Michele Fiori
DomusFM: A Foundation Model for Smart-Home Sensor Data
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Smart-home sensor data holds significant potential for several applications, including healthcare monitoring and assistive technologies. Existing approaches, however, face critical limitations. Supervised models require impractical amounts of labeled data. Foundation models for activity recognition focus only on inertial sensors, failing to address the unique characteristics of smart-home binary sensor events: their sparse, discrete nature combined with rich semantic associations. LLM-based approaches, while tested in this domain, still raise several issues regarding the need for natural language descriptions or prompting, and reliance on either external services or expensive hardware, making them infeasible in real-life scenarios due to privacy and cost concerns. We introduce DomusFM, the first foundation model specifically designed and pretrained for smart-home sensor data. DomusFM employs a self-supervised dual contrastive learning paradigm to capture both token-level semantic attributes and sequence-level temporal dependencies. By integrating semantic embeddings from a lightweight language model and specialized encoders for temporal patterns and binary states, DomusFM learns generalizable representations that transfer across environments and tasks related to activity and event analysis. Through leave-one-dataset-out evaluation across seven public smart-home datasets, we demonstrate that DomusFM outperforms state-of-the-art baselines on different downstream tasks, achieving superior performance even with only 5% of labeled training data available for fine-tuning. Our approach addresses data scarcity while maintaining practical deployability for real-world smart-home systems.
Improving Zero-shot ADL Recognition with Large Language Models through Event-based Context and Confidence
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Unobtrusive sensor-based recognition of Activities of Daily Living (ADLs) in smart homes by processing data collected from IoT sensing devices supports applications such as healthcare, safety, and energy management. Recent zero-shot methods based on Large Language Models (LLMs) have the advantage of removing the reliance on labeled ADL sensor data. However, existing approaches rely on time-based segmentation, which is poorly aligned with the contextual reasoning capabilities of LLMs. Moreover, existing approaches lack methods for estimating prediction confidence. This paper proposes to improve zero-shot ADL recognition with event-based segmentation and a novel method for estimating prediction confidence. Our experimental evaluation shows that event-based segmentation consistently outperforms time-based LLM approaches on complex, realistic datasets and surpasses supervised data-driven methods, even with relatively small LLMs (e.g., Gemma 3 27B). The proposed confidence measure effectively distinguishes correct from incorrect predictions.
The SERENADE project: Sensor-Based Explainable Detection of Cognitive Decline
Apr 11, 2025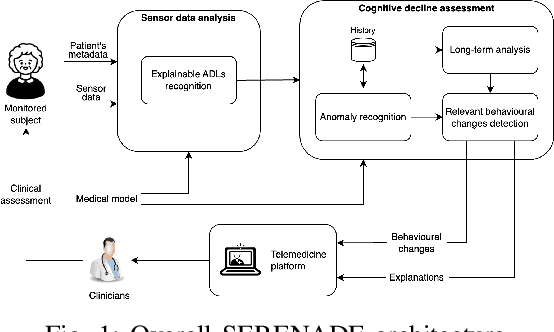
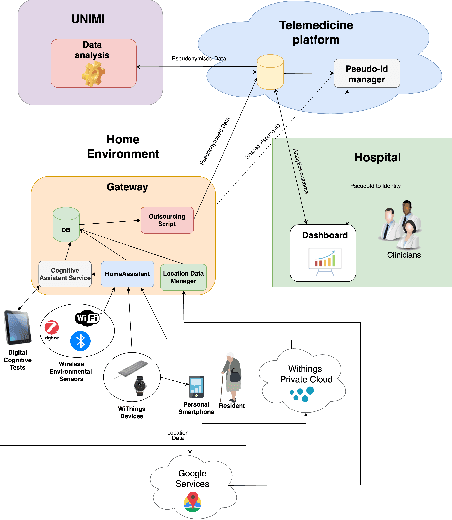
Abstract:Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) affects 12-18% of individuals over 60. MCI patients exhibit cognitive dysfunctions without significant daily functional loss. While MCI may progress to dementia, predicting this transition remains a clinical challenge due to limited and unreliable indicators. Behavioral changes, like in the execution of Activities of Daily Living (ADLs), can signal such progression. Sensorized smart homes and wearable devices offer an innovative solution for continuous, non-intrusive monitoring ADLs for MCI patients. However, current machine learning models for detecting behavioral changes lack transparency, hindering clinicians' trust. This paper introduces the SERENADE project, a European Union-funded initiative that aims to detect and explain behavioral changes associated with cognitive decline using explainable AI methods. SERENADE aims at collecting one year of data from 30 MCI patients living alone, leveraging AI to support clinical decision-making and offering a new approach to early dementia detection.
GNN-XAR: A Graph Neural Network for Explainable Activity Recognition in Smart Homes
Feb 25, 2025



Abstract:Sensor-based Human Activity Recognition (HAR) in smart home environments is crucial for several applications, especially in the healthcare domain. The majority of the existing approaches leverage deep learning models. While these approaches are effective, the rationale behind their outputs is opaque. Recently, eXplainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) approaches emerged to provide intuitive explanations to the output of HAR models. To the best of our knowledge, these approaches leverage classic deep models like CNNs or RNNs. Recently, Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) proved to be effective for sensor-based HAR. However, existing approaches are not designed with explainability in mind. In this work, we propose the first explainable Graph Neural Network explicitly designed for smart home HAR. Our results on two public datasets show that this approach provides better explanations than state-of-the-art methods while also slightly improving the recognition rate.
ContextGPT: Infusing LLMs Knowledge into Neuro-Symbolic Activity Recognition Models
Mar 11, 2024Abstract:Context-aware Human Activity Recognition (HAR) is a hot research area in mobile computing, and the most effective solutions in the literature are based on supervised deep learning models. However, the actual deployment of these systems is limited by the scarcity of labeled data that is required for training. Neuro-Symbolic AI (NeSy) provides an interesting research direction to mitigate this issue, by infusing common-sense knowledge about human activities and the contexts in which they can be performed into HAR deep learning classifiers. Existing NeSy methods for context-aware HAR rely on knowledge encoded in logic-based models (e.g., ontologies) whose design, implementation, and maintenance to capture new activities and contexts require significant human engineering efforts, technical knowledge, and domain expertise. Recent works show that pre-trained Large Language Models (LLMs) effectively encode common-sense knowledge about human activities. In this work, we propose ContextGPT: a novel prompt engineering approach to retrieve from LLMs common-sense knowledge about the relationship between human activities and the context in which they are performed. Unlike ontologies, ContextGPT requires limited human effort and expertise. An extensive evaluation carried out on two public datasets shows how a NeSy model obtained by infusing common-sense knowledge from ContextGPT is effective in data scarcity scenarios, leading to similar (and sometimes better) recognition rates than logic-based approaches with a fraction of the effort.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge