Mohammad Baradaran
Future Video Prediction from a Single Frame for Video Anomaly Detection
Aug 15, 2023


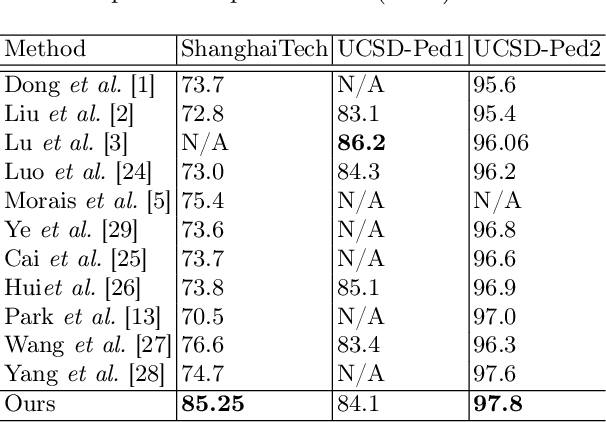
Abstract:Video anomaly detection (VAD) is an important but challenging task in computer vision. The main challenge rises due to the rarity of training samples to model all anomaly cases. Hence, semi-supervised anomaly detection methods have gotten more attention, since they focus on modeling normals and they detect anomalies by measuring the deviations from normal patterns. Despite impressive advances of these methods in modeling normal motion and appearance, long-term motion modeling has not been effectively explored so far. Inspired by the abilities of the future frame prediction proxy-task, we introduce the task of future video prediction from a single frame, as a novel proxy-task for video anomaly detection. This proxy-task alleviates the challenges of previous methods in learning longer motion patterns. Moreover, we replace the initial and future raw frames with their corresponding semantic segmentation map, which not only makes the method aware of object class but also makes the prediction task less complex for the model. Extensive experiments on the benchmark datasets (ShanghaiTech, UCSD-Ped1, and UCSD-Ped2) show the effectiveness of the method and the superiority of its performance compared to SOTA prediction-based VAD methods.
Multi-Task Learning based Video Anomaly Detection with Attention
Oct 14, 2022



Abstract:Multi-task learning based video anomaly detection methods combine multiple proxy tasks in different branches to detect video anomalies in different situations. Most existing methods either do not combine complementary tasks to effectively cover all motion patterns, or the class of the objects is not explicitly considered. To address the aforementioned shortcomings, we propose a novel multi-task learning based method that combines complementary proxy tasks to better consider the motion and appearance features. We combine the semantic segmentation and future frame prediction tasks in a single branch to learn the object class and consistent motion patterns, and to detect respective anomalies simultaneously. In the second branch, we added several attention mechanisms to detect motion anomalies with attention to object parts, the direction of motion, and the distance of the objects from the camera. Our qualitative results show that the proposed method considers the object class effectively and learns motion with attention to the aforementioned important factors which results in a precise motion modeling and a better motion anomaly detection. Additionally, quantitative results show the superiority of our method compared with state-of-the-art methods.
Object Class Aware Video Anomaly Detection through Image Translation
May 03, 2022



Abstract:Semi-supervised video anomaly detection (VAD) methods formulate the task of anomaly detection as detection of deviations from the learned normal patterns. Previous works in the field (reconstruction or prediction-based methods) suffer from two drawbacks: 1) They focus on low-level features, and they (especially holistic approaches) do not effectively consider the object classes. 2) Object-centric approaches neglect some of the context information (such as location). To tackle these challenges, this paper proposes a novel two-stream object-aware VAD method that learns the normal appearance and motion patterns through image translation tasks. The appearance branch translates the input image to the target semantic segmentation map produced by Mask-RCNN, and the motion branch associates each frame with its expected optical flow magnitude. Any deviation from the expected appearance or motion in the inference stage shows the degree of potential abnormality. We evaluated our proposed method on the ShanghaiTech, UCSD-Ped1, and UCSD-Ped2 datasets and the results show competitive performance compared with state-of-the-art works. Most importantly, the results show that, as significant improvements to previous methods, detections by our method are completely explainable and anomalies are localized accurately in the frames.
A Critical Study on the Recent Deep Learning Based Semi-Supervised Video Anomaly Detection Methods
Nov 02, 2021



Abstract:Video anomaly detection is one of the hot research topics in computer vision nowadays, as abnormal events contain a high amount of information. Anomalies are one of the main detection targets in surveillance systems, usually needing real-time actions. Regarding the availability of labeled data for training (i.e., there is not enough labeled data for abnormalities), semi-supervised anomaly detection approaches have gained interest recently. This paper introduces the researchers of the field to a new perspective and reviews the recent deep-learning based semi-supervised video anomaly detection approaches, based on a common strategy they use for anomaly detection. Our goal is to help researchers develop more effective video anomaly detection methods. As the selection of a right Deep Neural Network plays an important role for several parts of this task, a quick comparative review on DNNs is prepared first. Unlike previous surveys, DNNs are reviewed from a spatiotemporal feature extraction viewpoint, customized for video anomaly detection. This part of the review can help researchers in this field select suitable networks for different parts of their methods. Moreover, some of the state-of-the-art anomaly detection methods, based on their detection strategy, are critically surveyed. The review provides a novel and deep look at existing methods and results in stating the shortcomings of these approaches, which can be a hint for future works.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge