Michael Zock
LIF
Du TAL au TIL
Jan 20, 2012Abstract:Historically two types of NLP have been investigated: fully automated processing of language by machines (NLP) and autonomous processing of natural language by people, i.e. the human brain (psycholinguistics). We believe that there is room and need for another kind, INLP: interactive natural language processing. This intermediate approach starts from peoples' needs, trying to bridge the gap between their actual knowledge and a given goal. Given the fact that peoples' knowledge is variable and often incomplete, the aim is to build bridges linking a given knowledge state to a given goal. We present some examples, trying to show that this goal is worth pursuing, achievable and at a reasonable cost.
Système d'aide à l'accès lexical : trouver le mot qu'on a sur le bout de la langue
Jan 20, 2012
Abstract:The study of the Tip of the Tongue phenomenon (TOT) provides valuable clues and insights concerning the organisation of the mental lexicon (meaning, number of syllables, relation with other words, etc.). This paper describes a tool based on psycho-linguistic observations concerning the TOT phenomenon. We've built it to enable a speaker/writer to find the word he is looking for, word he may know, but which he is unable to access in time. We try to simulate the TOT phenomenon by creating a situation where the system knows the target word, yet is unable to access it. In order to find the target word we make use of the paradigmatic and syntagmatic associations stored in the linguistic databases. Our experiment allows the following conclusion: a tool like SVETLAN, capable to structure (automatically) a dictionary by domains can be used sucessfully to help the speaker/writer to find the word he is looking for, if it is combined with a database rich in terms of paradigmatic links like EuroWordNet.
Let's get the student into the driver's seat
Nov 23, 2007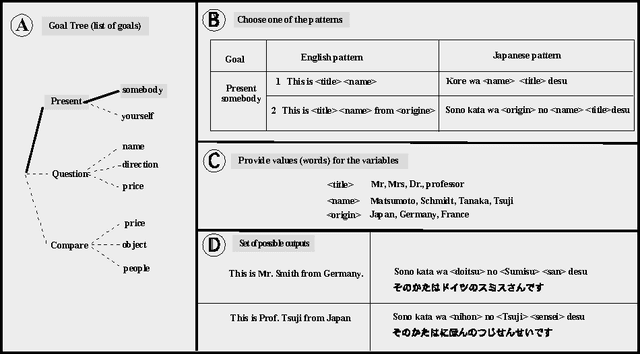



Abstract:Speaking a language and achieving proficiency in another one is a highly complex process which requires the acquisition of various kinds of knowledge and skills, like the learning of words, rules and patterns and their connection to communicative goals (intentions), the usual starting point. To help the learner to acquire these skills we propose an enhanced, electronic version of an age old method: pattern drills (henceforth PDs). While being highly regarded in the fifties, PDs have become unpopular since then, partially because of their lack of grounding (natural context) and rigidity. Despite these shortcomings we do believe in the virtues of this approach, at least with regard to the acquisition of basic linguistic reflexes or skills (automatisms), necessary to survive in the new language. Of course, the method needs improvement, and we will show here how this can be achieved. Unlike tapes or books, computers are open media, allowing for dynamic changes, taking users' performances and preferences into account. Building an electronic version of PDs amounts to building an open resource, accomodatable to the users' ever changing needs.
* 6 pages
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge