Mitsuru Kusumoto
A Graph Theoretic Framework of Recomputation Algorithms for Memory-Efficient Backpropagation
May 28, 2019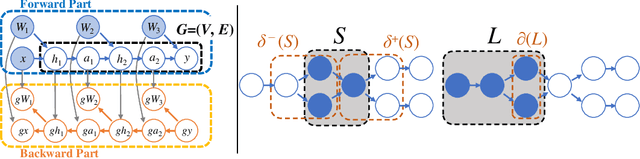
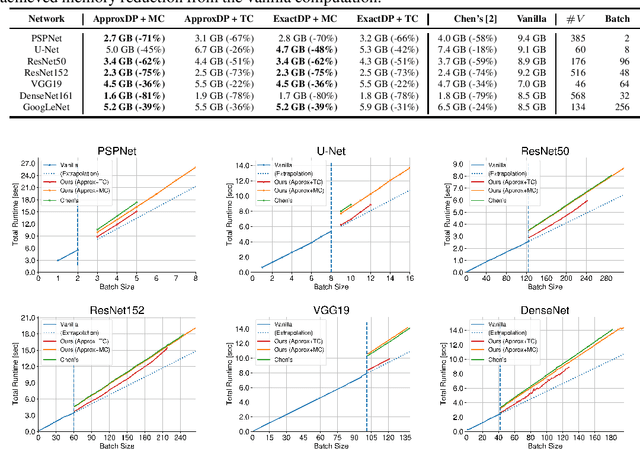
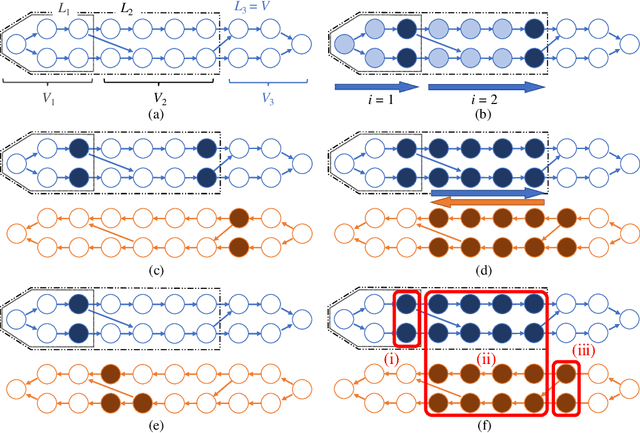
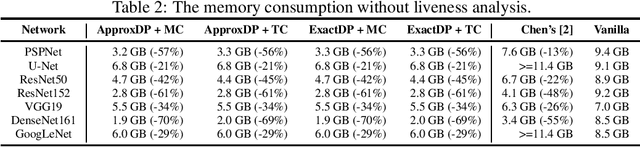
Abstract:Recomputation algorithms collectively refer to a family of methods that aims to reduce the memory consumption of the backpropagation by selectively discarding the intermediate results of the forward propagation and recomputing the discarded results as needed. In this paper, we will propose a novel and efficient recomputation method that can be applied to a wider range of neural nets than previous methods. We use the language of graph theory to formalize the general recomputation problem of minimizing the computational overhead under a fixed memory budget constraint, and provide a dynamic programming solution to the problem. Our method can reduce the peak memory consumption on various benchmark networks by 36%~81%, which outperforms the reduction achieved by other methods.
Automated Theorem Proving in Intuitionistic Propositional Logic by Deep Reinforcement Learning
Nov 02, 2018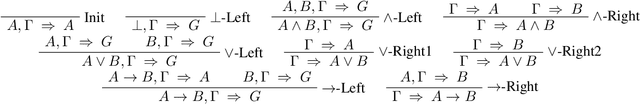
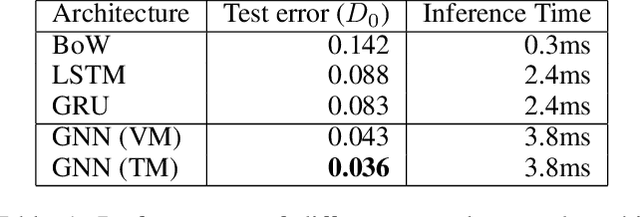
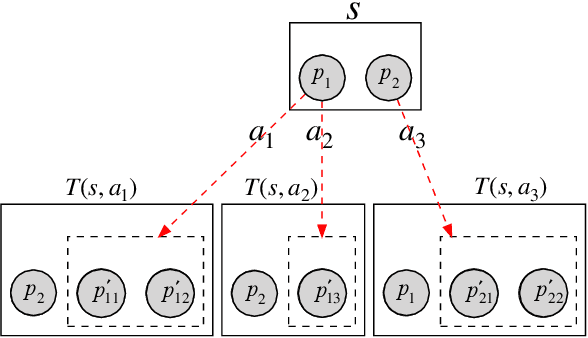
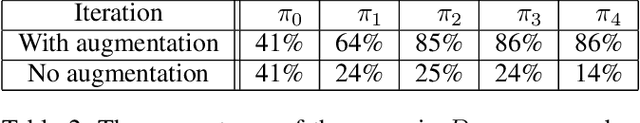
Abstract:The problem-solving in automated theorem proving (ATP) can be interpreted as a search problem where the prover constructs a proof tree step by step. In this paper, we propose a deep reinforcement learning algorithm for proof search in intuitionistic propositional logic. The most significant challenge in the application of deep learning to the ATP is the absence of large, public theorem database. We, however, overcame this issue by applying a novel data augmentation procedure at each iteration of the reinforcement learning. We also improve the efficiency of the algorithm by representing the syntactic structure of formulas by a novel compact graph representation. Using the large volume of augmented data, we train highly accurate graph neural networks that approximate the value function for the set of the syntactic structures of formulas. Our method is also cost-efficient in terms of computational time. We will show that our prover outperforms Coq's $\texttt{tauto}$ tactic, a prover based on human-engineered heuristics. Within the specified time limit, our prover solved 84% of the theorems in a benchmark library, while $\texttt{tauto}$ was able to solve only 52%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge