Meghna Roy Chowdhury
From Muscle to Text with MyoText: sEMG to Text via Finger Classification and Transformer-Based Decoding
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Surface electromyography (sEMG) provides a direct neural interface for decoding muscle activity and offers a promising foundation for keyboard-free text input in wearable and mixed-reality systems. Previous sEMG-to-text studies mainly focused on recognizing letters directly from sEMG signals, forming an important first step toward translating muscle activity into text. Building on this foundation, we present MyoText, a hierarchical framework that decodes sEMG signals to text through physiologically grounded intermediate stages. MyoText first classifies finger activations from multichannel sEMG using a CNN-BiLSTM-Attention model, applies ergonomic typing priors to infer letters, and reconstructs full sentences with a fine-tuned T5 transformer. This modular design mirrors the natural hierarchy of typing, linking muscle intent to language output and reducing the search space for decoding. Evaluated on 30 users from the emg2qwerty dataset, MyoText outperforms baselines by achieving 85.4% finger-classification accuracy, 5.4% character error rate (CER), and 6.5% word error rate (WER). Beyond accuracy gains, this methodology establishes a principled pathway from neuromuscular signals to text, providing a blueprint for virtual and augmented-reality typing interfaces that operate entirely without physical keyboards. By integrating ergonomic structure with transformer-based linguistic reasoning, MyoText advances the feasibility of seamless, wearable neural input for future ubiquitous computing environments.
Predicting and Understanding College Student Mental Health with Interpretable Machine Learning
Mar 11, 2025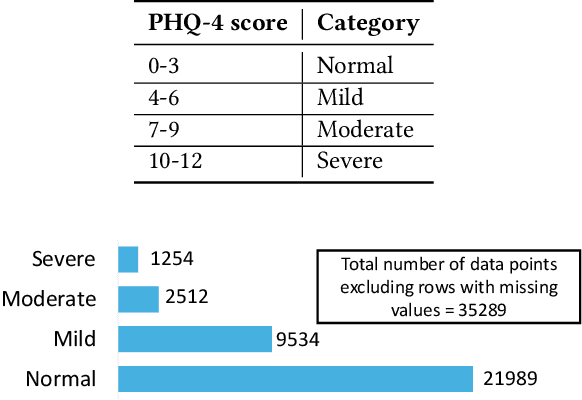
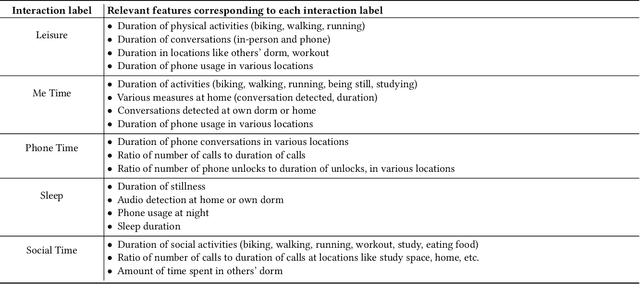
Abstract:Mental health issues among college students have reached critical levels, significantly impacting academic performance and overall wellbeing. Predicting and understanding mental health status among college students is challenging due to three main factors: the necessity for large-scale longitudinal datasets, the prevalence of black-box machine learning models lacking transparency, and the tendency of existing approaches to provide aggregated insights at the population level rather than individualized understanding. To tackle these challenges, this paper presents I-HOPE, the first Interpretable Hierarchical mOdel for Personalized mEntal health prediction. I-HOPE is a two-stage hierarchical model, validated on the College Experience Study, the longest longitudinal mobile sensing dataset. This dataset spans five years and captures data from both pre-pandemic periods and the COVID-19 pandemic. I-HOPE connects raw behavioral features to mental health status through five defined behavioral categories as interaction labels. This approach achieves a prediction accuracy of 91%, significantly surpassing the 60-70% accuracy of baseline methods. In addition, our model distills complex patterns into interpretable and individualized insights, enabling the future development of tailored interventions and improving mental health support. The code is available at https://github.com/roycmeghna/I-HOPE.
Unlocking Mental Health: Exploring College Students' Well-being through Smartphone Behaviors
Feb 12, 2025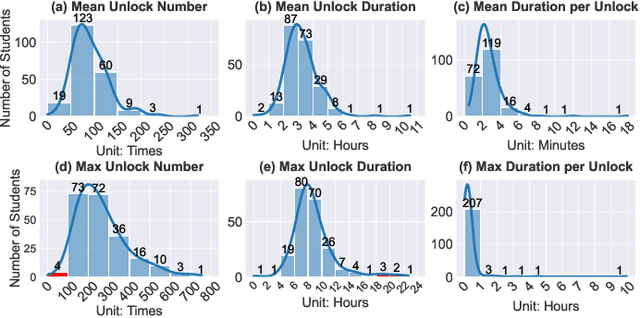
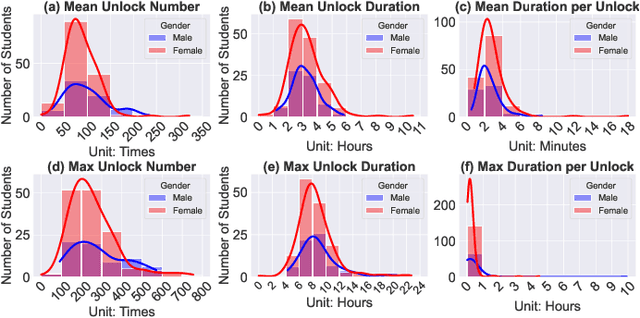
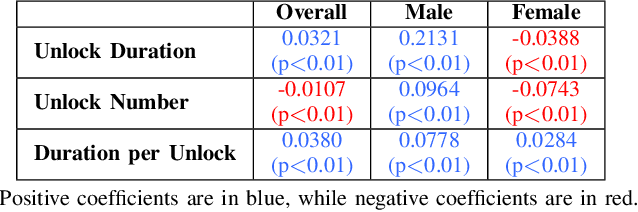
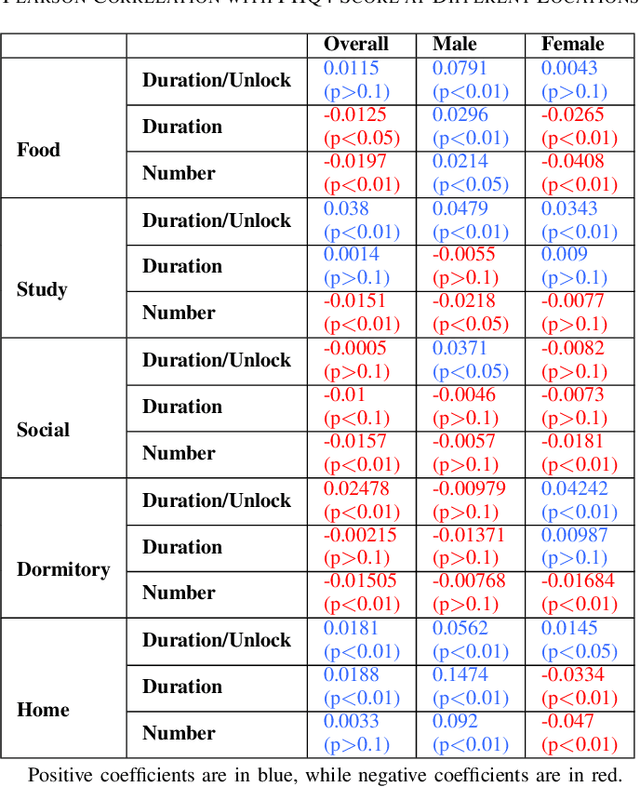
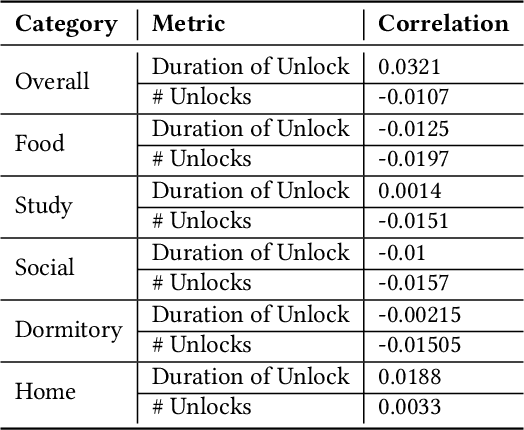
Abstract:The global mental health crisis is a pressing concern, with college students particularly vulnerable to rising mental health disorders. The widespread use of smartphones among young adults, while offering numerous benefits, has also been linked to negative outcomes such as addiction and regret, significantly impacting well-being. Leveraging the longest longitudinal dataset collected over four college years through passive mobile sensing, this study is the first to examine the relationship between students' smartphone unlocking behaviors and their mental health at scale in real-world settings. We provide the first evidence demonstrating the predictability of phone unlocking behaviors for mental health outcomes based on a large dataset, highlighting the potential of these novel features for future predictive models. Our findings reveal important variations in smartphone usage across genders and locations, offering a deeper understanding of the interplay between digital behaviors and mental health. We highlight future research directions aimed at mitigating adverse effects and promoting digital well-being in this population.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge