Melina Alberio Guerra
A Hybrid Solution to Learn Turn-Taking in Multi-Party Service-based Chat Groups
Jan 14, 2020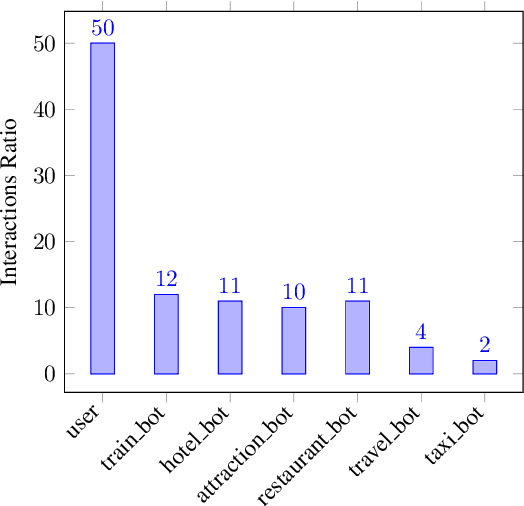
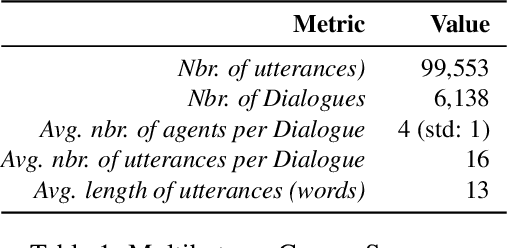
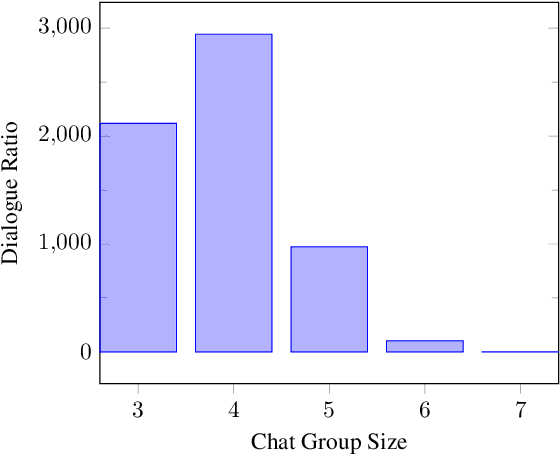
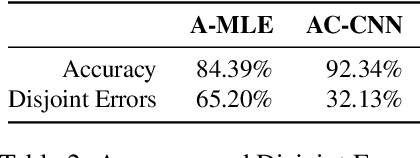
Abstract:To predict the next most likely participant to interact in a multi-party conversation is a difficult problem. In a text-based chat group, the only information available is the sender, the content of the text and the dialogue history. In this paper we present our study on how these information can be used on the prediction task through a corpus and architecture that integrates turn-taking classifiers based on Maximum Likelihood Expectation (MLE), Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) and Finite State Automata (FSA). The corpus is a synthetic adaptation of the Multi-Domain Wizard-of-Oz dataset (MultiWOZ) to a multiple travel service-based bots scenario with dialogue errors and was created to simulate user's interaction and evaluate the architecture. We present experimental results which show that the CNN approach achieves better performance than the baseline with an accuracy of 92.34%, but the integrated solution with MLE, CNN and FSA achieves performance even better, with 95.65%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge