Md. Ashraful Islam
CODESIM: Multi-Agent Code Generation and Problem Solving through Simulation-Driven Planning and Debugging
Feb 08, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have made significant strides in code generation and problem solving. Current approaches employ external tool-based iterative debuggers that use compiler or other tool-based runtime feedback to refine coarse programs generated by various methods. However, the effectiveness of these approaches heavily relies on the quality of the initial code generation, which remains an open challenge. In this paper, we introduce CodeSim, a novel multi-agent code generation framework that comprehensively addresses the stages of program synthesis-planning, coding, and debugging-through a human-like perception approach. As human verifies their understanding of any algorithms through visual simulation, CodeSim uniquely features a method of plan verification and internal debugging through the step-by-step simulation of input/output. Extensive experiments across seven challenging competitive problem-solving and program synthesis benchmarks demonstrate CodeSim's remarkable code generation capabilities. Our framework achieves new state-of-the-art (pass@1) results-(HumanEval 95.1%, MBPP 90.7%, APPS 22%, and CodeContests 29.1%). Furthermore, our method shows potential for even greater enhancement when cascaded with external debuggers. To facilitate further research and development in this area, we have open-sourced our framework in this link (https://kagnlp.github.io/codesim.github.io/).
MapCoder: Multi-Agent Code Generation for Competitive Problem Solving
May 18, 2024



Abstract:Code synthesis, which requires a deep understanding of complex natural language problem descriptions, generation of code instructions for complex algorithms and data structures, and the successful execution of comprehensive unit tests, presents a significant challenge. While large language models (LLMs) demonstrate impressive proficiency in natural language processing, their performance in code generation tasks remains limited. In this paper, we introduce a new approach to code generation tasks leveraging multi-agent prompting that uniquely replicates the full cycle of program synthesis as observed in human developers. Our framework, MapCoder, consists of four LLM agents specifically designed to emulate the stages of this cycle: recalling relevant examples, planning, code generation, and debugging. After conducting thorough experiments, with multiple LLM ablations and analyses across eight challenging competitive problem-solving and program synthesis benchmarks, MapCoder showcases remarkable code generation capabilities, achieving new state-of-the-art results (pass@1) on HumanEval (93.9%), MBPP (83.1%), APPS (22.0%), CodeContests (28.5%), and xCodeEval (45.3%). Moreover, our method consistently delivers superior performance across various programming languages and varying problem difficulties. We open-source our framework at https://github.com/Md-Ashraful-Pramanik/MapCoder.
A Survey on Deep Learning Based Point-Of-Interest Recommendations
Nov 20, 2020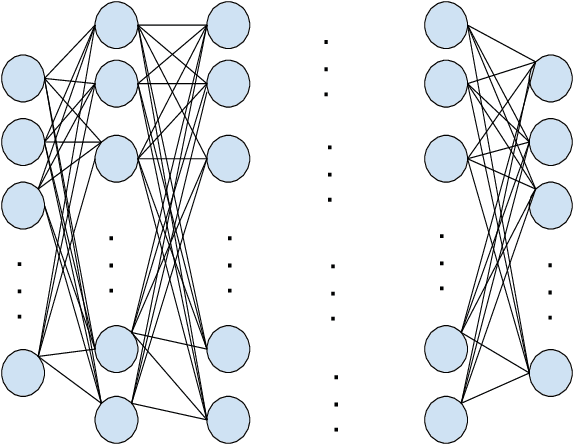
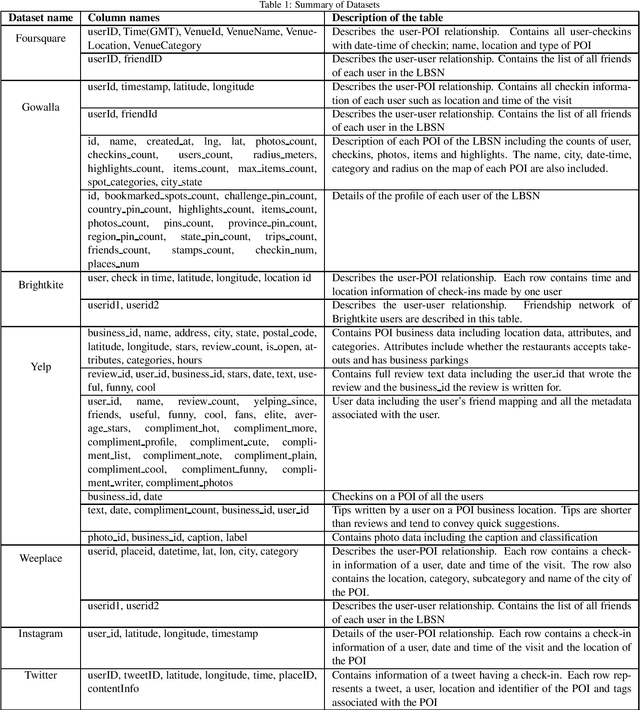
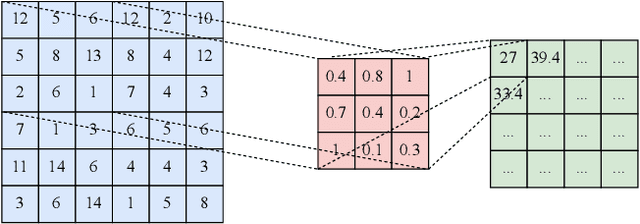
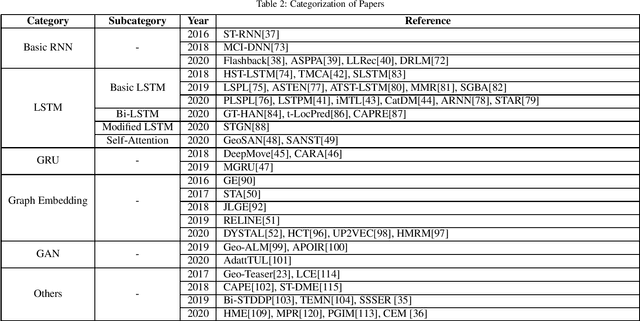
Abstract:Location-based Social Networks (LBSNs) enable users to socialize with friends and acquaintances by sharing their check-ins, opinions, photos, and reviews. Huge volume of data generated from LBSNs opens up a new avenue of research that gives birth to a new sub-field of recommendation systems, known as Point-of-Interest (POI) recommendation. A POI recommendation technique essentially exploits users' historical check-ins and other multi-modal information such as POI attributes and friendship network, to recommend the next set of POIs suitable for a user. A plethora of earlier works focused on traditional machine learning techniques by using hand-crafted features from the dataset. With the recent surge of deep learning research, we have witnessed a large variety of POI recommendation works utilizing different deep learning paradigms. These techniques largely vary in problem formulations, proposed techniques, used datasets, and features, etc. To the best of our knowledge, this work is the first comprehensive survey of all major deep learning-based POI recommendation works. Our work categorizes and critically analyzes the recent POI recommendation works based on different deep learning paradigms and other relevant features. This review can be considered a cookbook for researchers or practitioners working in the area of POI recommendation.
Comprehending Real Numbers: Development of Bengali Real Number Speech Corpus
Mar 27, 2018



Abstract:Speech recognition has received a less attention in Bengali literature due to the lack of a comprehensive dataset. In this paper, we describe the development process of the first comprehensive Bengali speech dataset on real numbers. It comprehends all the possible words that may arise in uttering any Bengali real number. The corpus has ten speakers from the different regions of Bengali native people. It comprises of more than two thousands of speech samples in a total duration of closed to four hours. We also provide a deep analysis of our corpus, highlight some of the notable features of it, and finally evaluate the performances of two of the notable Bengali speech recognizers on it.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge