Md. Ruhul Amin
Ranking the locations and predicting future crime occurrence by retrieving news from different Bangla online newspapers
May 18, 2023



Abstract:There have thousands of crimes are happening daily all around. But people keep statistics only few of them, therefore crime rates are increasing day by day. The reason behind can be less concern or less statistics of previous crimes. It is much more important to observe the previous crime statistics for general people to make their outing decision and police for catching the criminals are taking steps to restrain the crimes and tourists to make their travelling decision. National institute of justice releases crime survey data for the country, but does not offer crime statistics up to Union or Thana level. Considering all of these cases we have come up with an approach which can give an approximation to people about the safety of a specific location with crime ranking of different areas locating the crimes on a map including a future crime occurrence prediction mechanism. Our approach relies on different online Bangla newspapers for crawling the crime data, stemming and keyword extraction, location finding algorithm, cosine similarity, naive Bayes classifier, and a custom crime prediction model
GCA-Net : Utilizing Gated Context Attention for Improving Image Forgery Localization and Detection
Dec 08, 2021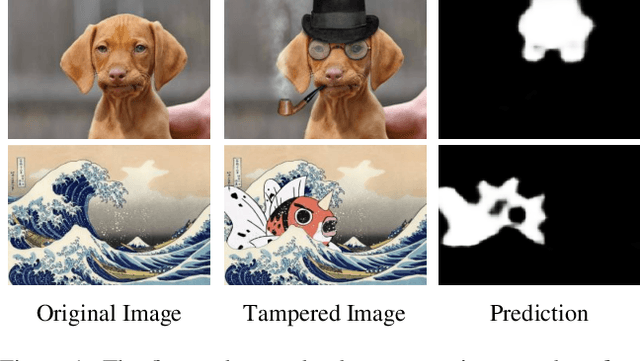
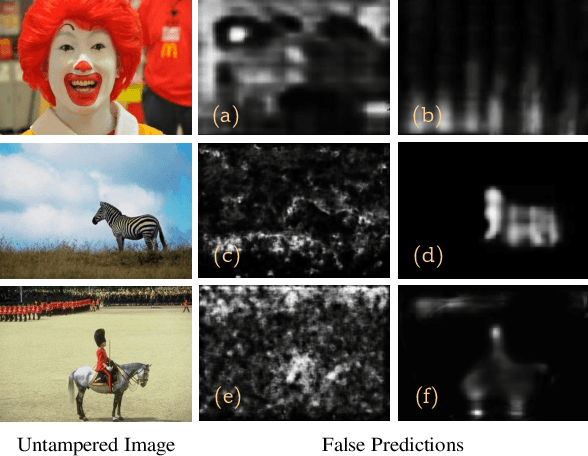


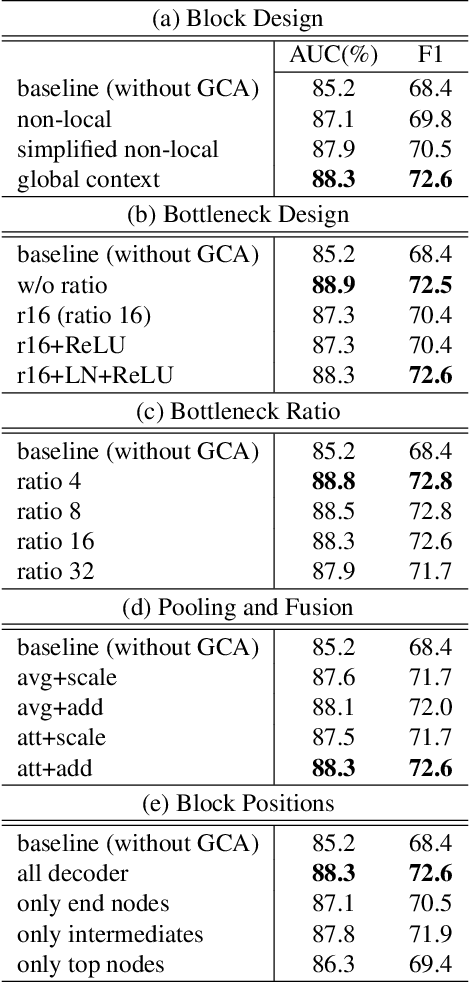
Abstract:Forensic analysis depends on the identification of hidden traces from manipulated images. Traditional neural networks fail in this task because of their inability in handling feature attenuation and reliance on the dominant spatial features. In this work we propose a novel Gated Context Attention Network (GCA-Net) that utilizes the non-local attention block for global context learning. Additionally, we utilize a gated attention mechanism in conjunction with a dense decoder network to direct the flow of relevant features during the decoding phase, allowing for precise localization. The proposed attention framework allows the network to focus on relevant regions by filtering the coarse features. Furthermore, by utilizing multi-scale feature fusion and efficient learning strategies, GCA-Net can better handle the scale variation of manipulated regions. We show that our method outperforms state-of-the-art networks by an average of 4.2%-5.4% AUC on multiple benchmark datasets. Lastly, we also conduct extensive ablation experiments to demonstrate the method's robustness for image forensics.
Improving DeepFake Detection Using Dynamic Face Augmentation
Feb 18, 2021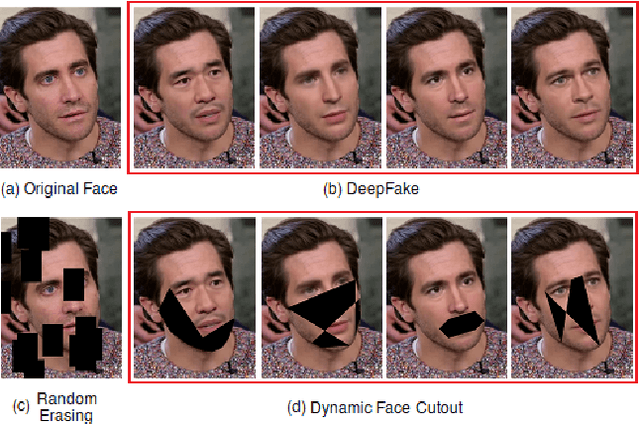
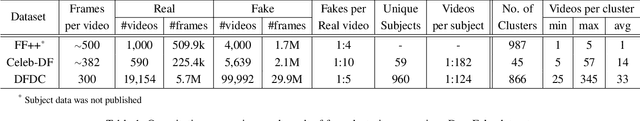
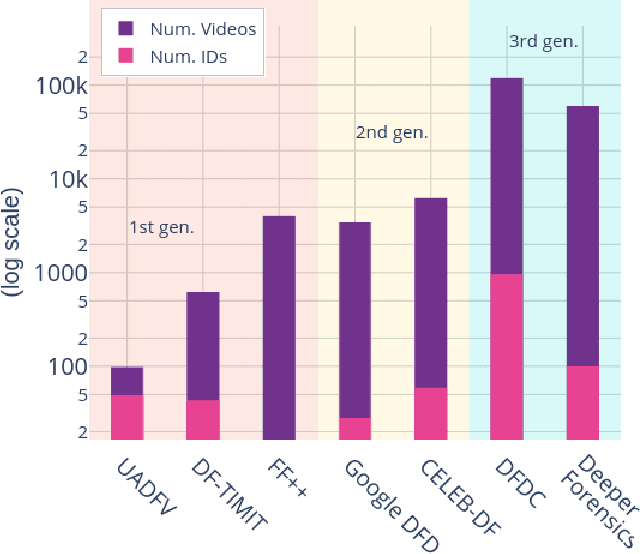
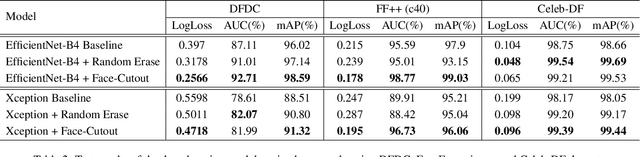
Abstract:The creation of altered and manipulated faces has become more common due to the improvement of DeepFake generation methods. Simultaneously, we have seen detection models' development for differentiating between a manipulated and original face from image or video content. We have observed that most publicly available DeepFake detection datasets have limited variations, where a single face is used in many videos, resulting in an oversampled training dataset. Due to this, deep neural networks tend to overfit to the facial features instead of learning to detect manipulation features of DeepFake content. As a result, most detection architectures perform poorly when tested on unseen data. In this paper, we provide a quantitative analysis to investigate this problem and present a solution to prevent model overfitting due to the high volume of samples generated from a small number of actors. We introduce Face-Cutout, a data augmentation method for training Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), to improve DeepFake detection. In this method, training images with various occlusions are dynamically generated using face landmark information irrespective of orientation. Unlike other general-purpose augmentation methods, it focuses on the facial information that is crucial for DeepFake detection. Our method achieves a reduction in LogLoss of 15.2% to 35.3% on different datasets, compared to other occlusion-based augmentation techniques. We show that Face-Cutout can be easily integrated with any CNN-based recognition model and improve detection performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge