Michele Trapletti
Reinforcement Learning for Credit Index Option Hedging
Jul 19, 2023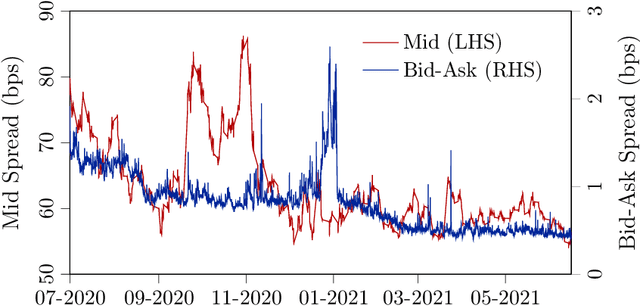
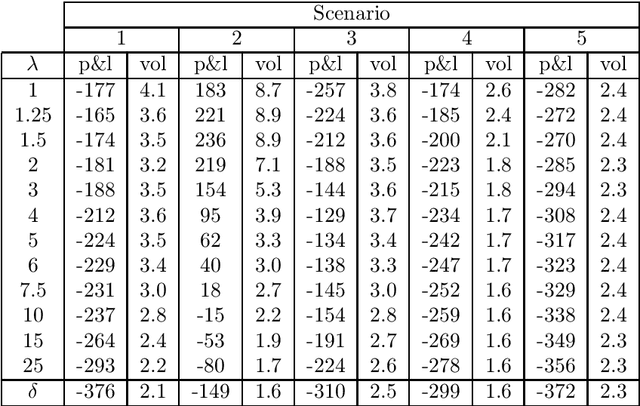
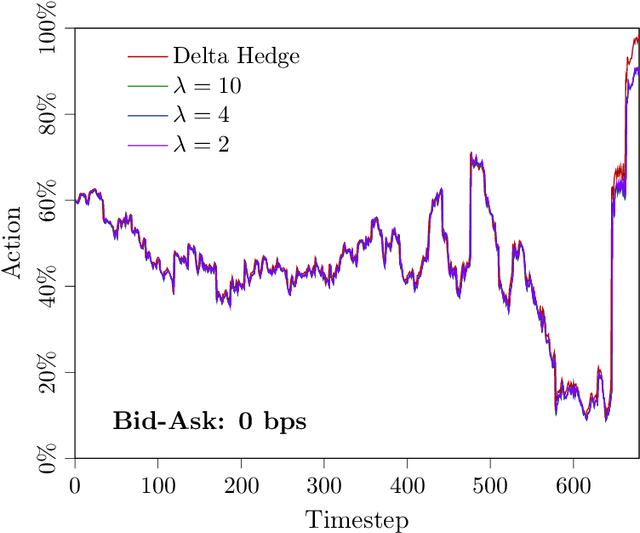
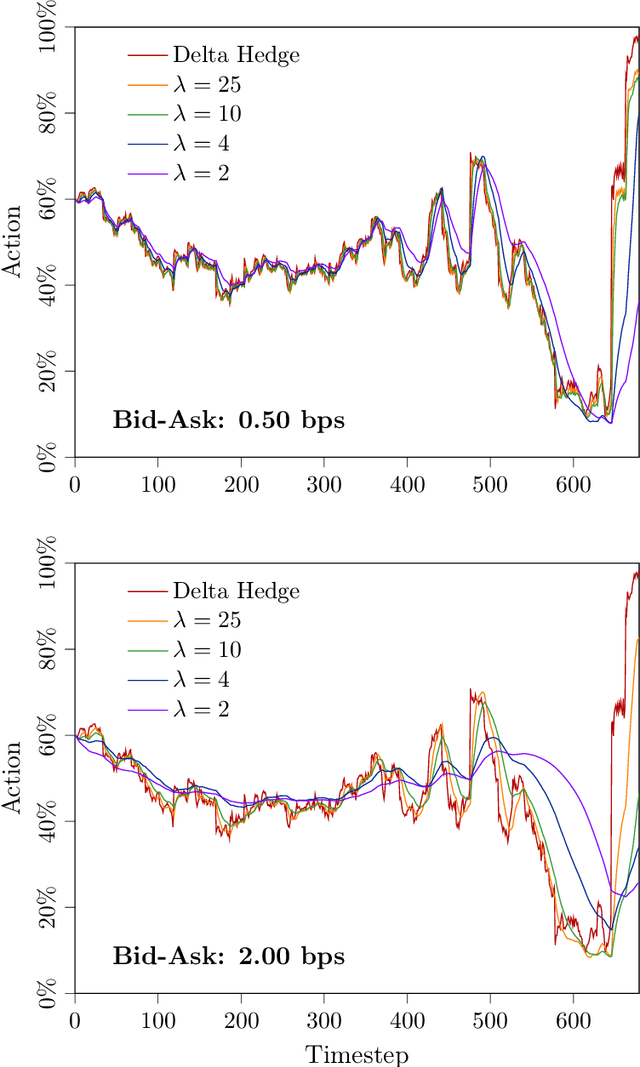
Abstract:In this paper, we focus on finding the optimal hedging strategy of a credit index option using reinforcement learning. We take a practical approach, where the focus is on realism i.e. discrete time, transaction costs; even testing our policy on real market data. We apply a state of the art algorithm, the Trust Region Volatility Optimization (TRVO) algorithm and show that the derived hedging strategy outperforms the practitioner's Black & Scholes delta hedge.
Option Hedging with Risk Averse Reinforcement Learning
Oct 23, 2020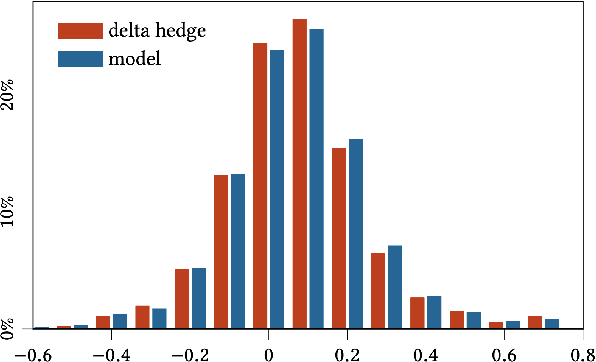
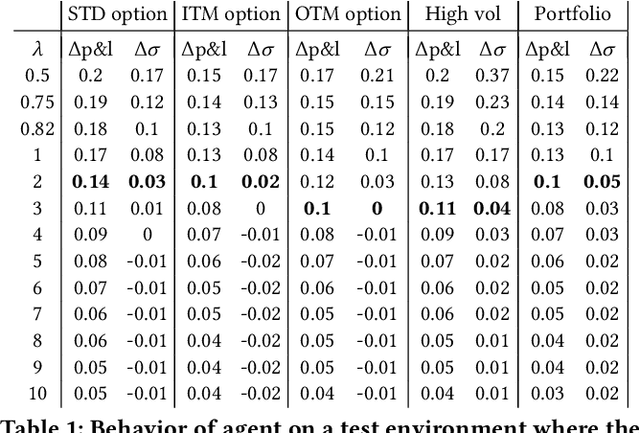
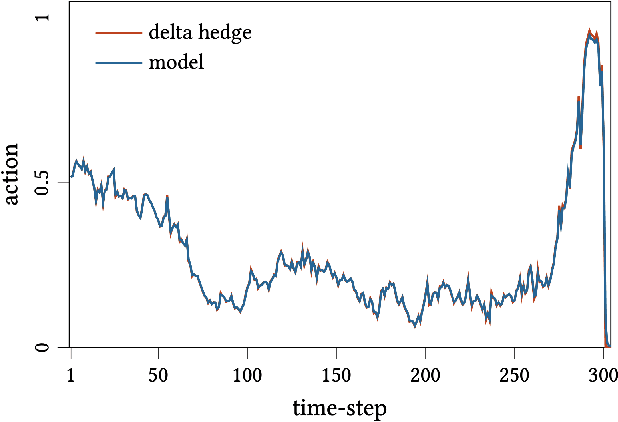
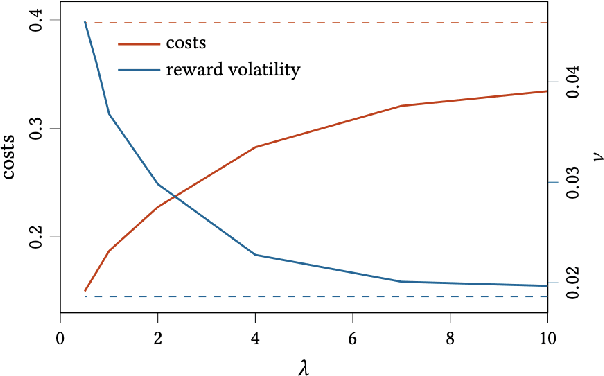
Abstract:In this paper we show how risk-averse reinforcement learning can be used to hedge options. We apply a state-of-the-art risk-averse algorithm: Trust Region Volatility Optimization (TRVO) to a vanilla option hedging environment, considering realistic factors such as discrete time and transaction costs. Realism makes the problem twofold: the agent must both minimize volatility and contain transaction costs, these tasks usually being in competition. We use the algorithm to train a sheaf of agents each characterized by a different risk aversion, so to be able to span an efficient frontier on the volatility-p\&l space. The results show that the derived hedging strategy not only outperforms the Black \& Scholes delta hedge, but is also extremely robust and flexible, as it can efficiently hedge options with different characteristics and work on markets with different behaviors than what was used in training.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge