Melkamu Mersha
Explainability in Neural Networks for Natural Language Processing Tasks
Dec 23, 2024Abstract:Neural networks are widely regarded as black-box models, creating significant challenges in understanding their inner workings, especially in natural language processing (NLP) applications. To address this opacity, model explanation techniques like Local Interpretable Model-Agnostic Explanations (LIME) have emerged as essential tools for providing insights into the behavior of these complex systems. This study leverages LIME to interpret a multi-layer perceptron (MLP) neural network trained on a text classification task. By analyzing the contribution of individual features to model predictions, the LIME approach enhances interpretability and supports informed decision-making. Despite its effectiveness in offering localized explanations, LIME has limitations in capturing global patterns and feature interactions. This research highlights the strengths and shortcomings of LIME and proposes directions for future work to achieve more comprehensive interpretability in neural NLP models.
Explainable Artificial Intelligence: A Survey of Needs, Techniques, Applications, and Future Direction
Aug 30, 2024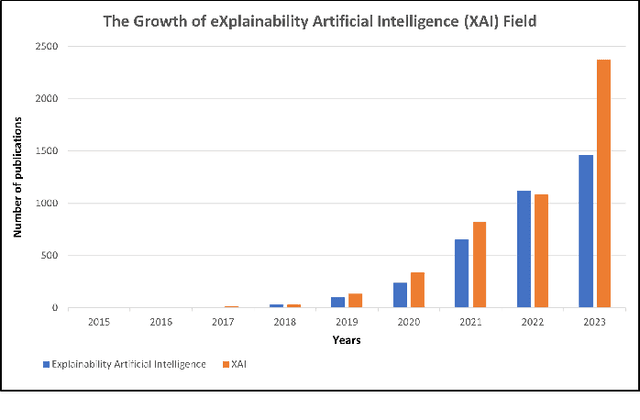
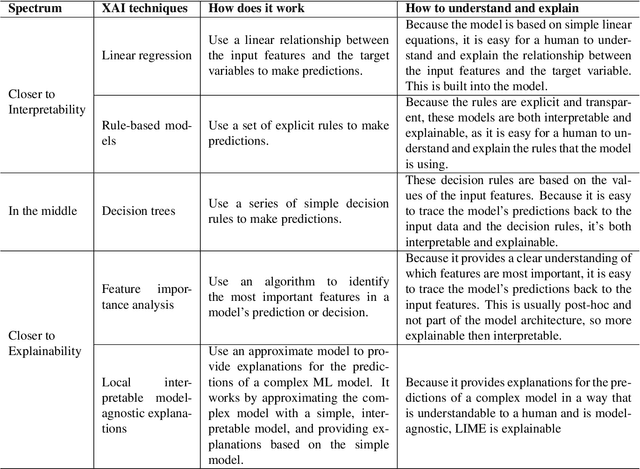
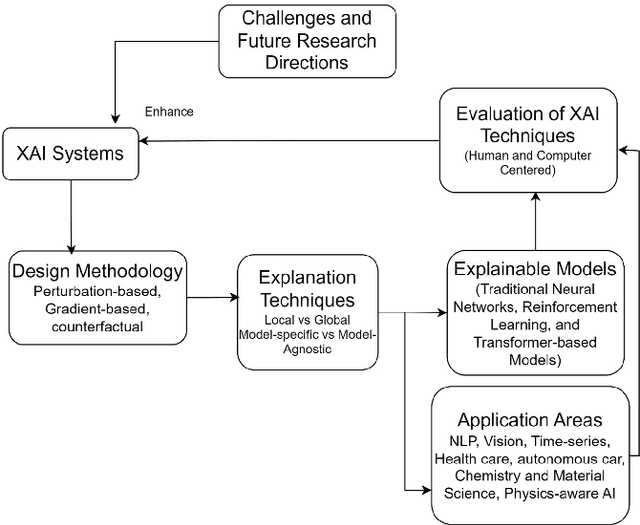
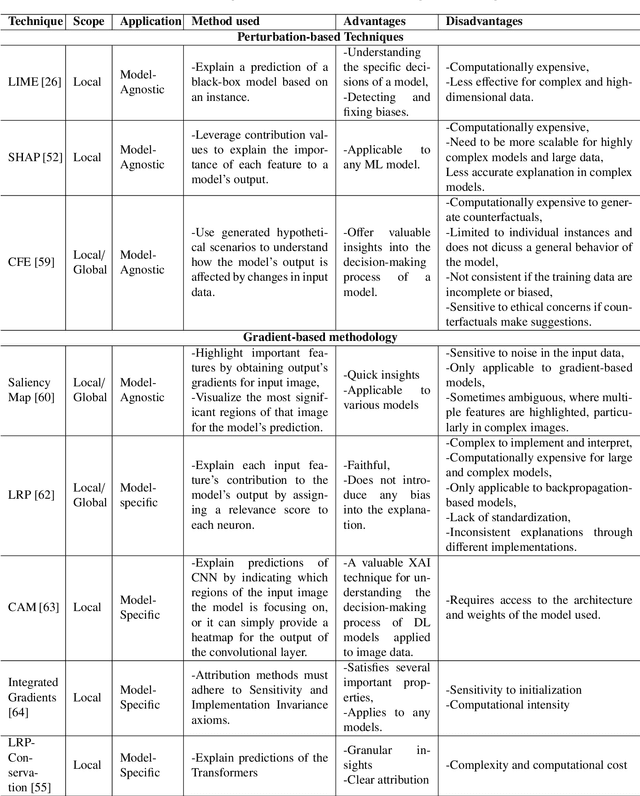
Abstract:Artificial intelligence models encounter significant challenges due to their black-box nature, particularly in safety-critical domains such as healthcare, finance, and autonomous vehicles. Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) addresses these challenges by providing explanations for how these models make decisions and predictions, ensuring transparency, accountability, and fairness. Existing studies have examined the fundamental concepts of XAI, its general principles, and the scope of XAI techniques. However, there remains a gap in the literature as there are no comprehensive reviews that delve into the detailed mathematical representations, design methodologies of XAI models, and other associated aspects. This paper provides a comprehensive literature review encompassing common terminologies and definitions, the need for XAI, beneficiaries of XAI, a taxonomy of XAI methods, and the application of XAI methods in different application areas. The survey is aimed at XAI researchers, XAI practitioners, AI model developers, and XAI beneficiaries who are interested in enhancing the trustworthiness, transparency, accountability, and fairness of their AI models.
First Attempt at Building Parallel Corpora for Machine Translation of Northeast India's Very Low-Resource Languages
Dec 08, 2023Abstract:This paper presents the creation of initial bilingual corpora for thirteen very low-resource languages of India, all from Northeast India. It also presents the results of initial translation efforts in these languages. It creates the first-ever parallel corpora for these languages and provides initial benchmark neural machine translation results for these languages. We intend to extend these corpora to include a large number of low-resource Indian languages and integrate the effort with our prior work with African and American-Indian languages to create corpora covering a large number of languages from across the world.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge