Mohammad Mehedy Masud
Contrastive Self-Supervised Learning Based Approach for Patient Similarity: A Case Study on Atrial Fibrillation Detection from PPG Signal
Jul 22, 2023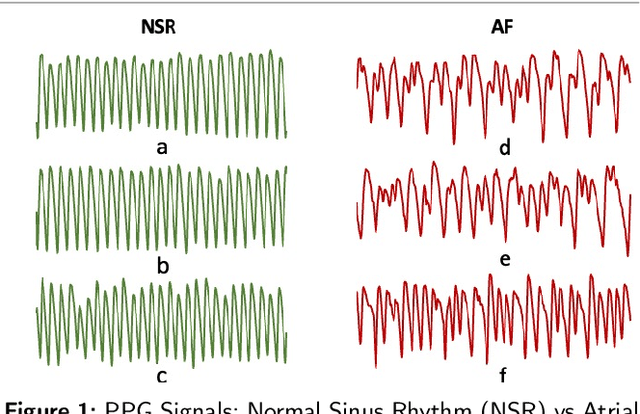
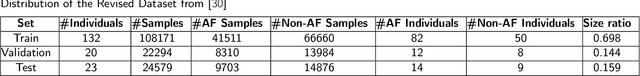
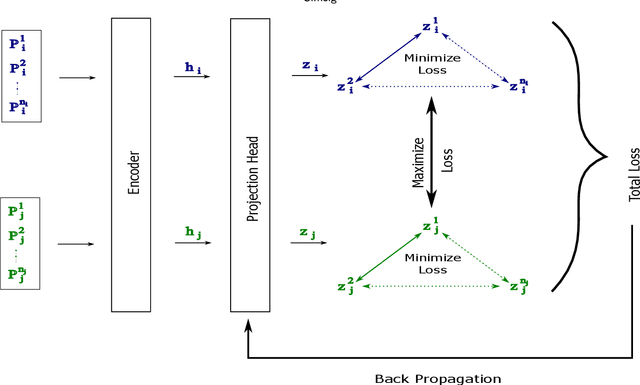
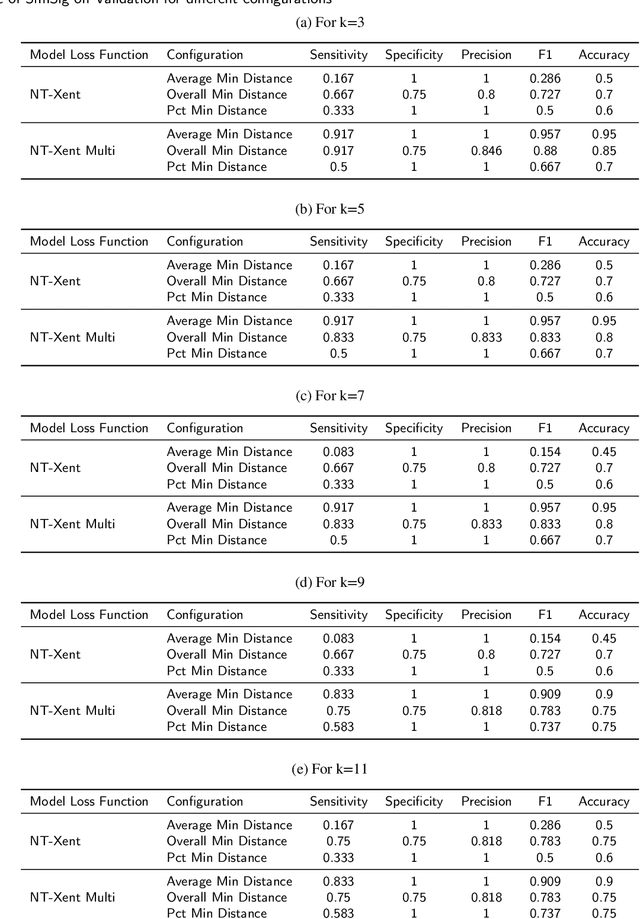
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel contrastive learning based deep learning framework for patient similarity search using physiological signals. We use a contrastive learning based approach to learn similar embeddings of patients with similar physiological signal data. We also introduce a number of neighbor selection algorithms to determine the patients with the highest similarity on the generated embeddings. To validate the effectiveness of our framework for measuring patient similarity, we select the detection of Atrial Fibrillation (AF) through photoplethysmography (PPG) signals obtained from smartwatch devices as our case study. We present extensive experimentation of our framework on a dataset of over 170 individuals and compare the performance of our framework with other baseline methods on this dataset.
BayesBeat: A Bayesian Deep Learning Approach for Atrial Fibrillation Detection from Noisy Photoplethysmography Data
Nov 02, 2020



Abstract:The increasing popularity of smartwatches as affordable and longitudinal monitoring devices enables us to capture photoplethysmography (PPG) sensor data for detecting Atrial Fibrillation (AF) in real-time. A significant challenge in AF detection from PPG signals comes from the inherent noise in the smartwatch PPG signals. In this paper, we propose a novel deep learning based approach, BayesBeat that leverages the power of Bayesian deep learning to accurately infer AF risks from noisy PPG signals, and at the same time provide the uncertainty estimate of the prediction. Bayesbeat is efficient, robust, flexible, and highly scalable which makes it particularly suitable for deployment in commercially available wearable devices. Extensive experiments on a recently published large dataset reveal that our proposed method BayesBeat substantially outperforms the existing state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge