Mehdi Nourbakhsh
Structural Design Recommendations in the Early Design Phase using Machine Learning
Jul 19, 2021



Abstract:Structural engineering knowledge can be of significant importance to the architectural design team during the early design phase. However, architects and engineers do not typically work together during the conceptual phase; in fact, structural engineers are often called late into the process. As a result, updates in the design are more difficult and time-consuming to complete. At the same time, there is a lost opportunity for better design exploration guided by structural feedback. In general, the earlier in the design process the iteration happens, the greater the benefits in cost efficiency and informed de-sign exploration, which can lead to higher-quality creative results. In order to facilitate an informed exploration in the early design stage, we suggest the automation of fundamental structural engineering tasks and introduce ApproxiFramer, a Machine Learning-based system for the automatic generation of structural layouts from building plan sketches in real-time. The system aims to assist architects by presenting them with feasible structural solutions during the conceptual phase so that they proceed with their design with adequate knowledge of its structural implications. In this paper, we describe the system and evaluate the performance of a proof-of-concept implementation in the domain of orthogonal, metal, rigid structures. We trained a Convolutional Neural Net to iteratively generate structural design solutions for sketch-level building plans using a synthetic dataset and achieved an average error of 2.2% in the predicted positions of the columns.
Building-GAN: Graph-Conditioned Architectural Volumetric Design Generation
Apr 27, 2021
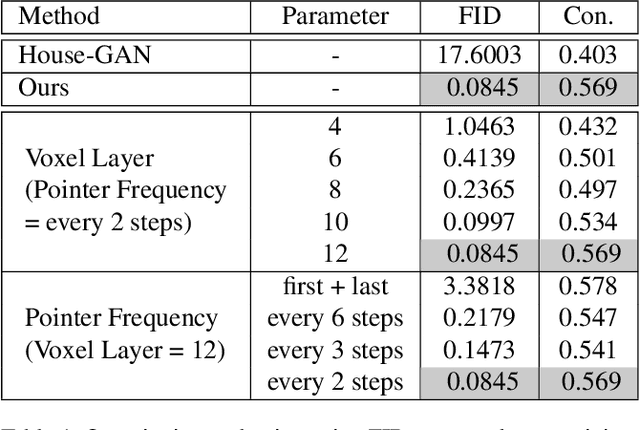
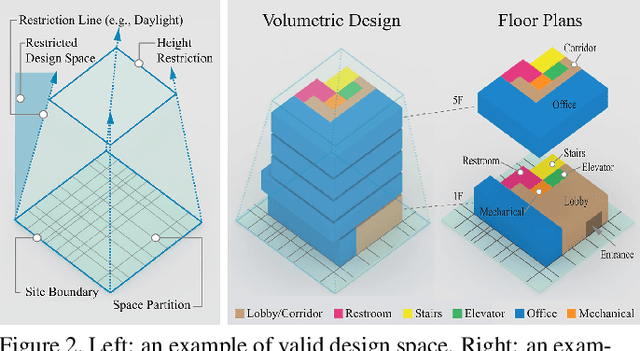
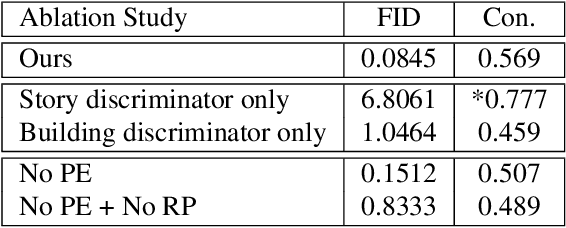
Abstract:Volumetric design is the first and critical step for professional building design, where architects not only depict the rough 3D geometry of the building but also specify the programs to form a 2D layout on each floor. Though 2D layout generation for a single story has been widely studied, there is no developed method for multi-story buildings. This paper focuses on volumetric design generation conditioned on an input program graph. Instead of outputting dense 3D voxels, we propose a new 3D representation named voxel graph that is both compact and expressive for building geometries. Our generator is a cross-modal graph neural network that uses a pointer mechanism to connect the input program graph and the output voxel graph, and the whole pipeline is trained using the adversarial framework. The generated designs are evaluated qualitatively by a user study and quantitatively using three metrics: quality, diversity, and connectivity accuracy. We show that our model generates realistic 3D volumetric designs and outperforms previous methods and baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge