Mohammad Hadi Goldani
An Ensemble Machine Learning Approach for Screening Covid-19 based on Urine Parameters
Nov 03, 2023
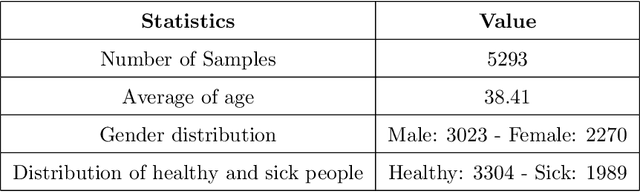
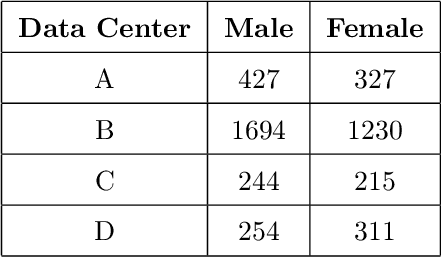
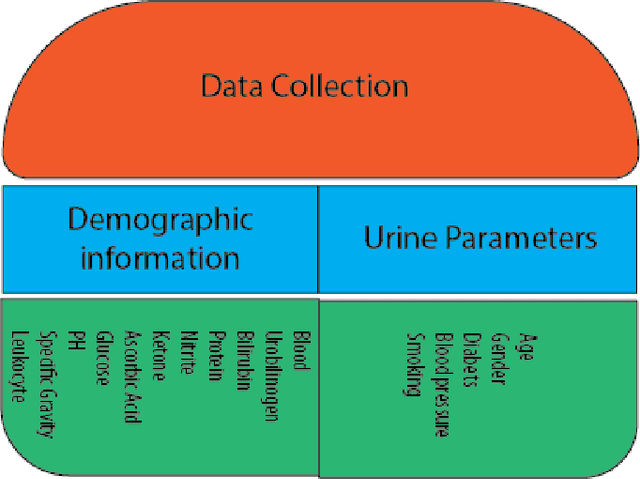
Abstract:The rapid spread of COVID-19 and the emergence of new variants underscore the importance of effective screening measures. Rapid diagnosis and subsequent quarantine of infected individuals can prevent further spread of the virus in society. While PCR tests are the gold standard for COVID-19 diagnosis, they are costly and time-consuming. In contrast, urine test strips are an inexpensive, non-invasive, and rapidly obtainable screening method that can provide important information about a patient's health status. In this study, we collected a new dataset and used the RGB (Red Green Blue) color space of urine test strips parameters to detect the health status of individuals. To improve the accuracy of our model, we converted the RGB space to 10 additional color spaces. After evaluating four different machine learning models, we proposed a new ensemble model based on a multi-layer perceptron neural network. Although the initial results were not strong, we were able to improve the model's screening performance for COVID-19 by removing uncertain regions of the model space. Ultimately, our model achieved a screening accuracy of 80% based on urine parameters. Our results suggest that urine test strips can be a useful tool for COVID-19 screening, particularly in resource-constrained settings where PCR testing may not be feasible. Further research is needed to validate our findings and explore the potential role of urine test strips in COVID-19 diagnosis and management.
X-CapsNet For Fake News Detection
Jul 23, 2023



Abstract:News consumption has significantly increased with the growing popularity and use of web-based forums and social media. This sets the stage for misinforming and confusing people. To help reduce the impact of misinformation on users' potential health-related decisions and other intents, it is desired to have machine learning models to detect and combat fake news automatically. This paper proposes a novel transformer-based model using Capsule neural Networks(CapsNet) called X-CapsNet. This model includes a CapsNet with dynamic routing algorithm paralyzed with a size-based classifier for detecting short and long fake news statements. We use two size-based classifiers, a Deep Convolutional Neural Network (DCNN) for detecting long fake news statements and a Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) for detecting short news statements. To resolve the problem of representing short news statements, we use indirect features of news created by concatenating the vector of news speaker profiles and a vector of polarity, sentiment, and counting words of news statements. For evaluating the proposed architecture, we use the Covid-19 and the Liar datasets. The results in terms of the F1-score for the Covid-19 dataset and accuracy for the Liar dataset show that models perform better than the state-of-the-art baselines.
Detecting Fake News with Capsule Neural Networks
Feb 03, 2020



Abstract:Fake news is dramatically increased in social media in recent years. This has prompted the need for effective fake news detection algorithms. Capsule neural networks have been successful in computer vision and are receiving attention for use in Natural Language Processing (NLP). This paper aims to use capsule neural networks in the fake news detection task. We use different embedding models for news items of different lengths. Static word embedding is used for short news items, whereas non-static word embeddings that allow incremental up-training and updating in the training phase are used for medium length or large news statements. Moreover, we apply different levels of n-grams for feature extraction. Our proposed architectures are evaluated on two recent well-known datasets in the field, namely ISOT and LIAR. The results show encouraging performance, outperforming the state-of-the-art methods by 7.8% on ISOT and 3.1% on the validation set, and 1% on the test set of the LIAR dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge