Mohammad Shamim Ahsan
Uncovering and Understanding FPR Manipulation Attack in Industrial IoT Networks
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:In the network security domain, due to practical issues -- including imbalanced data and heterogeneous legitimate network traffic -- adversarial attacks in machine learning-based NIDSs have been viewed as attack packets misclassified as benign. Due to this prevailing belief, the possibility of (maliciously) perturbed benign packets being misclassified as attack has been largely ignored. In this paper, we demonstrate that this is not only theoretically possible, but also a particular threat to NIDS. In particular, we uncover a practical cyberattack, FPR manipulation attack (FPA), especially targeting industrial IoT networks, where domain-specific knowledge of the widely used MQTT protocol is exploited and a systematic simple packet-level perturbation is performed to alter the labels of benign traffic samples without employing traditional gradient-based or non-gradient-based methods. The experimental evaluations demonstrate that this novel attack results in a success rate of 80.19% to 100%. In addition, while estimating impacts in the Security Operations Center, we observe that even a small fraction of false positive alerts, irrespective of different budget constraints and alert traffic intensities, can increase the delay of genuine alerts investigations up to 2 hr in a single day under normal operating conditions. Furthermore, a series of relevant statistical and XAI analyses is conducted to understand the key factors behind this remarkable success. Finally, we explore the effectiveness of the FPA packets to enhance models' robustness through adversarial training and investigate the changes in decision boundaries accordingly.
A Census-Based Genetic Algorithm for Target Set Selection Problem in Social Networks
Oct 02, 2024
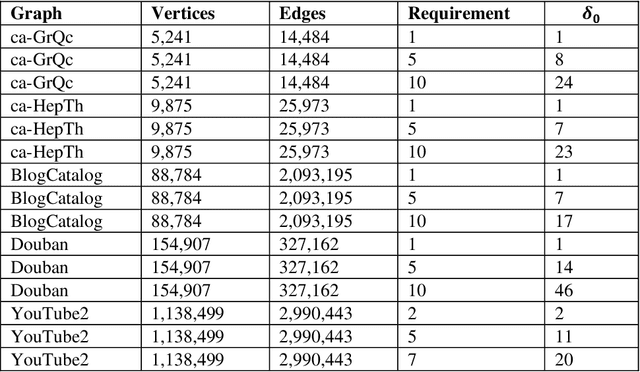
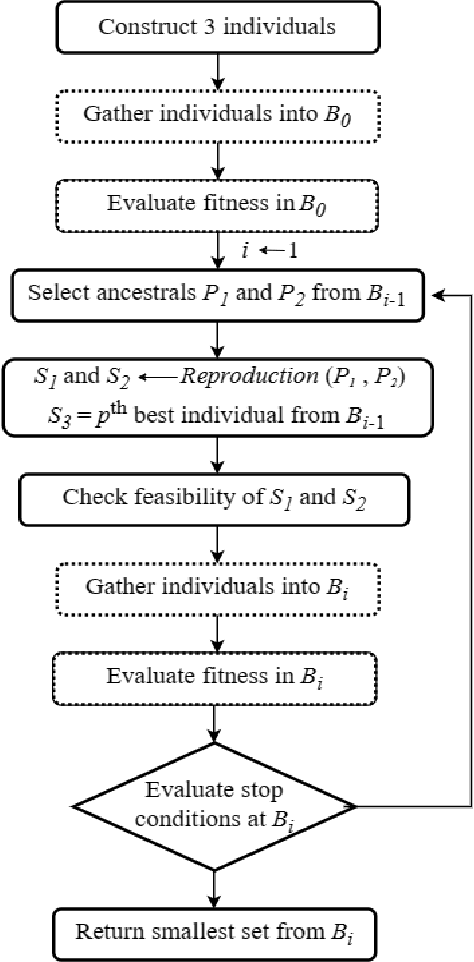
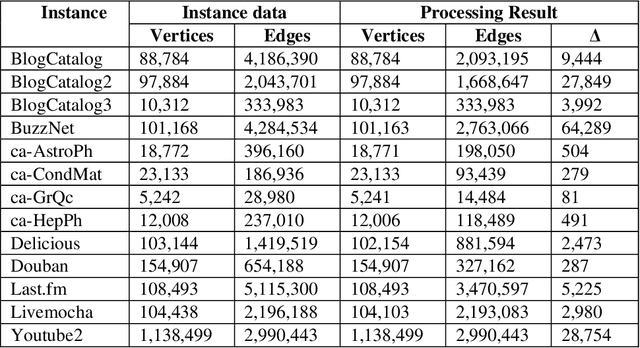
Abstract:This paper considers the Target Set Selection (TSS) Problem in social networks, a fundamental problem in viral marketing. In the TSS problem, a graph and a threshold value for each vertex of the graph are given. We need to find a minimum size vertex subset to "activate" such that all graph vertices are activated at the end of the propagation process. Specifically, we propose a novel approach called "a census-based genetic algorithm" for the TSS problem. In our algorithm, we use the idea of a census to gather and store information about each individual in a population and collect census data from the individuals constructed during the algorithm's execution so that we can achieve greater diversity and avoid premature convergence at locally optimal solutions. We use two distinct census information: (a) for each individual, the algorithm stores how many times it has been identified during the execution (b) for each network node, the algorithm counts how many times it has been included in a solution. The proposed algorithm can also self-adjust by using a parameter specifying the aggressiveness employed in each reproduction method. Additionally, the algorithm is designed to run in a parallelized environment to minimize the computational cost and check each individual's feasibility. Moreover, our algorithm finds the optimal solution in all cases while experimenting on random graphs. Furthermore, we execute the proposed algorithm on 14 large graphs of real-life social network instances from the literature, improving around 9.57 solution size (on average) and 134 vertices (in total) compared to the best solutions obtained in previous studies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge