Michael Schlechtinger
By Fair Means or Foul: Quantifying Collusion in a Market Simulation with Deep Reinforcement Learning
Jun 04, 2024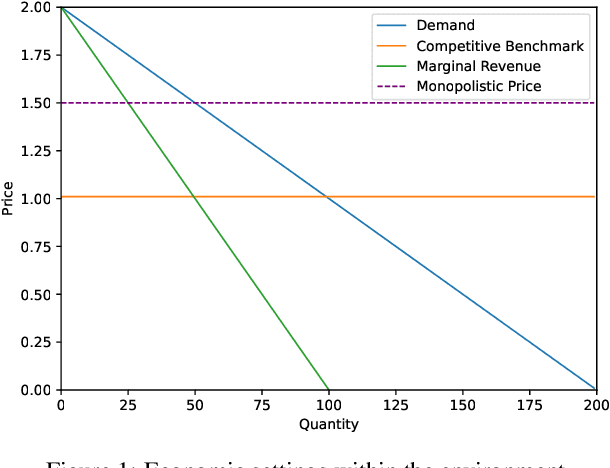
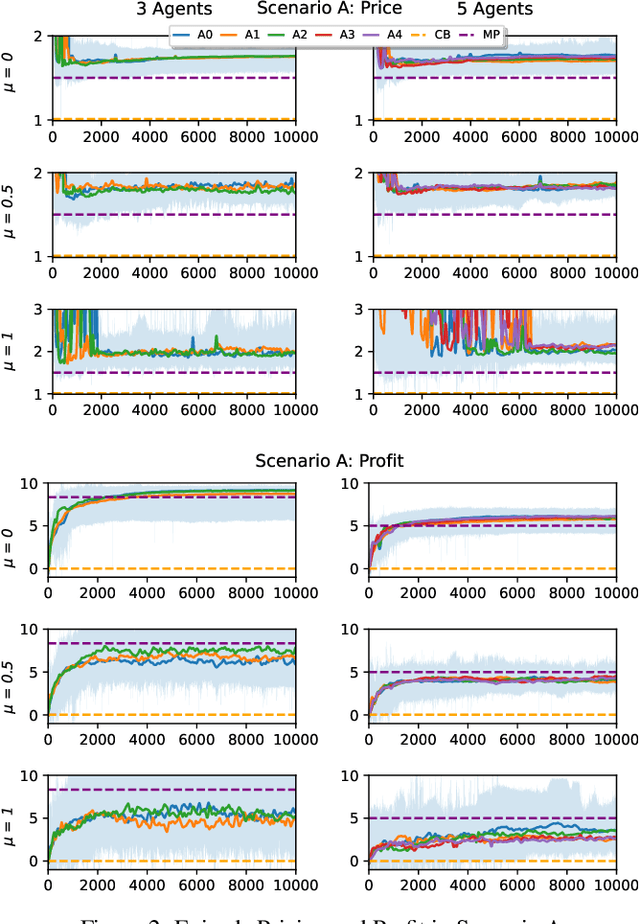
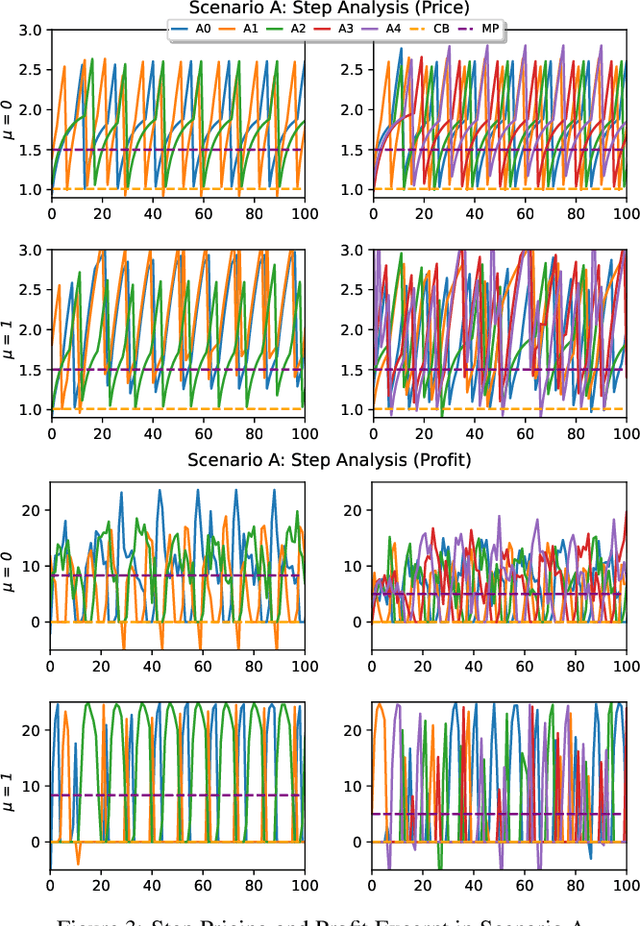
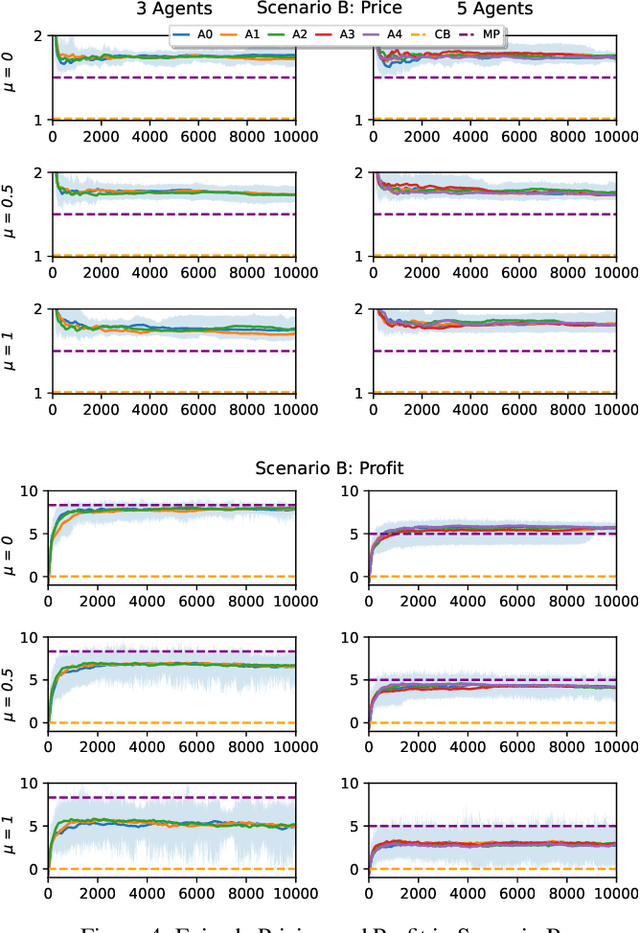
Abstract:In the rapidly evolving landscape of eCommerce, Artificial Intelligence (AI) based pricing algorithms, particularly those utilizing Reinforcement Learning (RL), are becoming increasingly prevalent. This rise has led to an inextricable pricing situation with the potential for market collusion. Our research employs an experimental oligopoly model of repeated price competition, systematically varying the environment to cover scenarios from basic economic theory to subjective consumer demand preferences. We also introduce a novel demand framework that enables the implementation of various demand models, allowing for a weighted blending of different models. In contrast to existing research in this domain, we aim to investigate the strategies and emerging pricing patterns developed by the agents, which may lead to a collusive outcome. Furthermore, we investigate a scenario where agents cannot observe their competitors' prices. Finally, we provide a comprehensive legal analysis across all scenarios. Our findings indicate that RL-based AI agents converge to a collusive state characterized by the charging of supracompetitive prices, without necessarily requiring inter-agent communication. Implementing alternative RL algorithms, altering the number of agents or simulation settings, and restricting the scope of the agents' observation space does not significantly impact the collusive market outcome behavior.
Winning at Any Cost -- Infringing the Cartel Prohibition With Reinforcement Learning
Jul 05, 2021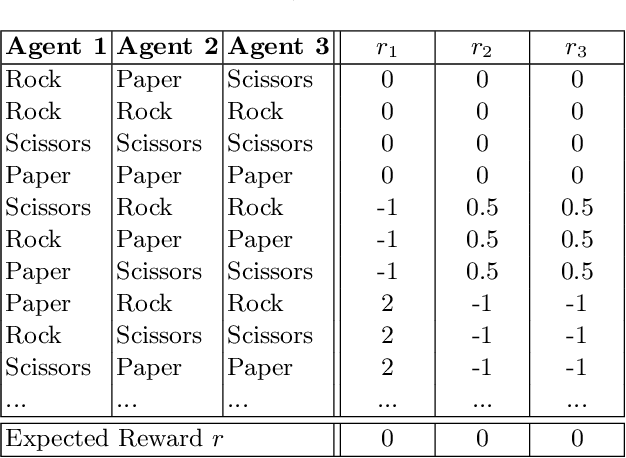
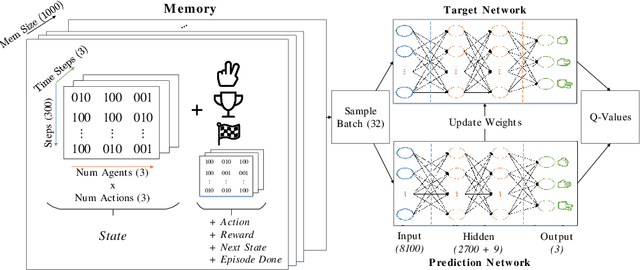
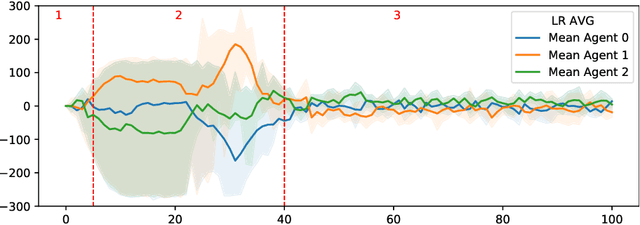
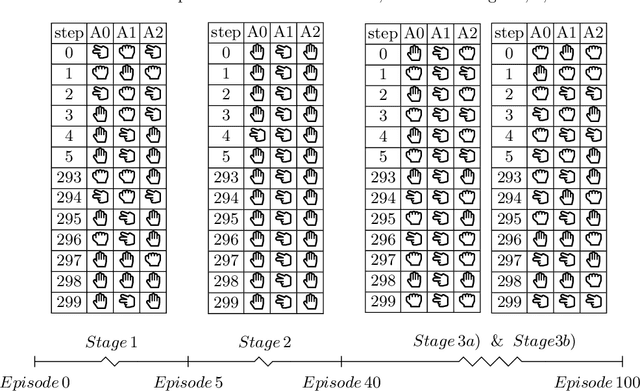
Abstract:Pricing decisions are increasingly made by AI. Thanks to their ability to train with live market data while making decisions on the fly, deep reinforcement learning algorithms are especially effective in taking such pricing decisions. In e-commerce scenarios, multiple reinforcement learning agents can set prices based on their competitor's prices. Therefore, research states that agents might end up in a state of collusion in the long run. To further analyze this issue, we build a scenario that is based on a modified version of a prisoner's dilemma where three agents play the game of rock paper scissors. Our results indicate that the action selection can be dissected into specific stages, establishing the possibility to develop collusion prevention systems that are able to recognize situations which might lead to a collusion between competitors. We furthermore provide evidence for a situation where agents are capable of performing a tacit cooperation strategy without being explicitly trained to do so.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge