Mohammad Firouz
An Adaptive Simulated Annealing-Based Machine Learning Approach for Developing an E-Triage Tool for Hospital Emergency Operations
Dec 22, 2022Abstract:Patient triage at emergency departments (EDs) is necessary to prioritize care for patients with critical and time-sensitive conditions. Different tools are used for patient triage and one of the most common ones is the emergency severity index (ESI), which has a scale of five levels, where level 1 is the most urgent and level 5 is the least urgent. This paper proposes a framework for utilizing machine learning to develop an e-triage tool that can be used at EDs. A large retrospective dataset of ED patient visits is obtained from the electronic health record of a healthcare provider in the Midwest of the US for three years. However, the main challenge of using machine learning algorithms is that most of them have many parameters and without optimizing these parameters, developing a high-performance model is not possible. This paper proposes an approach to optimize the hyperparameters of machine learning. The metaheuristic optimization algorithms simulated annealing (SA) and adaptive simulated annealing (ASA) are proposed to optimize the parameters of extreme gradient boosting (XGB) and categorical boosting (CaB). The newly proposed algorithms are SA-XGB, ASA-XGB, SA-CaB, ASA-CaB. Grid search (GS), which is a traditional approach used for machine learning fine-tunning is also used to fine-tune the parameters of XGB and CaB, which are named GS-XGB and GS-CaB. The six algorithms are trained and tested using eight data groups obtained from the feature selection phase. The results show ASA-CaB outperformed all the proposed algorithms with accuracy, precision, recall, and f1 of 83.3%, 83.2%, 83.3%, 83.2%, respectively.
An Integrated Optimization and Machine Learning Models to Predict the Admission Status of Emergency Patients
Feb 18, 2022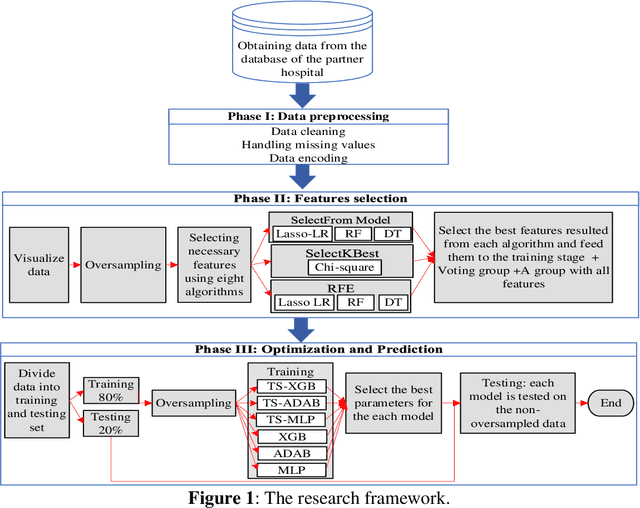
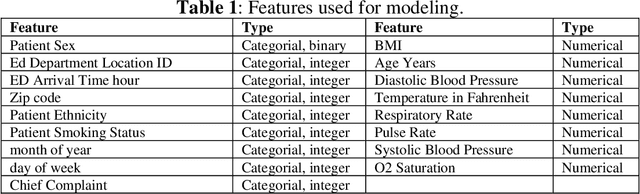

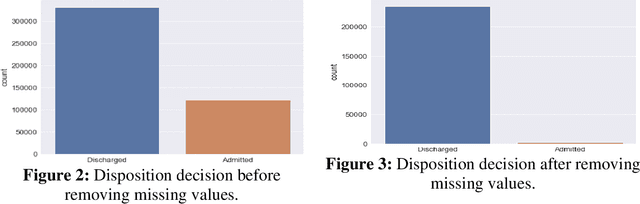
Abstract:This work proposes a framework for optimizing machine learning algorithms. The practicality of the framework is illustrated using an important case study from the healthcare domain, which is predicting the admission status of emergency department (ED) patients (e.g., admitted vs. discharged) using patient data at the time of triage. The proposed framework can mitigate the crowding problem by proactively planning the patient boarding process. A large retrospective dataset of patient records is obtained from the electronic health record database of all ED visits over three years from three major locations of a healthcare provider in the Midwest of the US. Three machine learning algorithms are proposed: T-XGB, T-ADAB, and T-MLP. T-XGB integrates extreme gradient boosting (XGB) and Tabu Search (TS), T-ADAB integrates Adaboost and TS, and T-MLP integrates multi-layer perceptron (MLP) and TS. The proposed algorithms are compared with the traditional algorithms: XGB, ADAB, and MLP, in which their parameters are tunned using grid search. The three proposed algorithms and the original ones are trained and tested using nine data groups that are obtained from different feature selection methods. In other words, 54 models are developed. Performance was evaluated using five measures: Area under the curve (AUC), sensitivity, specificity, F1, and accuracy. The results show that the newly proposed algorithms resulted in high AUC and outperformed the traditional algorithms. The T-ADAB performs the best among the newly developed algorithms. The AUC, sensitivity, specificity, F1, and accuracy of the best model are 95.4%, 99.3%, 91.4%, 95.2%, 97.2%, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge