Mehmet Yigit Yildirim
Leveraging Uncertainty in Deep Learning for Selective Classification
May 23, 2019
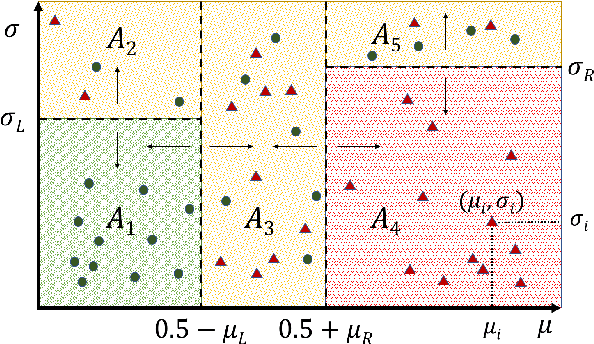
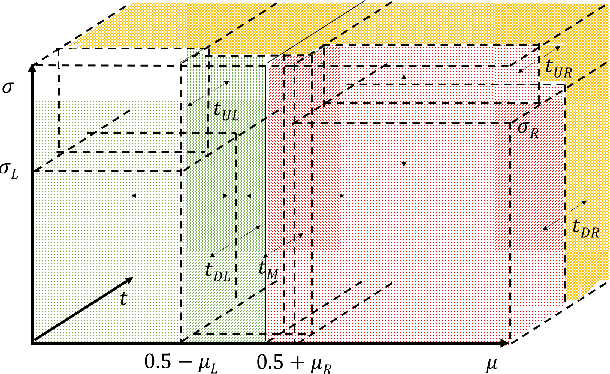
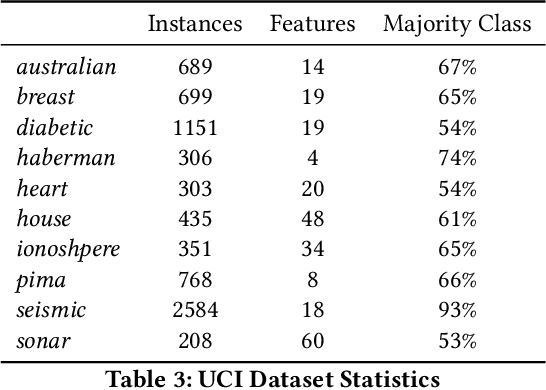
Abstract:The wide and rapid adoption of deep learning by practitioners brought unintended consequences in many situations such as in the infamous case of Google Photos' racist image recognition algorithm; thus, necessitated the utilization of the quantified uncertainty for each prediction. There have been recent efforts towards quantifying uncertainty in conventional deep learning methods (e.g., dropout as Bayesian approximation); however, their optimal use in decision making is often overlooked and understudied. In this study, we propose a mixed-integer programming framework for classification with reject option (also known as selective classification), that investigates and combines model uncertainty and predictive mean to identify optimal classification and rejection regions. Our results indicate superior performance of our framework both in non-rejected accuracy and rejection quality on several publicly available datasets. Moreover, we extend our framework to cost-sensitive settings and show that our approach outperforms industry standard methods significantly for online fraud management in real-world settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge