Michael Hunter Klein
Multiple Domain Causal Networks
May 13, 2022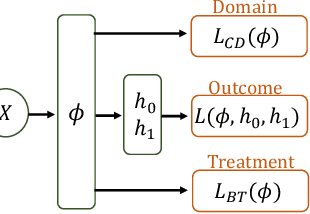


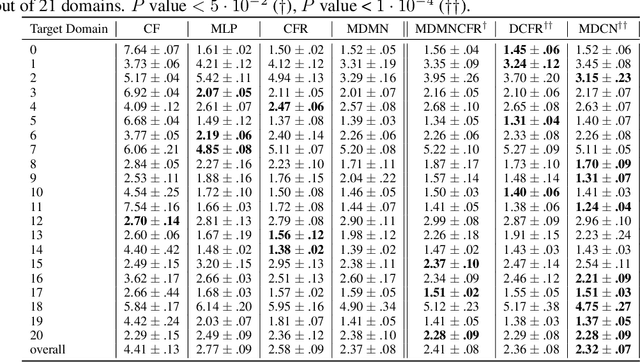
Abstract:Observational studies are regarded as economic alternatives to randomized trials, often used in their stead to investigate and determine treatment efficacy. Due to lack of sample size, observational studies commonly combine data from multiple sources or different sites/centers. Despite the benefits of an increased sample size, a naive combination of multicenter data may result in incongruities stemming from center-specific protocols for generating cohorts or reactions towards treatments distinct to a given center, among other things. These issues arise in a variety of other contexts, including capturing a treatment effect related to an individual's unique biological characteristics. Existing methods for estimating heterogeneous treatment effects have not adequately addressed the multicenter context, but rather treat it simply as a means to obtain sufficient sample size. Additionally, previous approaches to estimating treatment effects do not straightforwardly generalize to the multicenter design, especially when required to provide treatment insights for patients from a new, unobserved center. To address these shortcomings, we propose Multiple Domain Causal Networks (MDCN), an approach that simultaneously strengthens the information sharing between similar centers while addressing the selection bias in treatment assignment through learning of a new feature embedding. In empirical evaluations, MDCN is consistently more accurate when estimating the heterogeneous treatment effect in new centers compared to benchmarks that adjust solely based on treatment imbalance or general center differences. Finally, we justify our approach by providing theoretical analyses that demonstrate that MDCN improves on the generalization bound of the new, unobserved target center.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge