Md Zakirul Alam Bhuiyan
Privacy-Preserving Federated Depression Detection from Multi-Source Mobile Health Data
Mar 07, 2021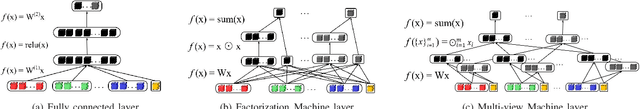
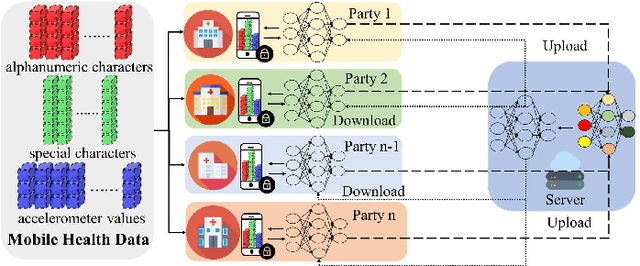
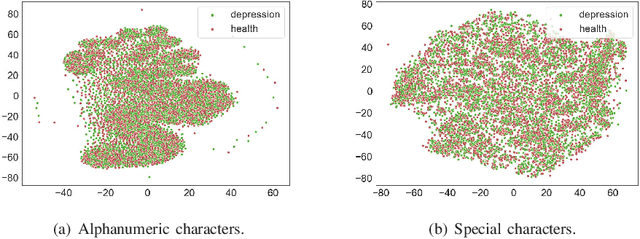
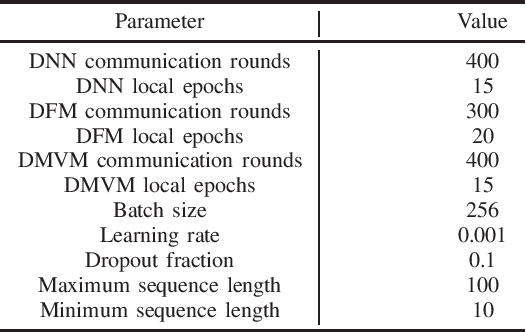
Abstract:Depression is one of the most common mental illness problems, and the symptoms shown by patients are not consistent, making it difficult to diagnose in the process of clinical practice and pathological research.Although researchers hope that artificial intelligence can contribute to the diagnosis and treatment of depression, the traditional centralized machine learning needs to aggregate patient data, and the data privacy of patients with mental illness needs to be strictly confidential, which hinders machine learning algorithms clinical application.To solve the problem of privacy of the medical history of patients with depression, we implement federated learning to analyze and diagnose depression. First, we propose a general multi-view federated learning framework using multi-source data,which can extend any traditional machine learning model to support federated learning across different institutions or parties.Secondly, we adopt late fusion methods to solve the problem of inconsistent time series of multi-view data.Finally, we compare the federated framework with other cooperative learning frameworks in performance and discuss the related results.
A Semi-Dynamic Bus Routing Infrastructure based on MBTA Bus Data
Mar 29, 2020



Abstract:Transportation is quickly evolving in the emerging smart city ecosystem with personalized ride sharing services quickly advancing. Yet, the public bus infrastructure has been slow to respond to these trends. With our research, we propose a semi-dynamic bus routing framework that is data-driven and responsive to relevant parameters in bus transport. We use newly published bus event data from a bus line in Boston and several algorithmic heuristics to create this framework and demonstrate the capabilities and results. We find that this approach yields a very promising routing infrastructure that is smarter and more dynamic than the existing system.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge