Minjae Kwon
Safety Generalization Under Distribution Shift in Safe Reinforcement Learning: A Diabetes Testbed
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Safe Reinforcement Learning (RL) algorithms are typically evaluated under fixed training conditions. We investigate whether training-time safety guarantees transfer to deployment under distribution shift, using diabetes management as a safety-critical testbed. We benchmark safe RL algorithms on a unified clinical simulator and reveal a safety generalization gap: policies satisfying constraints during training frequently violate safety requirements on unseen patients. We demonstrate that test-time shielding, which filters unsafe actions using learned dynamics models, effectively restores safety across algorithms and patient populations. Across eight safe RL algorithms, three diabetes types, and three age groups, shielding achieves Time-in-Range gains of 13--14\% for strong baselines such as PPO-Lag and CPO while reducing clinical risk index and glucose variability. Our simulator and benchmark provide a platform for studying safety under distribution shift in safety-critical control domains. Code is available at https://github.com/safe-autonomy-lab/GlucoSim and https://github.com/safe-autonomy-lab/GlucoAlg.
Adaptive Reward Design for Reinforcement Learning in Complex Robotic Tasks
Dec 14, 2024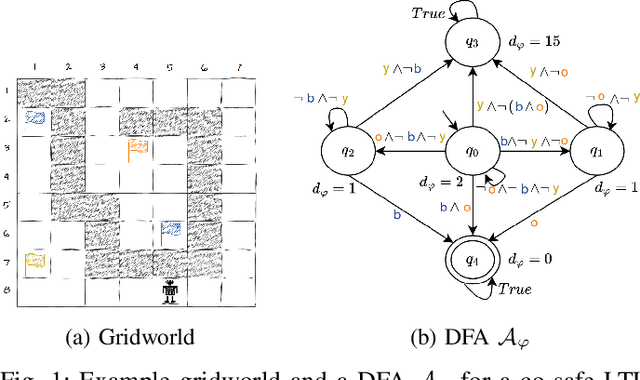
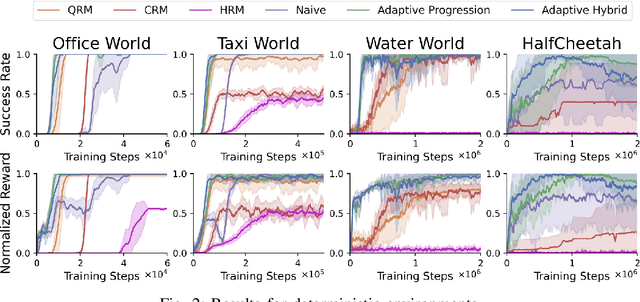
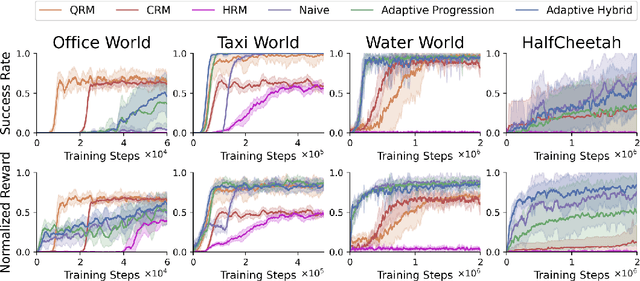
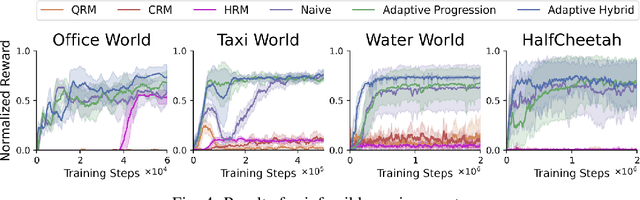
Abstract:There is a surge of interest in using formal languages such as Linear Temporal Logic (LTL) and finite automata to precisely and succinctly specify complex tasks and derive reward functions for reinforcement learning (RL) in robotic applications. However, existing methods often assign sparse rewards (e.g., giving a reward of 1 only if a task is completed and 0 otherwise), necessitating extensive exploration to converge to a high-quality policy. To address this limitation, we propose a suite of reward functions that incentivize an RL agent to make measurable progress on tasks specified by LTL formulas and develop an adaptive reward shaping approach that dynamically updates these reward functions during the learning process. Experimental results on a range of RL-based robotic tasks demonstrate that the proposed approach is compatible with various RL algorithms and consistently outperforms baselines, achieving earlier convergence to better policies with higher task success rates and returns.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge