critical tasks depend upon OOD detection subsystems in order to restore the CPS to a known state or interrupt execution to prevent safety from being compromised. However, it is difficult to guarantee the performance of OOD detectors as it is difficult to characterize the OOD aspect of an instance, especially in high-dimensional unstructured data. To distinguish between OOD data and data known to the learning component through the training process, an emerging technique is to incorporate variational autoencoders (VAE) within systems and apply classification or anomaly detection techniques on their latent spaces. The rationale for doing so is the reduction of the data domain size through the encoding process, which benefits real-time systems through decreased processing requirements, facilitates feature analysis for unstructured data and allows more explainable techniques to be implemented. This study places probably approximately correct (PAC) based guarantees on OOD detection using the encoding process within VAEs to quantify image features and apply conformal constraints over them. This is used to bound the detection error on unfamiliar instances with user-defined confidence. The approach used in this study is to empirically establish these bounds by sampling the latent probability distribution and evaluating the error with respect to the constraint violations that are encountered. The guarantee is then verified using data generated from CARLA, an open-source driving simulator.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge