Mohand Said Allili
Texture image retrieval using a classification and contourlet-based features
Mar 10, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a new framework for improving Content Based Image Retrieval (CBIR) for texture images. This is achieved by using a new image representation based on the RCT-Plus transform which is a novel variant of the Redundant Contourlet transform that extracts a richer directional information in the image. Moreover, the process of image search is improved through a learning-based approach where the images of the database are classified using an adapted similarity metric to the statistical modeling of the RCT-Plus transform. A query is then first classified to select the best texture class after which the retained class images are ranked to select top ones. By this, we have achieved significant improvements in the retrieval rates compared to previous CBIR schemes.
Efficient embedding network for 3D brain tumor segmentation
Nov 22, 2020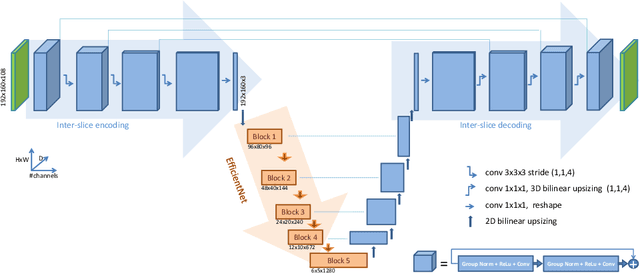
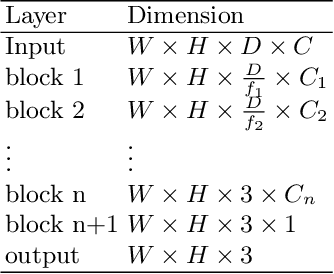
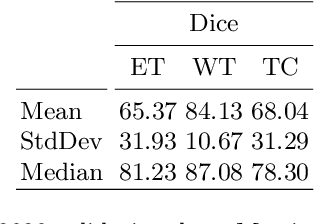
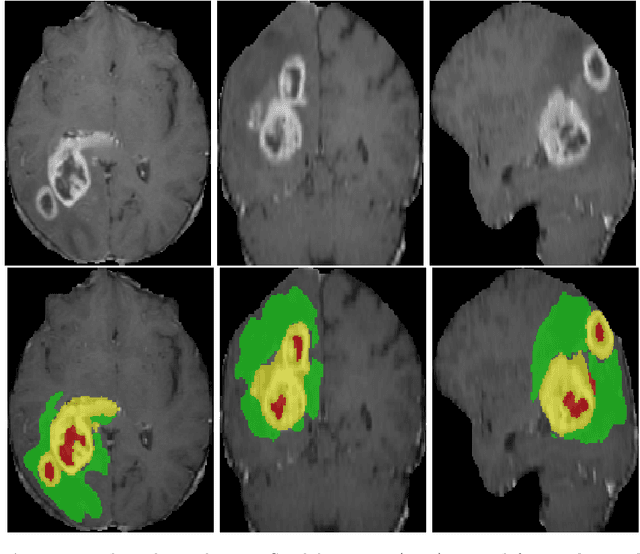
Abstract:3D medical image processing with deep learning greatly suffers from a lack of data. Thus, studies carried out in this field are limited compared to works related to 2D natural image analysis, where very large datasets exist. As a result, powerful and efficient 2D convolutional neural networks have been developed and trained. In this paper, we investigate a way to transfer the performance of a two-dimensional classiffication network for the purpose of three-dimensional semantic segmentation of brain tumors. We propose an asymmetric U-Net network by incorporating the EfficientNet model as part of the encoding branch. As the input data is in 3D, the first layers of the encoder are devoted to the reduction of the third dimension in order to fit the input of the EfficientNet network. Experimental results on validation and test data from the BraTS 2020 challenge demonstrate that the proposed method achieve promising performance.
* Multimodal Brain Tumor Segmentation Challenge 2020
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge