Minsung Yoon
Learning-based Adaptive Control of Quadruped Robots for Active Stabilization on Moving Platforms
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:A quadruped robot faces balancing challenges on a six-degrees-of-freedom moving platform, like subways, buses, airplanes, and yachts, due to independent platform motions and resultant diverse inertia forces on the robot. To alleviate these challenges, we present the Learning-based Active Stabilization on Moving Platforms (\textit{LAS-MP}), featuring a self-balancing policy and system state estimators. The policy adaptively adjusts the robot's posture in response to the platform's motion. The estimators infer robot and platform states based on proprioceptive sensor data. For a systematic training scheme across various platform motions, we introduce platform trajectory generation and scheduling methods. Our evaluation demonstrates superior balancing performance across multiple metrics compared to three baselines. Furthermore, we conduct a detailed analysis of the \textit{LAS-MP}, including ablation studies and evaluation of the estimators, to validate the effectiveness of each component.
Enhancing Navigation Efficiency of Quadruped Robots via Leveraging Personal Transportation Platforms
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Quadruped robots face limitations in long-range navigation efficiency due to their reliance on legs. To ameliorate the limitations, we introduce a Reinforcement Learning-based Active Transporter Riding method (\textit{RL-ATR}), inspired by humans' utilization of personal transporters, including Segways. The \textit{RL-ATR} features a transporter riding policy and two state estimators. The policy devises adequate maneuvering strategies according to transporter-specific control dynamics, while the estimators resolve sensor ambiguities in non-inertial frames by inferring unobservable robot and transporter states. Comprehensive evaluations in simulation validate proficient command tracking abilities across various transporter-robot models and reduced energy consumption compared to legged locomotion. Moreover, we conduct ablation studies to quantify individual component contributions within the \textit{RL-ATR}. This riding ability could broaden the locomotion modalities of quadruped robots, potentially expanding the operational range and efficiency.
Learning-based Initialization of Trajectory Optimization for Path-following Problems of Redundant Manipulators
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Trajectory optimization (TO) is an efficient tool to generate a redundant manipulator's joint trajectory following a 6-dimensional Cartesian path. The optimization performance largely depends on the quality of initial trajectories. However, the selection of a high-quality initial trajectory is non-trivial and requires a considerable time budget due to the extremely large space of the solution trajectories and the lack of prior knowledge about task constraints in configuration space. To alleviate the issue, we present a learning-based initial trajectory generation method that generates high-quality initial trajectories in a short time budget by adopting example-guided reinforcement learning. In addition, we suggest a null-space projected imitation reward to consider null-space constraints by efficiently learning kinematically feasible motion captured in expert demonstrations. Our statistical evaluation in simulation shows the improved optimality, efficiency, and applicability of TO when we plug in our method's output, compared with three other baselines. We also show the performance improvement and feasibility via real-world experiments with a seven-degree-of-freedom manipulator.
Uncertainty-Aware Non-Prehensile Manipulation with Mobile Manipulators under Object-Induced Occlusion
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Non-prehensile manipulation using onboard sensing presents a fundamental challenge: the manipulated object occludes the sensor's field of view, creating occluded regions that can lead to collisions. We propose CURA-PPO, a reinforcement learning framework that addresses this challenge by explicitly modeling uncertainty under partial observability. By predicting collision possibility as a distribution, we extract both risk and uncertainty to guide the robot's actions. The uncertainty term encourages active perception, enabling simultaneous manipulation and information gathering to resolve occlusions. When combined with confidence maps that capture observation reliability, our approach enables safe navigation despite severe sensor occlusion. Extensive experiments across varying object sizes and obstacle configurations demonstrate that CURA-PPO achieves up to 3X higher success rates than the baselines, with learned behaviors that handle occlusions. Our method provides a practical solution for autonomous manipulation in cluttered environments using only onboard sensing.
Efficient Navigation Among Movable Obstacles using a Mobile Manipulator via Hierarchical Policy Learning
Jun 18, 2025Abstract:We propose a hierarchical reinforcement learning (HRL) framework for efficient Navigation Among Movable Obstacles (NAMO) using a mobile manipulator. Our approach combines interaction-based obstacle property estimation with structured pushing strategies, facilitating the dynamic manipulation of unforeseen obstacles while adhering to a pre-planned global path. The high-level policy generates pushing commands that consider environmental constraints and path-tracking objectives, while the low-level policy precisely and stably executes these commands through coordinated whole-body movements. Comprehensive simulation-based experiments demonstrate improvements in performing NAMO tasks, including higher success rates, shortened traversed path length, and reduced goal-reaching times, compared to baselines. Additionally, ablation studies assess the efficacy of each component, while a qualitative analysis further validates the accuracy and reliability of the real-time obstacle property estimation.
Central Angle Optimization for 360-degree Holographic 3D Content
Nov 10, 2023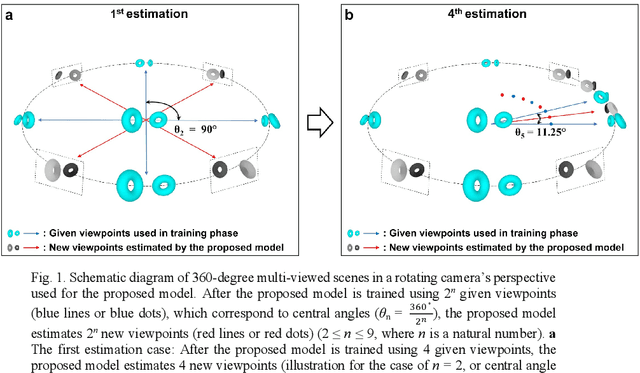
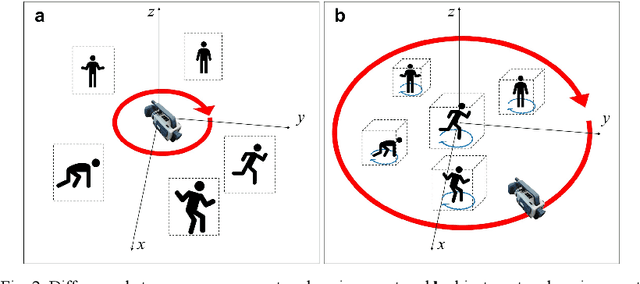
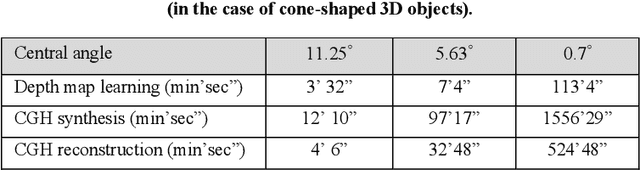
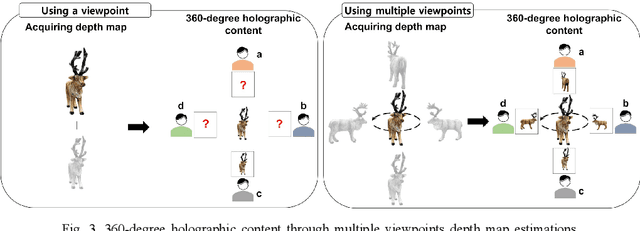
Abstract:In this study, we propose a method to find an optimal central angle in deep learning-based depth map estimation used to produce realistic holographic content. The acquisition of RGB-depth map images as detailed as possible must be performed to generate holograms of high quality, despite the high computational cost. Therefore, we introduce a novel pipeline designed to analyze various values of central angles between adjacent camera viewpoints equidistant from the origin of an object-centered environment. Then we propose the optimal central angle to generate high-quality holographic content. The proposed pipeline comprises key steps such as comparing estimated depth maps and comparing reconstructed CGHs (Computer-Generated Holograms) from RGB images and estimated depth maps. We experimentally demonstrate and discuss the relationship between the central angle and the quality of digital holographic content.
Genetic Algorithm for Constrained Molecular Inverse Design
Dec 23, 2021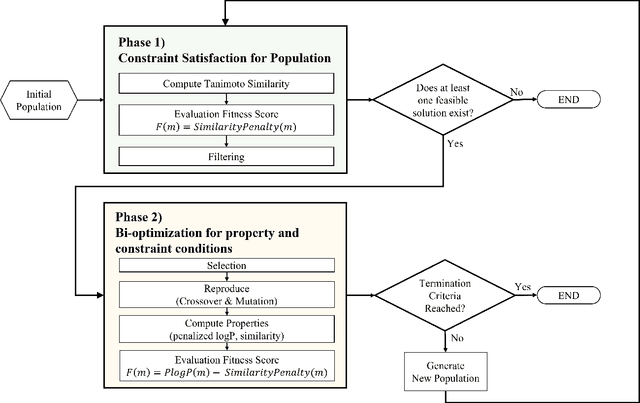
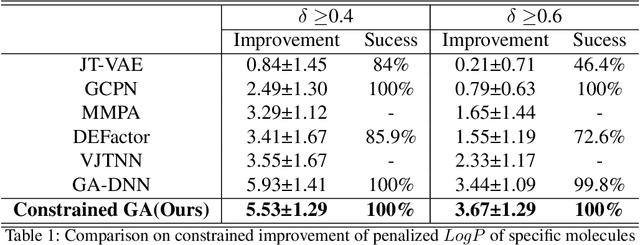
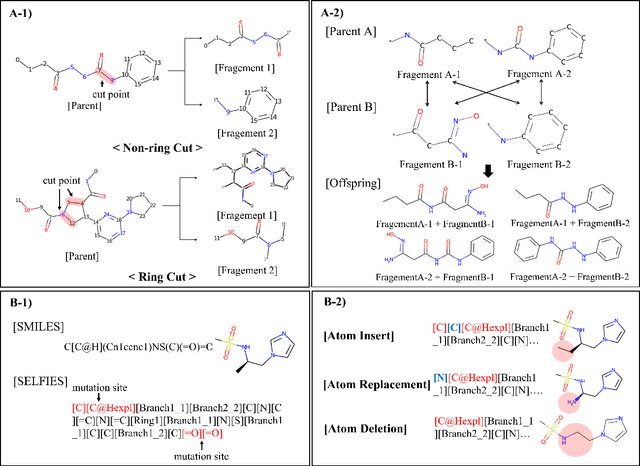
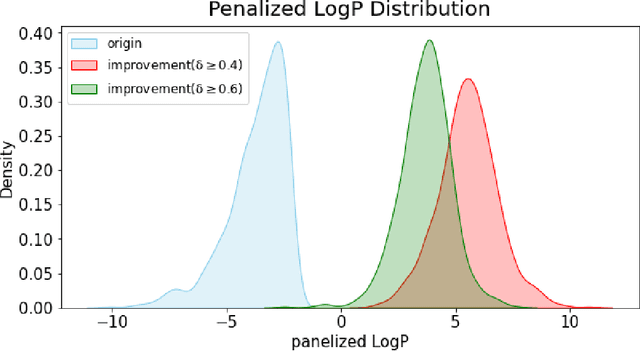
Abstract:A genetic algorithm is suitable for exploring large search spaces as it finds an approximate solution. Because of this advantage, genetic algorithm is effective in exploring vast and unknown space such as molecular search space. Though the algorithm is suitable for searching vast chemical space, it is difficult to optimize pharmacological properties while maintaining molecular substructure. To solve this issue, we introduce a genetic algorithm featuring a constrained molecular inverse design. The proposed algorithm successfully produces valid molecules for crossover and mutation. Furthermore, it optimizes specific properties while adhering to structural constraints using a two-phase optimization. Experiments prove that our algorithm effectively finds molecules that satisfy specific properties while maintaining structural constraints.
An Effective GCN-based Hierarchical Multi-label classification for Protein Function Prediction
Dec 06, 2021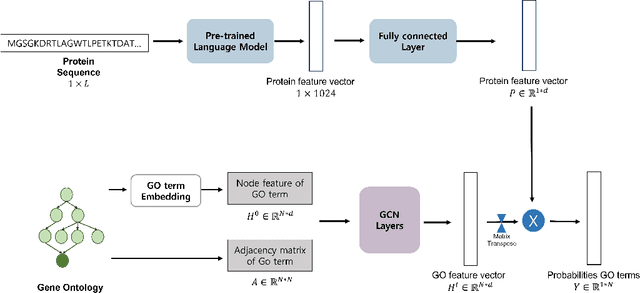
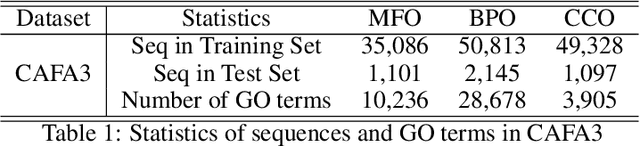
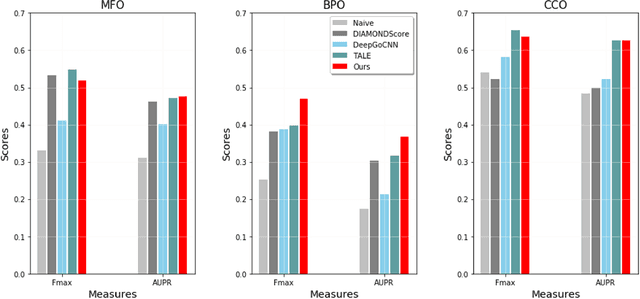
Abstract:We propose an effective method to improve Protein Function Prediction (PFP) utilizing hierarchical features of Gene Ontology (GO) terms. Our method consists of a language model for encoding the protein sequence and a Graph Convolutional Network (GCN) for representing GO terms. To reflect the hierarchical structure of GO to GCN, we employ node(GO term)-wise representations containing the whole hierarchical information. Our algorithm shows effectiveness in a large-scale graph by expanding the GO graph compared to previous models. Experimental results show that our method outperformed state-of-the-art PFP approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge