Minkyu Shin
Enhancing Human Persuasion With Large Language Models
Nov 28, 2023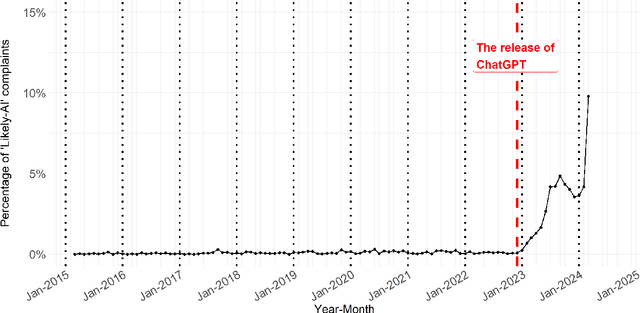
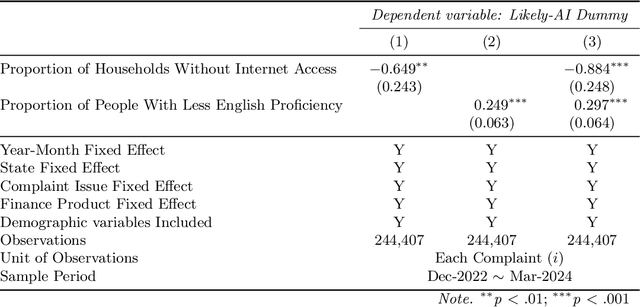
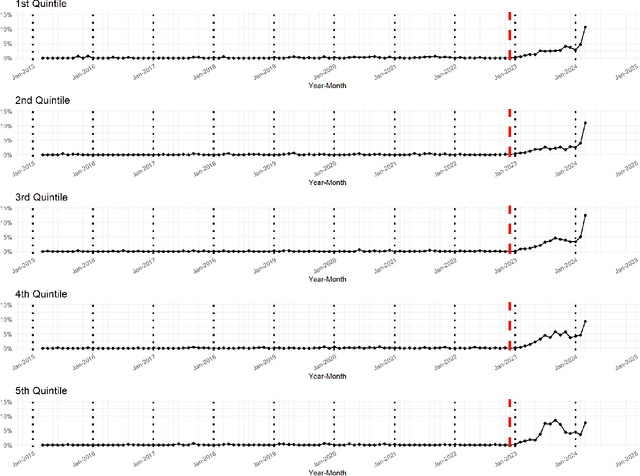
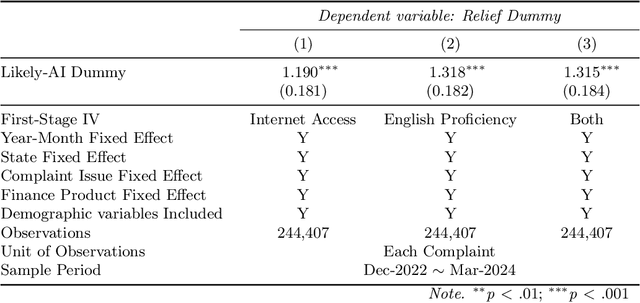
Abstract:Although large language models (LLMs) are reshaping various aspects of human life, our current understanding of their impacts remains somewhat constrained. Here we investigate the impact of LLMs on human communication, in the context of consumer complaints in the financial industry. Employing an AI detection tool on more than 780K complaints gathered by the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB), we find evidence of LLM usage in the writing of complaints - shortly after the release of ChatGPT. Our analyses reveal that LLM usage is positively correlated with the likelihood of obtaining desirable outcomes (i.e., offer of relief from financial firms) and suggest that this positive correlation may be partly due to the linguistic features improved by LLMs. We test this conjecture with a preregistered experiment, which reveals results consistent with those from observational studies: Consumer complaints written with ChatGPT for improved linguistic qualities were more likely to receive hypothetical relief offers than the original consumer complaints, demonstrating the LLM's ability to enhance message persuasiveness in human communication. Being some of the earliest empirical evidence on LLM usage for enhancing persuasion, our results highlight the transformative potential of LLMs in human communication.
Superhuman Artificial Intelligence Can Improve Human Decision Making by Increasing Novelty
Mar 13, 2023Abstract:How will superhuman artificial intelligence (AI) affect human decision making? And what will be the mechanisms behind this effect? We address these questions in a domain where AI already exceeds human performance, analyzing more than 5.8 million move decisions made by professional Go players over the past 71 years (1950-2021). To address the first question, we use a superhuman AI program to estimate the quality of human decisions across time, generating 58 billion counterfactual game patterns and comparing the win rates of actual human decisions with those of counterfactual AI decisions. We find that humans began to make significantly better decisions following the advent of superhuman AI. We then examine human players' strategies across time and find that novel decisions (i.e., previously unobserved moves) occurred more frequently and became associated with higher decision quality after the advent of superhuman AI. Our findings suggest that the development of superhuman AI programs may have prompted human players to break away from traditional strategies and induced them to explore novel moves, which in turn may have improved their decision-making.
* An edited version of this paper is published online at PNAS: https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.2214840120
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge