Md. Hanif Seddiqui
Comparison of Classical Machine Learning Approaches on Bangla Textual Emotion Analysis
Jul 18, 2019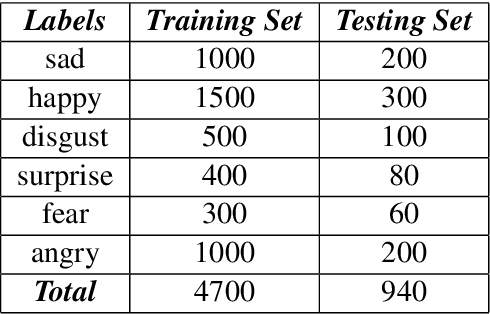
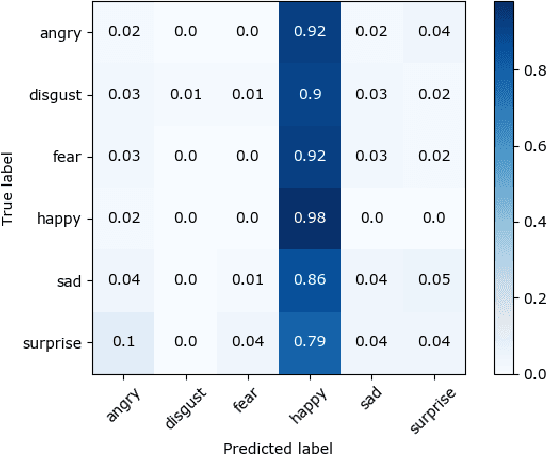
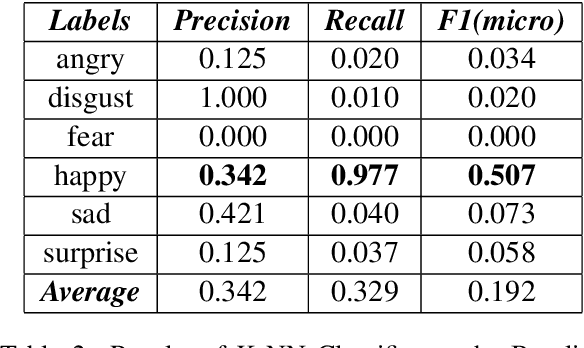
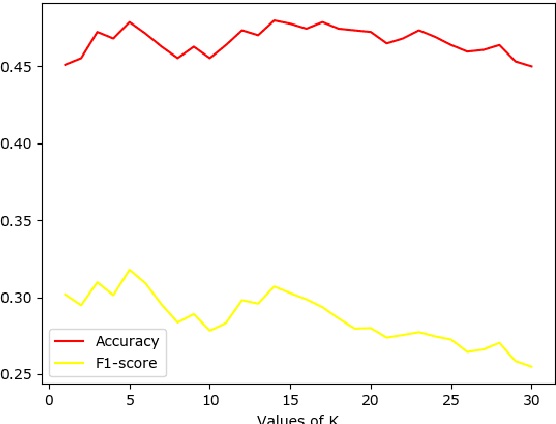
Abstract:Detecting emotions from text is an extension of simple sentiment polarity detection. Instead of considering only positive or negative sentiments, emotions are conveyed using more tangible manner; thus, they can be expressed as many shades of gray. This paper manifests the results of our experimentation for fine-grained emotion analysis on Bangla text. We gathered and annotated a text corpus consisting of user comments from several Facebook groups regarding socio-economic and political issues, and we made efforts to extract the basic emotions (sadness, happiness, disgust, surprise, fear, anger) conveyed through these comments. Finally, we compared the results of the five most popular classical machine learning techniques namely Naive Bayes, Decision Tree, k-Nearest Neighbor (k-NN), Support Vector Machine (SVM) and K-Means Clustering with several combinations of features. Our best model (SVM with a non-linear radial-basis function (RBF) kernel) achieved an overall average accuracy score of 52.98% and an F1 score (macro) of 0.3324
An Efficient Metric of Automatic Weight Generation for Properties in Instance Matching Technique
Feb 12, 2015
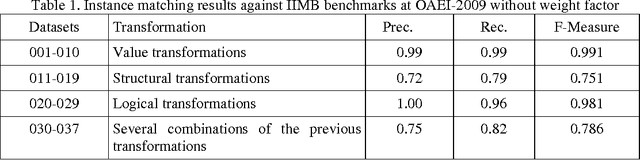
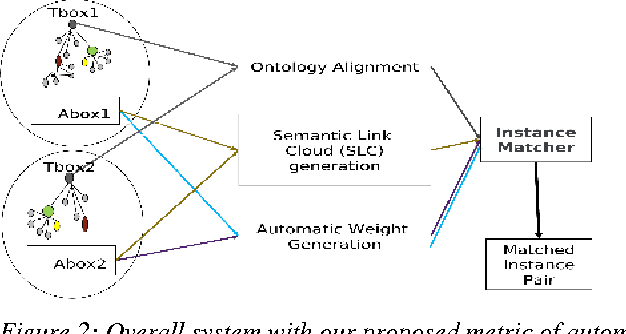
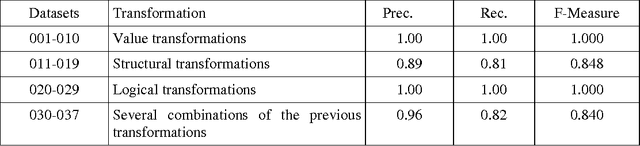
Abstract:The proliferation of heterogeneous data sources of semantic knowledge base intensifies the need of an automatic instance matching technique. However, the efficiency of instance matching is often influenced by the weight of a property associated to instances. Automatic weight generation is a non-trivial, however an important task in instance matching technique. Therefore, identifying an appropriate metric for generating weight for a property automatically is nevertheless a formidable task. In this paper, we investigate an approach of generating weights automatically by considering hypotheses: (1) the weight of a property is directly proportional to the ratio of the number of its distinct values to the number of instances contain the property, and (2) the weight is also proportional to the ratio of the number of distinct values of a property to the number of instances in a training dataset. The basic intuition behind the use of our approach is the classical theory of information content that infrequent words are more informative than frequent ones. Our mathematical model derives a metric for generating property weights automatically, which is applied in instance matching system to produce re-conciliated instances efficiently. Our experiments and evaluations show the effectiveness of our proposed metric of automatic weight generation for properties in an instance matching technique.
* 17 pages, 5 figures, 3 tables, pp. 1-17, publication year 2015, journal publication, vol. 6 number 1
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge