Mengjiao Zhang
Subword Embedding from Bytes Gains Privacy without Sacrificing Accuracy and Complexity
Oct 21, 2024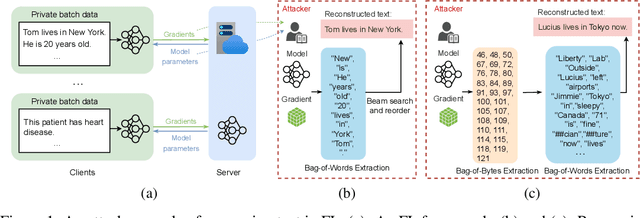
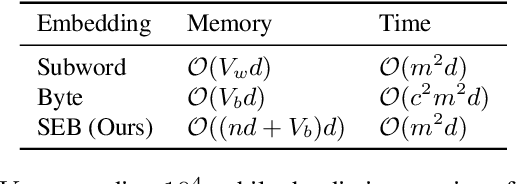
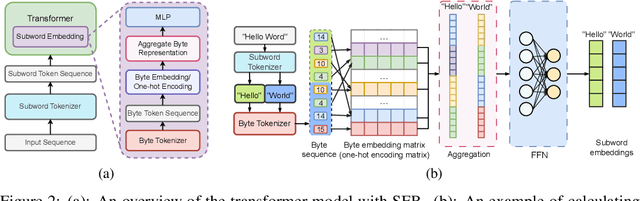

Abstract:While NLP models significantly impact our lives, there are rising concerns about privacy invasion. Although federated learning enhances privacy, attackers may recover private training data by exploiting model parameters and gradients. Therefore, protecting against such embedding attacks remains an open challenge. To address this, we propose Subword Embedding from Bytes (SEB) and encode subwords to byte sequences using deep neural networks, making input text recovery harder. Importantly, our method requires a smaller memory with $256$ bytes of vocabulary while keeping efficiency with the same input length. Thus, our solution outperforms conventional approaches by preserving privacy without sacrificing efficiency or accuracy. Our experiments show SEB can effectively protect against embedding-based attacks from recovering original sentences in federated learning. Meanwhile, we verify that SEB obtains comparable and even better results over standard subword embedding methods in machine translation, sentiment analysis, and language modeling with even lower time and space complexity.
Retrieval Augmented Generation for Domain-specific Question Answering
Apr 23, 2024



Abstract:Question answering (QA) has become an important application in the advanced development of large language models. General pre-trained large language models for question-answering are not trained to properly understand the knowledge or terminology for a specific domain, such as finance, healthcare, education, and customer service for a product. To better cater to domain-specific understanding, we build an in-house question-answering system for Adobe products. We propose a novel framework to compile a large question-answer database and develop the approach for retrieval-aware finetuning of a Large Language model. We showcase that fine-tuning the retriever leads to major improvements in the final generation. Our overall approach reduces hallucinations during generation while keeping in context the latest retrieval information for contextual grounding.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge