Michel Albonico
Automatic Extraction of Time-windowed ROS Computation Graphs from ROS Bag Files
May 25, 2023
Abstract:Robotic systems react to different environmental stimuli, potentially resulting in the dynamic reconfiguration of the software controlling such systems. One effect of such dynamism is the reconfiguration of the software architecture reconfiguration of the system at runtime. Such reconfigurations might severely impact the runtime properties of robotic systems, e.g., in terms of performance and energy efficiency. The ROS \emph{rosbag} package enables developers to record and store timestamped data related to the execution of robotic missions, implicitly containing relevant information about the architecture of the monitored system during its execution. In this study, we discuss about our approach for statically extracting (time-windowed) architectural information from ROS bag files. The proposed approach can support the robotics community in better discussing and reasoning the software architecture (and its runtime reconfigurations) of ROS-based systems. We evaluate our approach against hundreds of ROS bag files systematically mined from 4,434 public GitHub repositories.
* 2 pages, workshop paper
Mining Energy-Related Practices in Robotics Software
Mar 25, 2021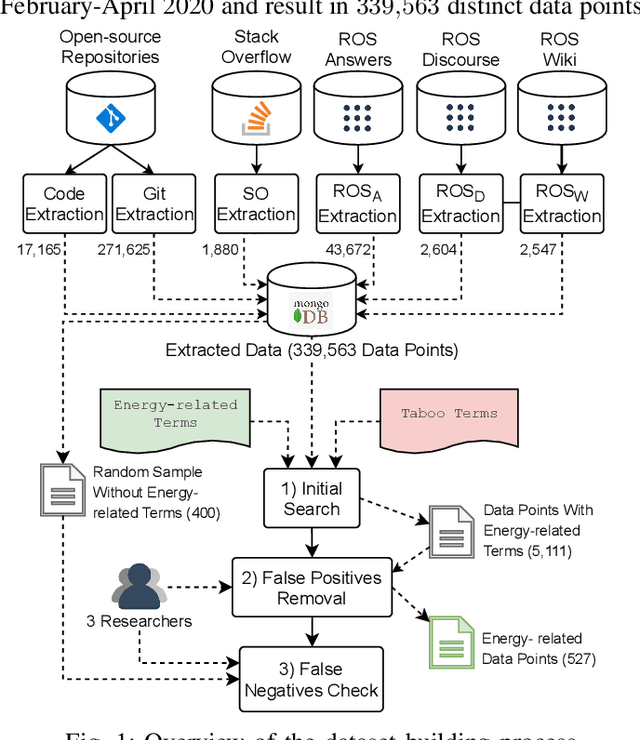
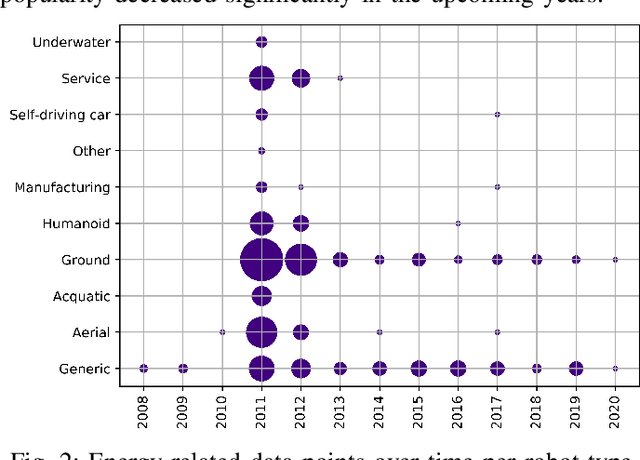
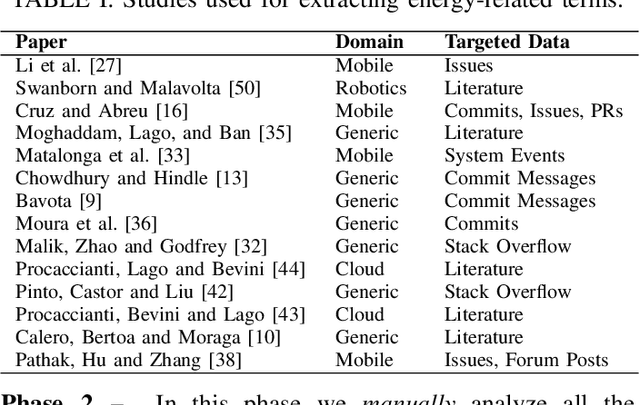
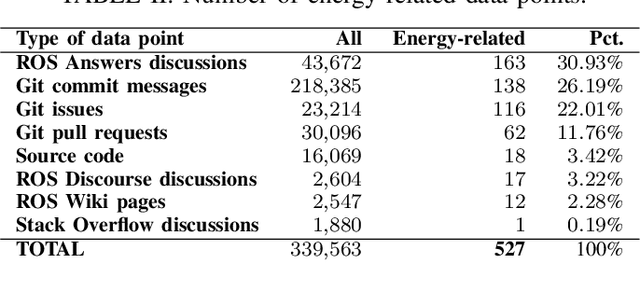
Abstract:Robots are becoming more and more commonplace in many industry settings. This successful adoption can be partly attributed to (1) their increasingly affordable cost and (2) the possibility of developing intelligent, software-driven robots. Unfortunately, robotics software consumes significant amounts of energy. Moreover, robots are often battery-driven, meaning that even a small energy improvement can help reduce its energy footprint and increase its autonomy and user experience. In this paper, we study the Robot Operating System (ROS) ecosystem, the de-facto standard for developing and prototyping robotics software. We analyze 527 energy-related data points (including commits, pull-requests, and issues on ROS-related repositories, ROS-related questions on StackOverflow, ROS Discourse, ROS Answers, and the official ROS Wiki). Our results include a quantification of the interest of roboticists on software energy efficiency, 10 recurrent causes, and 14 solutions of energy-related issues, and their implied trade-offs with respect to other quality attributes. Those contributions support roboticists and researchers towards having energy-efficient software in future robotics projects.
* 11 pages
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge