Mohammed Sowket Ali
Multi-class heart disease Detection, Classification, and Prediction using Machine Learning Models
Dec 06, 2024



Abstract:Heart disease is a leading cause of premature death worldwide, particularly among middle-aged and older adults, with men experiencing a higher prevalence. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), non-communicable diseases, including heart disease, account for 25\% (17.9 million) of global deaths, with over 43,204 annual fatalities in Bangladesh. However, the development of heart disease detection (HDD) systems tailored to the Bangladeshi population remains underexplored due to the lack of benchmark datasets and reliance on manual or limited-data approaches. This study addresses these challenges by introducing new, ethically sourced HDD dataset, BIG-Dataset and CD dataset which incorporates comprehensive data on symptoms, examination techniques, and risk factors. Using advanced machine learning techniques, including Logistic Regression and Random Forest, we achieved a remarkable testing accuracy of up to 96.6\% with Random Forest. The proposed AI-driven system integrates these models and datasets to provide real-time, accurate diagnostics and personalized healthcare recommendations. By leveraging structured datasets and state-of-the-art machine learning algorithms, this research offers an innovative solution for scalable and effective heart disease detection, with the potential to reduce mortality rates and improve clinical outcomes.
BAUST Lipi: A BdSL Dataset with Deep Learning Based Bangla Sign Language Recognition
Aug 20, 2024
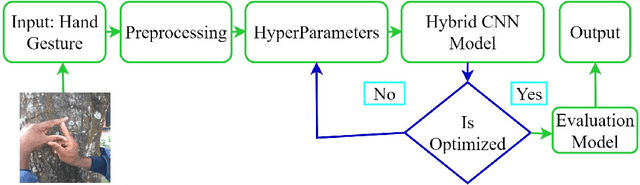

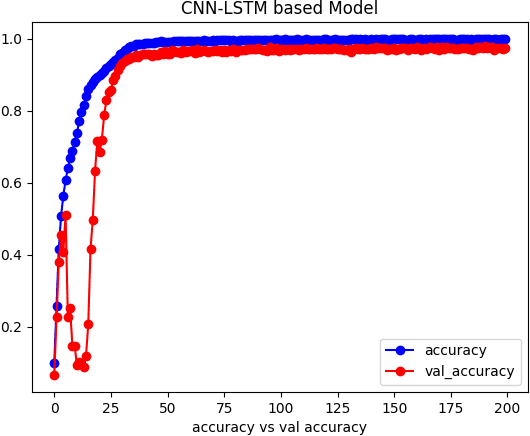
Abstract:People commonly communicate in English, Arabic, and Bengali spoken languages through various mediums. However, deaf and hard-of-hearing individuals primarily use body language and sign language to express their needs and achieve independence. Sign language research is burgeoning to enhance communication with the deaf community. While many researchers have made strides in recognizing sign languages such as French, British, Arabic, Turkish, and American, there has been limited research on Bangla sign language (BdSL) with less-than-satisfactory results. One significant barrier has been the lack of a comprehensive Bangla sign language dataset. In our work, we introduced a new BdSL dataset comprising alphabets totaling 18,000 images, with each image being 224x224 pixels in size. Our dataset encompasses 36 Bengali symbols, of which 30 are consonants and the remaining six are vowels. Despite our dataset contribution, many existing systems continue to grapple with achieving high-performance accuracy for BdSL. To address this, we devised a hybrid Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) model, integrating multiple convolutional layers, activation functions, dropout techniques, and LSTM layers. Upon evaluating our hybrid-CNN model with the newly created BdSL dataset, we achieved an accuracy rate of 97.92\%. We are confident that both our BdSL dataset and hybrid CNN model will be recognized as significant milestones in BdSL research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge