Mercedes López-Morales
Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian
Improving Earth-like planet detection in radial velocity using deep learning
May 21, 2024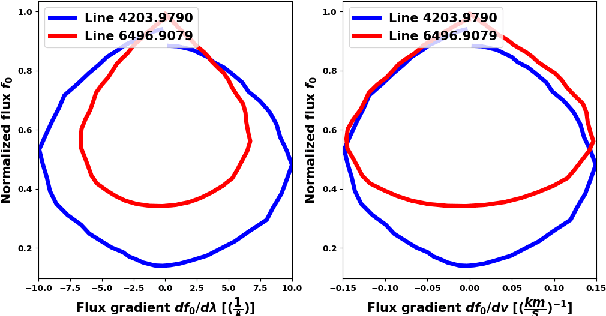
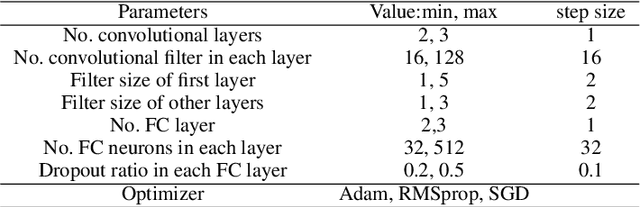
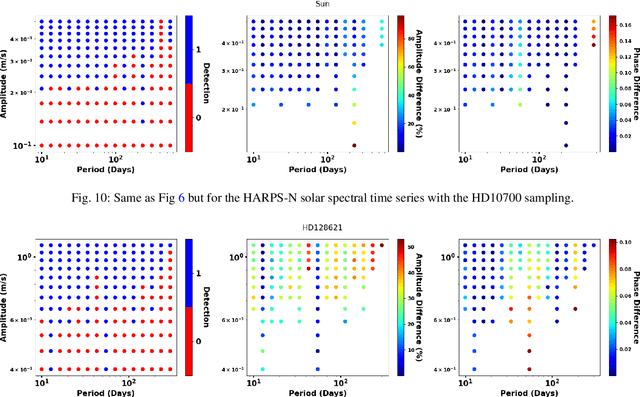

Abstract:Many novel methods have been proposed to mitigate stellar activity for exoplanet detection as the presence of stellar activity in radial velocity (RV) measurements is the current major limitation. Unlike traditional methods that model stellar activity in the RV domain, more methods are moving in the direction of disentangling stellar activity at the spectral level. The goal of this paper is to present a novel convolutional neural network-based algorithm that efficiently models stellar activity signals at the spectral level, enhancing the detection of Earth-like planets. We trained a convolutional neural network to build the correlation between the change in the spectral line profile and the corresponding RV, full width at half maximum (FWHM) and bisector span (BIS) values derived from the classical cross-correlation function. This algorithm has been tested on three intensively observed stars: Alpha Centauri B (HD128621), Tau ceti (HD10700), and the Sun. By injecting simulated planetary signals at the spectral level, we demonstrate that our machine learning algorithm can achieve, for HD128621 and HD10700, a detection threshold of 0.5 m/s in semi-amplitude for planets with periods ranging from 10 to 300 days. This threshold would correspond to the detection of a $\sim$4$\mathrm{M}_{\oplus}$ in the habitable zone of those stars. On the HARPS-N solar dataset, our algorithm is even more efficient at mitigating stellar activity signals and can reach a threshold of 0.2 m/s, which would correspond to a 2.2$\mathrm{M}_{\oplus}$ planet on the orbit of the Earth. To the best of our knowledge, it is the first time that such low detection thresholds are reported for the Sun, but also for other stars, and therefore this highlights the efficiency of our convolutional neural network-based algorithm at mitigating stellar activity in RV measurements.
Simulation-based Inference for Exoplanet Atmospheric Retrieval: Insights from winning the Ariel Data Challenge 2023 using Normalizing Flows
Sep 17, 2023Abstract:Advancements in space telescopes have opened new avenues for gathering vast amounts of data on exoplanet atmosphere spectra. However, accurately extracting chemical and physical properties from these spectra poses significant challenges due to the non-linear nature of the underlying physics. This paper presents novel machine learning models developed by the AstroAI team for the Ariel Data Challenge 2023, where one of the models secured the top position among 293 competitors. Leveraging Normalizing Flows, our models predict the posterior probability distribution of atmospheric parameters under different atmospheric assumptions. Moreover, we introduce an alternative model that exhibits higher performance potential than the winning model, despite scoring lower in the challenge. These findings highlight the need to reevaluate the evaluation metric and prompt further exploration of more efficient and accurate approaches for exoplanet atmosphere spectra analysis. Finally, we present recommendations to enhance the challenge and models, providing valuable insights for future applications on real observational data. These advancements pave the way for more effective and timely analysis of exoplanet atmospheric properties, advancing our understanding of these distant worlds.
Identifying Exoplanets with Deep Learning. IV. Removing Stellar Activity Signals from Radial Velocity Measurements Using Neural Networks
Nov 04, 2020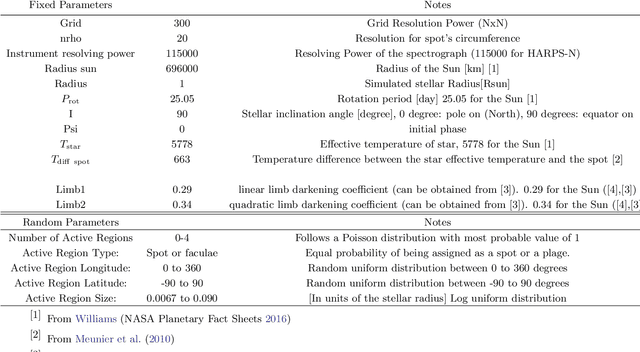
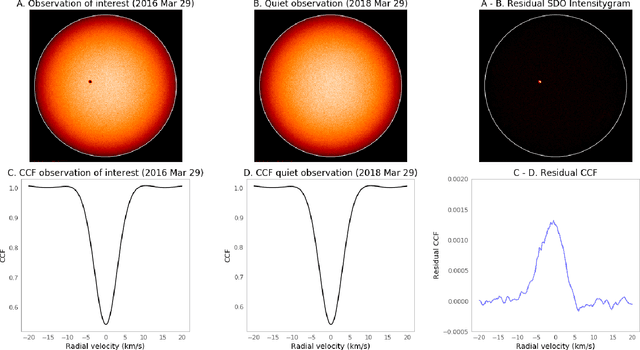
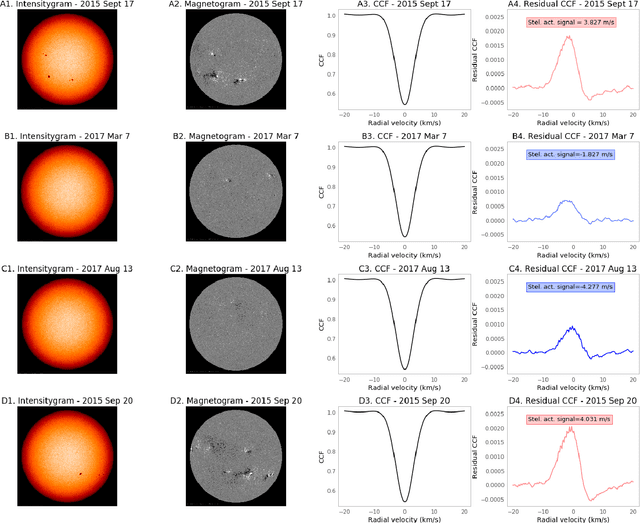
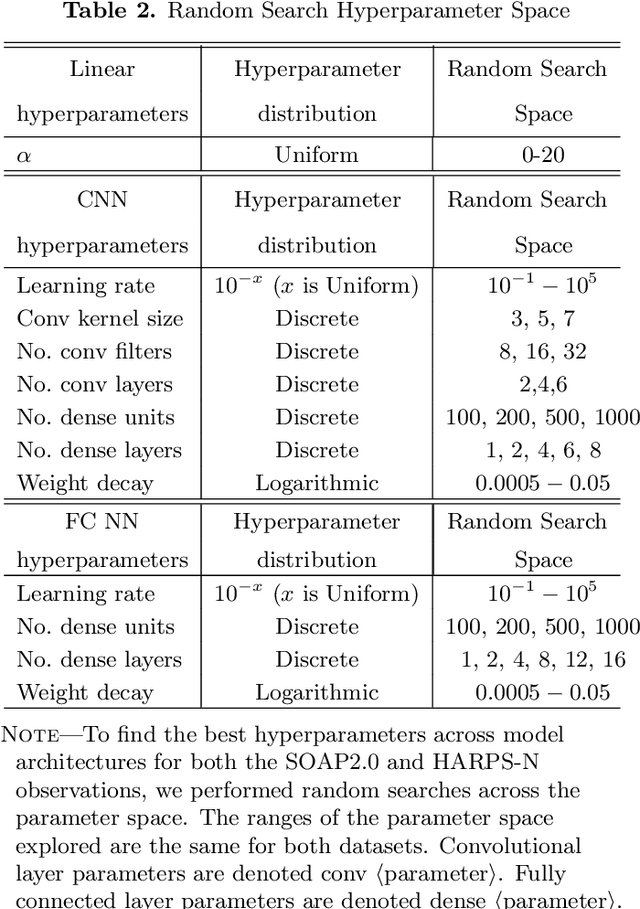
Abstract:Exoplanet detection with precise radial velocity (RV) observations is currently limited by spurious RV signals introduced by stellar activity. We show that machine learning techniques such as linear regression and neural networks can effectively remove the activity signals (due to starspots/faculae) from RV observations. Previous efforts focused on carefully filtering out activity signals in time using modeling techniques like Gaussian Process regression (e.g. Haywood et al. 2014). Instead, we systematically remove activity signals using only changes to the average shape of spectral lines, and no information about when the observations were collected. We trained our machine learning models on both simulated data (generated with the SOAP 2.0 software; Dumusque et al. 2014) and observations of the Sun from the HARPS-N Solar Telescope (Dumusque et al. 2015; Phillips et al. 2016; Collier Cameron et al. 2019). We find that these techniques can predict and remove stellar activity from both simulated data (improving RV scatter from 82 cm/s to 3 cm/s) and from more than 600 real observations taken nearly daily over three years with the HARPS-N Solar Telescope (improving the RV scatter from 1.47 m/s to 0.78 m/s, a factor of ~ 1.9 improvement). In the future, these or similar techniques could remove activity signals from observations of stars outside our solar system and eventually help detect habitable-zone Earth-mass exoplanets around Sun-like stars.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge